Large corporations work on a massive scale, often spanning multiple departments, geographical locations, and user bases. They require SaaS enterprise solutions that seamlessly integrate with their existing systems, adapt to complex workflows, and ensure uncompromised data privacy and security.
To successfully navigate these challenges, SaaS startups must be SaaS enterprise-ready — have the cutting-edge technology, infrastructure, scalability, security, and support capabilities to fulfill the needs of large corporations.
But how can SaaS startups ensure they’re fully prepared to meet the needs of enterprise clients? What strategies can help them deliver successful implementations and create long-term collaborations?
This article will dive into the top SaaS enterprise software implementation strategies, offering valuable insights and practical tips to help startups navigate this challenging landscape.
Meeting Specific Requirements
As a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) startup, your product or service will be used by diverse companies, each with its own unique requirements and user roles. So, it’s crucial to consider their needs during ideation.
But which requirements should you meet? Let’s take a look at some of them:
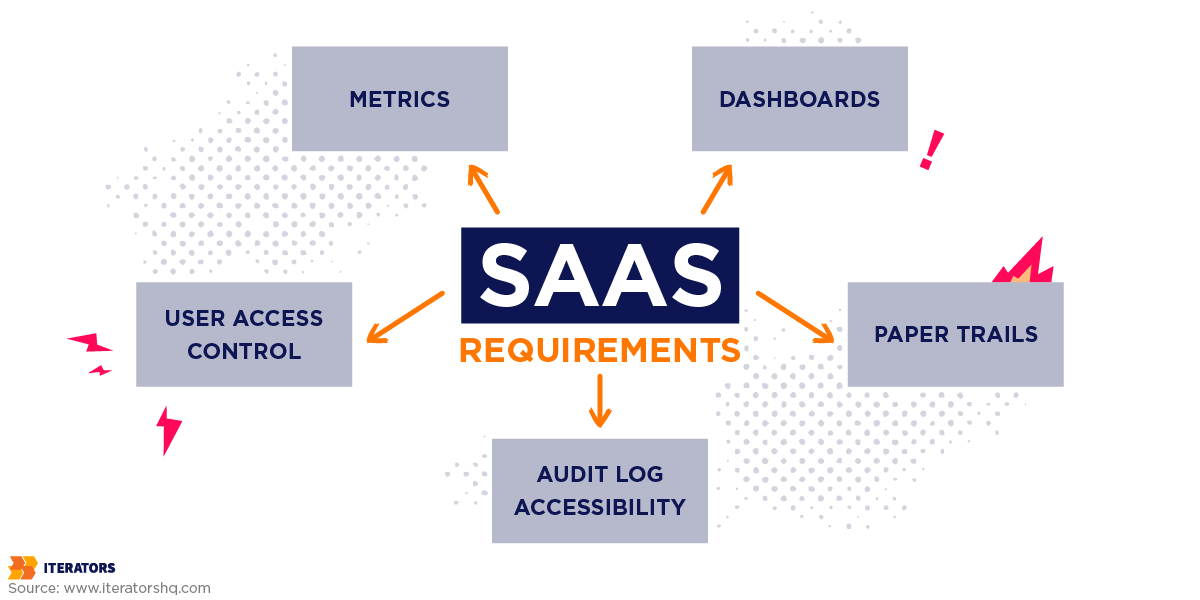
Metrics
SaaS metrics are performance benchmarks that companies use to evaluate and monitor their progress and development. They enable SaaS companies to understand their goals, prepare for upcoming plans, and adapt their strategies as necessary.
While metric requirements vary depending on a corporation’s needs, some stay consistent across all corporations, such as customer churn, customer lifetime value, customer turnover, monthly recurring revenue, customer acquisition cost, and more.
For instance, customer churn measures the amount of business lost over a specific timeframe. This helps large corporations understand why customers are leaving or disengaging from their products.
Dashboards
Dashboards allow large corporations or SaaS clients to visualize data from various departments like sales, finances, and marketing, helping them understand their performance and maximize profitability.
They also provide a user-friendly method for discovering data-driven patterns, evaluating strengths and weaknesses, making educated decisions, and enabling the sharing of the right information with relevant stakeholders.
Paper Trails
A SaaS paper trail is a documented record or trail of activities, transactions, or events related to the SaaS application or service. It’s an electronic or digital trail instead of a physical paper trail and is made up of logs, records, audit trails, or other forms of documentation that track the actions taken within the SaaS platform.
Companies use paper trails to get access to an easily searchable method for storing and preserving logs from their infrastructure to fulfill retention and security standards. Paper trails also help them understand whether tasks were completed or not.
Audit Log Accessibility
An audit log is a record of events or documented records showing the chronological order of activities that have impacted a specific operation, procedure, or event.
The underlying principle is straightforward: whenever a modification to a system results in a change in its behavior, that particular change should be documented within an audit log.
Audit logs are vital in addressing data-related inquiries, security, and system status, making them essential for ensuring security and compliance. They also facilitate the tracking of system activities by multiple stakeholders within an organization.
If you are a software-as-a-service (SaaS) provider, it’s likely that many potential customers will expect your product to include an audit logging feature. In fact, certain regulations mandate that enterprise-grade companies maintain audit logs for all the platforms they utilize.
Your clients will require functionalities for managing and reviewing audit logs. The primary use cases for their audit logs will revolve around activity tracking, compliance, and security. So, make sure your product offers robust capabilities for managing and reviewing audit logs.
User Access Control
At times, users may require the ability to perform actions that aren’t aligned with their assigned user roles and permissions. This can vary depending on users’ industry, operational maturity, and organizational structure.
So, the implementation of precise user access controls becomes necessary. These controls enable the software to fulfill its intended purpose and meet the intricate authorization requirements of enterprise environments, all while ensuring application security, performance, and data integrity.
Meeting the Requirements
A SaaS startup company must strike a balance between the goals for the initial product line and the administrative support required to guarantee customer success. It’s simple to overlook the onboarding process as a component of the SaaS business model.
However, SaaS startups need solid plans to attract and retain new clients. And one way to do that is by using a SaaS business model. Here’s why you should use it:
- Consistent flow of income from recurring payments, like those made monthly or annually
- Increased customer retention by offering paid tiers and upgrades rather than one-time payments to maintain income stability
- Updates offer chances to raise client retention rates while learning what customers think of the newest product iterations through surveys
- Metrics on consumer preferences provide trustworthy data
- Tracking of monetary figures by the recurring revenue measurements of MRR and ARR
More specific approaches that SaaS startups can use include the following:
Market Research

SaaS businesses should conduct in-depth market research to understand huge corporations’ requirements and pain concerns.
This helps them identify the most important KPIs, dashboarding options, paper trail specifications, access audit logs, and granular access control capabilities for enterprise clients.
Startups can use this information to adjust their product development and feature roadmaps.
Scalable Infrastructure
SaaS firms must have a scalable infrastructure that can support major corporations’ data volumes and performance requirements.
This entails investing in dependable cloud infrastructure, optimizing database structures, and using technologies like load balancing and horizontal scaling to guarantee scalability and high availability.
Customization and Integration
Major organizations frequently need customization and seamless system integration. SaaS firms should consider flexibility and extension when designing their solutions so that they’re simple to customize and fit the unique requirements of each enterprise client.
Plus, strong APIs and integration capabilities enable efficient data transfer between the SaaS product and other enterprise systems.
Data Security and Compliance
For big businesses, data security is of utmost importance. SaaS firms should prioritize strong security measures like encryption, access limits, and routine security audits.
To earn the trust of business clients, compliance with industry rules such as HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI-DSS is crucial. Startups must spend money on security best practices, submit to external audits, and acquire required certifications.
Analytics and Reporting Capabilities

Decision-making in large organizations is frequently informed by data. Startups using SaaS should concentrate on giving their products advanced analytics and reporting features.
To enable enterprise clients to draw valuable insights from their data, they should create customizable dashboards, data visualization tools, and report production functionalities.
Large organizations must be able to track and analyze critical indicators in real-time to make wise decisions.
Customer Support and Account Management
Startups should prioritize giving enterprise clients outstanding customer care, prompt assistance, and ongoing training.
Building trusting connections with important organizational stakeholders facilitates addressing their needs, obtaining feedback, and enhancing the product offering over time.
Scalability and Customization
Scalability is essential for SaaS businesses to meet rising user demands while preserving performance. This means creating and putting in place a flexible infrastructure that can easily accommodate traffic peaks and changes in user activity.
Scalability
Utilizing the strength of cloud computing services like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure is a well-liked method for scaling up. These platforms offer flexible pay-as-you-go pricing and seamless on-demand scaling.
So, SaaS providers can scale back down as demand declines and quickly add more servers or resources to accommodate spikes in traffic or user activity. It may help in lowering infrastructure costs and enhancing operational effectiveness.
Customization
Customization enables SaaS firms to design their products to match business clients’ unique needs and specifications. So, the client receives a tailored solution that aligns with their company objectives.
Plus, by providing customizable choices, startups allow their clients to set up the SaaS solution following their preferences, workflows, and branding. This enhances the general user experience and increases the software’s adoption within the company.
SaaS firms also distinguish themselves from competitors by offering flexible customization options instead of prescriptive, one-size-fits-all solutions. This promotes the firm as a versatile and client-focused provider, luring business clients searching for a solution that can be customized to their particular needs.
With so many benefits, SaaS startups are becoming increasingly aware of the importance of customization as a critical difference in a cutthroat industry. Some examples of customization options include:
Multi-tenancy Deployment
Multi-tenancy deployment is a customization choice that enables SaaS businesses to provide services to numerous customers (tenants) from a single instance of their software. So, every customer has a dedicated environment with unique databases, configurations, and user access controls within the SaaS offering.
This customization option enables the SaaS firm to scale, be cost-effective, and have centralized control while enabling enterprise clients to have isolated and customized program instances.
Enterprises that are scaling benefit most from this mode of customization because a single platform deals with multiple clients at the same time. The same set of resources is shared by a single cloud vendor’s multiple customers.
On-Premise Deployment
With this customization option, enterprise clients can host and run the SaaS program on their infrastructure rather than relying on the servers of the SaaS provider.
As customers can directly access their data and modify the program to match their needs, this solution gives clients greater control, security, and compliance.
White-labeling and Branding
SaaS businesses can offer white-labeling and branding customization choices, enabling business clients to alter the software’s visual aesthetic to better reflect their own corporate identity. Some examples include customizing the user interface and applying company logos, color schemes, and other visual components representing their brand.
White labeling improves client brand recognition and streamlines user interaction within the client’s company.
Custom Reporting and Analytics
SaaS firms may provide choices for customization in reporting and analytics, enabling corporate clients to design unique reports, dashboards, and data visualizations tailored to their needs.
Thanks to this personalization, clients can analyze and present data in a way that is useful and pertinent to their decision-making processes.
Security and Compliance
Startups should conduct risk analyses to find any compliance and security holes. This means assessing the risks posed by data privacy concerns, security threats, and crucial legislative requirements particular to their sector and target market.
Ensuring Security and Compliance
Let’s understand how startups can implement best practices for security:
Use Software-specific Restrictions
To ensure client security, you should use encryption to safeguard data both in transit and at rest, put strong access restrictions and authentication procedures in place, and frequently patch and update software to address security vulnerabilities.
You should also conduct regular security audits and perform penetration testing to make sure your security measures are holding up.
Comply with Industry Standards
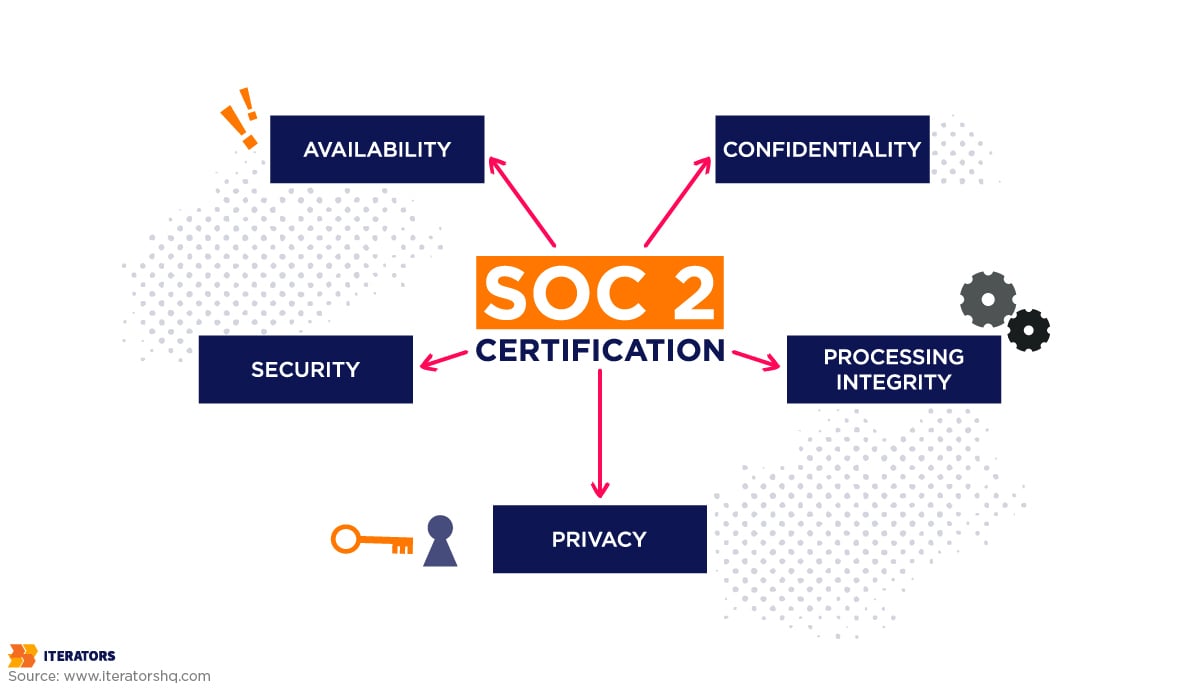
Startups must work towards obtaining accreditations or attestations that prove they comply with industry standards like the following:
- SOC2 – When companies don’t have certain expertise nor the capital to bear the costs, they outsource to third-party service providers. In this case, that is you. However, the company has to make sure their data is safe with you. SOC 2 compliance is designed to achieve just that.
- PCI-DSS – The payment card industry data security standard (PCI-DSS) is a collection of 12 security standards, such as unique IDs, firewalls, encryption, and restricted access, that have to be implemented by any business that manages payment card data.
- ISO – A foundation for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system is provided by ISO standards like ISO 27001 or ISO 27001.
Prioritize Data Protection and Privacy
Startups need to make sure they adhere to all applicable data privacy laws, such as the General Data Privacy Regulation (GDPR). This means obtaining user approval for data collection and processing, putting data minimization practices into place, and giving data subjects ways to exercise their rights.
Regular training and awareness programs should be implemented for staff to understand their roles and responsibilities in upholding security and compliance. Employee training on safe data handling procedures, learning to spot phishing scams, and observing internal security regulations are all part of this.
Security Concerns for Clients
Enterprise clients frequently have security concerns that must be addressed when considering implementing SaaS solutions. These include the following:
Unauthorized Server Access
Clients seek confirmation that their data will be protected against unauthorized access, breaches, or abuse because data privacy is a top issue. They anticipate reliable data encryption technologies to protect the confidentiality and integrity of data both in transit and at rest.
Measures like multifactor authentication (MFA) and implementing a role-based access control (RBAC) mechanism can also reduce the risk. They limit access to information and monitor all activities across the software.
Lack of Firewalls
Firewalls provide security to the organization’s network and prevent any adverse impacts of malicious cyber activity. You’ll need an off-site deployment for a SaaS firewall to protect all data and sensitive information effectively.
Malicious Cyber Activity

With cybercrime worsening over time, enterprise clients will want to make sure that cyber incidents like malware, trojan horses, system takeovers, and data leaks don’t hamper their operations.
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) can prevent this from happening by monitoring internet traffic to detect any malicious or unwanted cyber activity and prevent it from happening altogether.
Industry Standard Noncompliance
It’s critical for large companies to comply with rules specific to their sector, including GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or SOC2. SaaS startups can build confidence with business clients by addressing these security issues transparently and giving thorough information about security procedures.
Certifications and Audits to Pursue
SaaS companies can make sure their security and compliance readiness by pursuing the following certifications and audits:
- SOC 2 – This certification is crucial for compliance and security readiness for any SaaS provider.
- ISO 27001 – It’s crucial for data privacy and information security.
- PCI-DSS – It’s needed by all SaaS providers dealing with payment card information.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) – It’s essential if you’re working with healthcare organizations.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) Certification – It’s crucial if the enterprise is part of the European Union.
User Management and Organization Structure
User management means gathering information on the usage of SaaS in the enterprise for a greater SaaS stack return. It enables staff members to avoid inefficient use of time and resources at work.
SaaS products have to facilitate user management using structures that suit enterprise clients. These include the following:
- Countries – Business clients who operate in many nations may need to manage user access based on those regulations.
- Sites – Big businesses frequently have several physical locations, or sites, each with its own set of users and rights.
- Service Lines – Within their company, enterprise clients may have various departments or service lines, each with its user management framework.
- Teams – Within an organization, teams may require particular user management features, including team leaders, team members, and specialized permissions.
- Departments – Enterprise clients may have a variety of departments, including IT, HR, finance, marketing, and more, each with unique user management needs.
Roles and Permissions for Different Types of Users
User roles are assigned based on their needs and workloads, whereas admins manage user permissions as they assign and adjust roles accordingly.
To cater to the needs of various user types, SaaS firms should offer a variety of roles and permissions. Typical roles include:
- Organization Administrator – These individuals have complete authority and supervision over all user management, preferences, and configurations throughout the organization.
- Local Administrators – These are users with administrative rights for certain sites, places, or nations.
- Manager/Supervisor – They have the right to manage and oversee a team or department within the solution.
- Employees – They have enough access to perform their daily tasks.
- Team Leaders – These users have additional duties and rights to oversee particular teams or projects within the company.
- Reporting User/Analysts/Accountants – They have the ability to access analytics, generate reports, and extract data from the SaaS solution.
- Client/External User – They have limited access to the SaaS platform.
- Help Desk/Support – They have problem troubleshooting privileges.
Role-based access control (RBAC) solutions are crucial because they enable startups to create roles and give appropriate access based on user responsibilities inside the organization. This guarantees that users can only access the features and information necessary for their responsibilities.
It’s simpler to manage users at many levels, such as a nation, site, department, or team, thanks to hierarchical user management features that enable the design of a structure that reflects the organizational hierarchy.
Designing Products to Accommodate Complex Organizational Structures
An organizational structure defines how work flows through an organization and characterizes how groups work together under a hierarchy. A chain of command has to be outlined to ensure the smooth operation of all activities.
You can make sure your SaaS product meets the size and scale of your enterprise clients by building flexibility into your product, making sure it can scale, implementing an RBAC system, and facilitating data exchanges through webhooks.
The Takeaway
SaaS enterprise readiness is crucial if you want your SaaS startup to succeed in the SaaS industry. That’s because enterprise clients have complex requirements, intricate security and compliance standards, and larger user bases. These make it difficult for SaaS startups to meet enterprise standards.
However, you can take several measures, like developing a scalable infrastructure, ensuring security and compliance through SOC2 or ISO standard certifications, and targeting features integration capabilities, customer service, and customization, to make sure you’re prepared for your clients’ needs.
And while you have to offer value to the customer, differentiation is also key to the process. You are about to become a part of a highly competitive market, so you must stand out. And though it might seem intimidating to meet all these requirements, focusing on your product and your customer’s demands can get you across the finish line.
