Did you know that user interfaces can shape powerful user experiences for your products? User interfaces are the gateway of your web and mobile application. The quality of your application’s UI can determine whether users love to use your app or not.
This guide to the world of user interfaces explores all facets of developing highly engaging designs that empower the user to trust your business. We cover what user interfaces are, how to approach interface design projects, and modern approaches to nurture desirable user experiences.
What is UI
User Interface, or UI, comprises the visual and interactive components of software, applications, or devices that make it possible for users to communicate with and control them.
UI’s elements include displays and buttons. They work together to make the user experience efficient, intuitive, and visually engaging.
When you build web applications for your business, your developers may focus on building UIs that users love. They work to build a point of communication between the user and the system, giving users a way to input commands, provide information, and receive feedback in an understandable and user-friendly manner.
Do you need help with creating a visually engaging UI? At Iterators we can help design, build, and maintain custom software solutions for both startups and enterprise businesses.
Schedule a free consultation with Iterators today. We’d be happy to help you find the right software solution to help your company.
UI design encompasses several elements, including:
- Visual Elements: This includes the layout, color schemes, typography, icons, images, and overall UI aesthetics. These elements are essential to an appealing and user-friendly design.
- Interactive Elements: Your application typically includes buttons, forms, menus, and sliders. These and other interactive components enable users to perform actions, input data, or make selections within the interface.
- Information Display: The user interface should effectively present information. Charts, graphics, text, and multimedia elements all contribute to this purpose, depending on the context and purpose of the interface.
- Navigation: Menus, links, breadcrumbs, search bars, and other navigational elements support users to move around your interface to find the content or functionality they need.
- Feedback and Response: User interfaces should give feedback after performing actions. It may come as textual messages, animations, or visual cues to confirm the completion of an action or to alert users to errors.
- Layout and Structure: Logic and intuition are crucial in laying out application components and ensuring a good user experience. Your front-end devs will often consider the hierarchy of information and the flow of tasks.
- Accessibility: It’s recommended that every well-designed UI be accessible to users with disabilities. For instance, you may provide alternative text (alt text) for images, keyboard navigation options, and more features that allow all types of people to use the interface satisfactorily.
- Consistency: Consistent design elements and interaction patterns across your application or website support users in understanding how to use it. You can achieve consistency by using style guides and following standard design principles.
- Usability and User Experience (UX): User interface design should prioritize usability and a positive user experience. It means you have to understand your users’ needs, conduct user testing, and fine-tune the interface based on the feedback you receive.
User interface design can take varying forms depending on the context and platform. For example, the UI for your mobile apps could differ significantly from the desktop and web applications. Besides, when building modern apps that embrace emerging technologies such as voice interfaces and virtual reality (VR), you’ll encounter new challenges and opportunities for UI design.
“UI is the bridge between intention and action—when it’s well-built, users cross effortlessly. When it’s confusing, they get lost along the way. It’s the foundation of a smooth user experience, connecting what users want with how they achieve it.”
Izabela Kurkiewicz
Overall, user interface is the doorway to your software application or device, enabling users to interact with it and, ultimately, your business. Effective UI design ensures users can easily and intuitively navigate, use, and benefit from your application and business.
Key Components of UI

Your application’s UI aims to facilitate communication between users and computers or other devices. Its role is to be the point of interaction where customers can input commands, receive feedback, and navigate through your applications.
The key components of user interfaces include:
- Input Controls
- Buttons: Clickable elements that trigger actions or commands when pressed.
- Text Fields: Areas where users can input text or numeric values.
- Checkboxes and Radio Buttons: Used to select options or make choices.
- Dropdown Lists: Provide a list of options for users to choose from.
- Sliders: Allow customers to select values within a range.
- Toggle Switches: Enable users to turn options or features on/off.
- Information Display
- Text: Displayed in various fonts, sizes, and styles to convey information.
- Images: Graphics, icons, and pictures used for visual representation.
- Icons: Small, symbolic images that represent actions or concepts.
- Data Visualization: Charts, graphs, and diagrams are used to present data.
- Alerts and Notifications: Pop-up messages or indicators for important updates.
- Navigation Components
- Menus: Lists of options or commands for users to select from.
- Tabs: Organize content into separate sections or views.
- Breadcrumbs: Show users their current location within a hierarchy.
- Search Bars: Allow customers to search for specific content.
- Links: Text or elements that, when clicked, take users to another location.
- Feedback Mechanisms
- Tooltips: Small informational pop-ups that appear when hovering over an element.
- Progress Indicators: Show the status of ongoing processes or tasks.
- Error Messages: Inform users when something goes wrong and provide guidance.
- Confirmation Dialogs: Ask for customer confirmation before performing critical actions.
- Layout and Composition
- Grids and Alignment: Ensure content is organized and visually pleasing.
- Whitespace: Create separation between elements to reduce clutter.
- Responsive Design: Adapt to different screen sizes and orientations.
- Typography: Choose fonts, sizes, and spacing for readability.
- User Assistance
- Help Documentation: Provide user manuals, FAQs, or guides.
- Tutorials and Walkthroughs: Step-by-step instructions for new customers.
- Contextual Help: Offer tooltips or information relevant to the current task.
- Accessibility Features
- Keyboard Navigation: Allow users to navigate without a mouse.
- Screen Readers: Support for customers with visual impairments.
- Color Contrast: Ensure readability for users with color vision deficiencies.
- Alternative Text: Descriptions for non-text elements (images, icons) for screen readers.
- Interactivity
- Animations and Transitions: Add visual feedback and smooth transitions.
- Drag-and-Drop: Enable users to interact with elements through dragging.
- Gestures and Touch: Support touchscreens and gesture-based interactions.
- User Feedback Mechanisms
- Surveys and Forms: Collect feedback and user data.
- Ratings and Reviews: Allow users to rate products or services.
- Contact and Support Channels: Provide ways for customers to get in touch.
- Security and Privacy Features
- User Authentication: Logins, passwords, and security measures.
- Data Privacy Controls: Options for managing personal data.
- Permissions: Grant or restrict access to certain features or information.
Effective user interface design focuses on the user’s needs, tasks, and preferences. But it also works towards providing a hitch-free and intuitive experience. A good UI needs to be adaptable and responsive to accommodate various devices and screen sizes.
Importance of UI for Software Products

There are several reasons why your apps need a UI. These critical reasons include:
- User Experience (UX)
UI directly impacts the overall user experience. A well-designed UI makes it easier for users to interact with the software, leading to a more positive and enjoyable experience. A poor UI can frustrate users and drive them away from the product. - Usability
An intuitive and user-friendly UI design enhances the usability of the software. Customers should be able to accomplish their tasks efficiently and with minimal effort. A good UI anticipates user needs and guides them through the software seamlessly. - Customer Satisfaction
A well-crafted UI can lead to higher customer satisfaction. When users find a product easy to use and visually appealing, they’re more likely to have a positive perception of the software and the company behind it. - Competitive Advantage
A superior UI can set a software product apart from its competitors in a competitive market. Users are more likely to choose a product that offers a better UI and user experience, even if the underlying features are similar. - Reduced Support and Training Costs
Intuitive UIs reduce the need for extensive user training and support. Customers who can easily understand and navigate the software are less likely to require assistance, saving the company time and resources. - Increased Productivity
A well-designed UI can boost user productivity. They can complete tasks more quickly and efficiently, improving work efficiency and potentially increasing revenue for businesses. - Lower Error Rates
A clear and intuitive UI reduces the likelihood of user errors. Customers who can easily understand how to use the software are less likely to make mistakes that could lead to data loss or other issues. - Accessibility
A well-thought-out UI considers accessibility needs, ensuring that individuals with disabilities can also use the software effectively. This inclusivity is ethically important and may be legally required in some regions. - Adoption and Retention
A user-friendly UI can encourage users to adopt the software more readily and continue using it over time. It can lead to higher user retention rates and potentially recurring revenue for subscription-based products. - Feedback and Improvement
UI design is an iterative process. User feedback and analytics gathered through the UI can provide valuable insights for improving the software and adding new features that align with user preferences and needs. - Branding and Image
The UI often serves as the face of the product and the brand. A visually appealing and consistent UI can reinforce brand identity and create a positive image in users’ minds.
In summary, a well-designed UI is essential for software products because it directly impacts user satisfaction, usability, productivity, and competitiveness. Investing in UI design and considering user needs throughout development can lead to a more successful and user-centric product.
How Does User Interface Impact User Experience
User Interface (UI) profoundly impacts User Experience (UX) because it serves as the primary point of interaction between users and a software product or system. UI significantly influences how users perceive, interact with, and ultimately experience a product.
“Good design is actually a lot harder to notice than poor design, in part because good designs fit our needs so well that the design is invisible, serving us without drawing attention to itself. Bad design, on the other hand, screams out its inadequacies, making itself very noticeable.”
Donald A. Norman
Here are thirteen ways in which UI impacts UX:
- It creates a solid first impression. Your UI is often the first thing users see when they interact with your business or product. A visually appealing and well-designed UI creates a positive first impression, setting the visitor up for a memorable user experience.
- It makes your product easy to use. A user-friendly UI helps your customer easily navigate your software, access features, and perform tasks. An intuitive UI flattens the learning curve, helping users easily accomplish their goals.
- It’s efficient. An efficient UI design enables users to complete tasks quickly without much hassle. Streamlined workflows, strategically placed controls, and clear labeling make for a more efficient UX.
- It’s clear and easy to understand. A well-designed UI communicates information effectively. Clear icons, labels, and visual cues assist users in understanding the purpose and functionality of different elements.
- It’s consistent, and a consistent UI design ensures that users understand how elements behave across the application. Familiar layouts and patterns help customers know how to move around different parts of the application.
- It’s accessible, showing a high consideration for the needs of all users. When you properly implement accessibility features in your app, you’ll significantly improve the UX for a wider audience. Such features include keyboard navigation and screen reader support.
- It offers significant feedback and guidance. UI elements can provide feedback to users, showing the success or failure of their actions. Informative error messages, progress indicators, and tooltips provide guidance, enhancing the overall user experience.
- It presents a reasonable visual appeal. Design choices such as color schemes, imagery, and typography influence users’ emotional response. An eye-catching UI can spark positive emotions and improve the overall experience.
- It’s adaptable. A responsive UI design preserves the user experience regardless of device or screen size. Your customers should have a seamless experience using your application on their mobile phone, tablet, or desktop machine.
- It offers high performance. UI design easily defines the perceived performance of an app. Is it responsive? Does it offer smooth transitions? How efficient are the loading times? If you tick “Yes” in all these boxes for your software, then your users are likely to report a positive user experience.
- It offers room for customization because when UI elements enable users to personalize their experience, they’re more likely to enjoy using the product on their terms. Settings for theme options and preferences can improve satisfaction by an order of magnitude.
- It makes room for handling errors. Does your application user interface handle errors or unexpected situations in a way that prioritizes the user experience? Clear and informative error messages assist your customers in recovering from mistakes or issues gracefully.
- It reinforces a positive brand identity. User interface can reflect your brand’s identity and values, enhancing brand recognition and loyalty. Consistent branding elements within the UI reinforce the brand’s image.
In summary, your app’s user interface design is a key component of UX design. It directly determines how users perceive and interact with your product, and a thoughtful, user-centered UI design can significantly improve the overall user experience, leading to greater user satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty.
Key Principles of Effective UI Design
User Interface design creates digital spaces where users interact with software or applications. Effective UI design is essential so that customers have a seamless and enjoyable experience with your app. We’ll explore the key principles of effective UI design under three main subheadings.
Creating a Visually Appealing UI
Visual appeal plays a crucial role in UI design. A visually appealing interface can attract users and leave a lasting positive impression. Here are some broad strokes to focus on to achieve resounding visual appeal:
- Color Harmony: Choose a good color palette that conveys the right mood and message. Use contrasting colors for text and backgrounds to ensure readability. Be consistent in your color choices throughout the UI.
- Typography: Use easy-to-read that align with the overall design aesthetics. Establish a hierarchy using varying font sizes and weights for headers, body text, and other elements. Note that proper spacing and alignment also enhance readability.
- Whitespace: Keep your UI lean on elements. Whitespace (or negative space) is your friend, providing breathing room, helping users focus on content, and keeping your UI clean and organized.
- Images and Icons: Use only relevant, high-quality images, icons, and graphics. Icons must be intuitive, conveying what they mean without textual explanations. Pay attention to file sizes for high performance.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in your visual design elements, including buttons, menus, and icons. Consistency helps your users build mental models of your application UI, helping them to navigate and understand.
Best Practices for Organizing UI Elements
The organization of UI elements is critical in ensuring usability and ease of navigation. Here are some best practices for organizing UI elements effectively:
- Information Hierarchy: Keep content and actions front and center, depending on their importance. Secondary elements should be less prominent but still easily accessible.
- Grouping: Related elements need to sit together in a logical arrangement. For example, navigation menus should be at the top, and form fields should be grouped inside a container. It helps users to understand the relationships between different parts of the UI.
- Layout Consistency: Using a consistent layout across your UI will establish familiarity, keeping the placement of navigation menus, logos, and other key elements consistent across pages or screens.
- Progressive Disclosure: Users prefer to have only a bit of relevant information at once. Progressive disclosure is a good way to reveal additional options or details when the user requests them, reducing clutter and cognitive load.
- Navigation: Your app’s navigation is more intuitive when you use clear labels and organize menus logically. Breadcrumbs or a sitemap will help users understand their present location within the application.
Consistency and Coherence in UI Design
Two fundamental principles of effective UI design are consistency and coherence. They enable users to build a mental model of the system. Here are ways to achieve both in your app:
- Design Patterns: Stick with established design patterns and conventions that users understand. For instance, use a standard icon for “Settings” instead of inventing a new one. Industry standards enhance usability and have the quality of consistency.
- Style Guides: A style guide or design system provides documentation for your UI elements. It ensures that all team members adhere to a consistent design language.
- User Testing: Conduct user testing to gather feedback on your user interface. It can reveal inconsistencies or areas where the design can be improved. Iterative testing and refinement lead to a more coherent UI.
- Feedback Loops: Encourage feedback from users and stakeholders. Use constructive feedback to address any issues with consistency or coherence promptly.
UI design that focuses on the user is essential for creating a positive user experience. By dealing with visual appeal, organizing UI elements thoughtfully, and ensuring consistency and coherence, your designers can build UIs that are visually pleasing, user-friendly, and easy to navigate.
Ultimately, an effective UI promotes application usability and overall user satisfaction, contributing to the success of the software or application.
Understanding User Behavior
User behavior is the heartbeat of effective app and UI design. Creating engaging, satisfying, and user-converting interfaces means designers must delve into the intricate workings of human psychology. The factors influencing user behavior within a UI, strategies for optimizing UI for different user demographics, and the pivotal role of cognitive psychology in UI design are critical to an app’s success.
Factors that Influence User Behavior within a UI
Understanding user behavior begins with recognizing the multifaceted factors that come into play when users interact with an interface:
- Visual Appeal: The visual aspects of a user interface significantly impact user behavior. Attractive design elements can attract users, instilling trust and confidence in your company.
- Ease of Use: Users are more likely to engage with intuitive and easy-to-navigate interfaces. Streamlining user interactions and minimizing friction points can reinforce positive user behavior.
- Content Relevance: The content presented within a user interface needs to align with the user’s needs and interests. Users are more likely to engage with valuable and relevant information.
- Emotional Engagement: Emotions are important in user behavior. Design elements need to elicit positive emotions like joy or satisfaction. It enhances user engagement and conversion rates.
- Feedback and Rewards: Providing timely feedback and rewards for user actions can positively reinforce desired behaviors. It may include acknowledging completed tasks, gamification elements, or incentives for continued engagement.
Optimizing UI for Different User Demographics
Optimizing UI for diverse user demographics is essential to ensure inclusivity and enhance user engagement:
- User Research: Use regular user research experiments to understand various user demographics’ preferences, needs, and pain points. This information serves as a foundation for UI customization.
- Segmentation: Split your user base into distinct segments based on demographics, including age, gender, location, and interests. UI elements, content, and interactions should suit each segment.
- Personalization: Implement personalization features that align with user behavior- and preference-based preferences. It includes content filtering, personalized recommendations, or user-specific dashboards.
- Accessibility: Your user interface should be usable to customers with diverse disabilities. Features like contrast adjustment, keyboard navigation, and screen readers will help your app accommodate more users than if it didn’t.
- Language and Cultural Considerations: Adapt your UI to different languages and cultural specifics. Use culturally sensitive imagery, symbols, and colors to resonate with diverse audiences.
Cognitive Psychology in UI Design
Cognitive psychology is the bedrock of effective user interface design. It covers how users perceive, process, and interact with information:
- Information Processing: Cognitive psychology principles guide the presentation of information within a UI. Use techniques like chunking, clear labeling, and progressive disclosure to facilitate cognitive processing.
- Attention and Perception: Understanding how users allocate attention and perceive visual elements helps create UIs that direct user focus. Employ techniques like contrast, hierarchy, and visual cues to guide attention effectively.
- Memory and Recall: Cognitive psychology informs UI design by considering human memory limitations. Minimize cognitive load by simplifying complex tasks and using familiar patterns that aid memory recall.
- Decision Making: User Interfaces for your applications need to support users’ decision-making processes. Present information logically, provide comparisons and reduce choice overload to assist users in making informed decisions.
- Feedback and Error Handling: Cognitive psychology emphasizes the importance of clear and immediate feedback. Design user interfaces that inform users about the outcomes of their actions and guide them in error recovery.
Understanding user behavior is central to create UIs that resonate with users and drive desired actions. By considering the factors influencing user behavior, optimizing UI for different user demographics, and integrating cognitive psychology principles, your product designers can build visually appealing, engaging, user-friendly, and aligned with all aspects of human cognition. This understanding will empower designers to create interfaces that guarantee exceptional user experiences and build lasting user engagement.
Usability Testing and Feedback
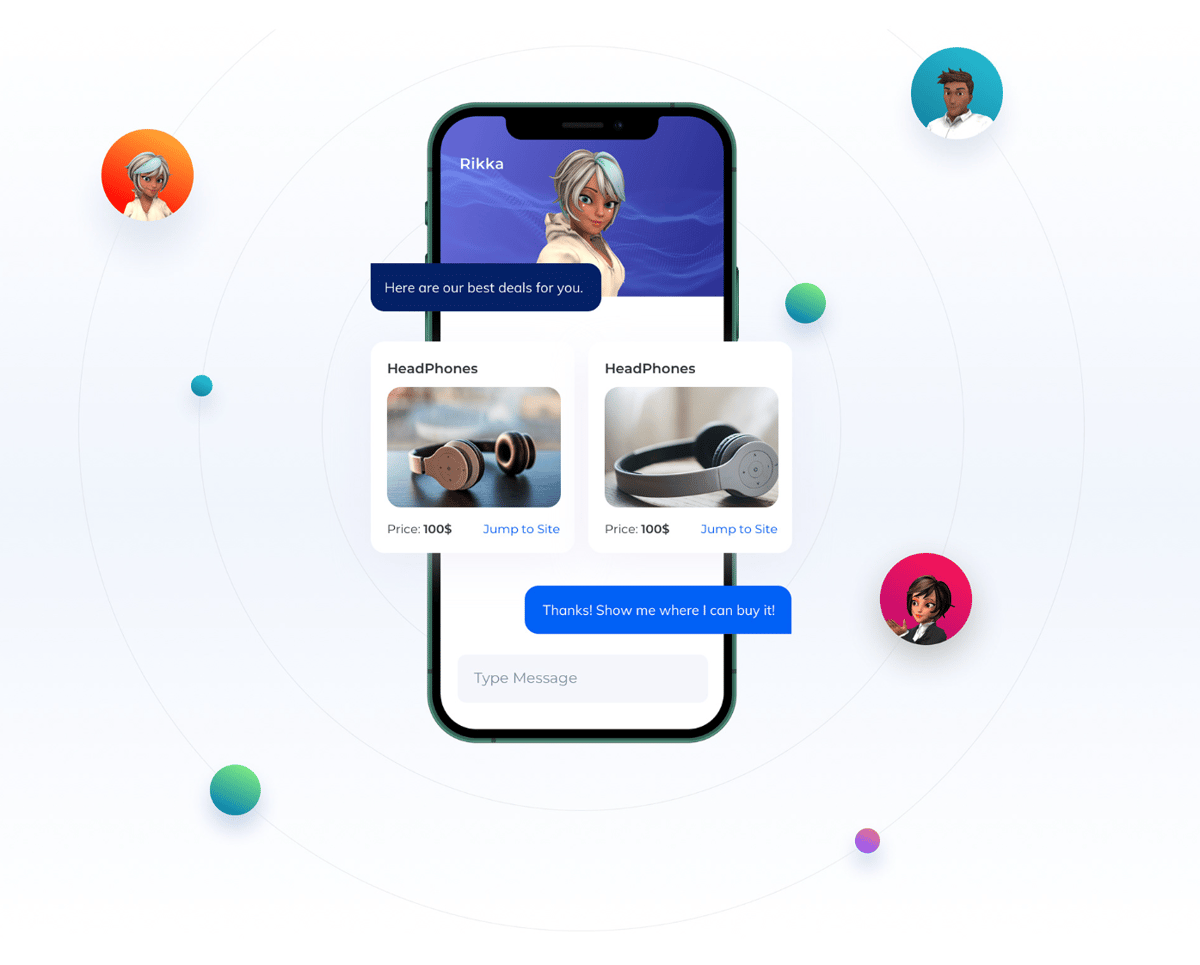
User Interface development can be a complex undertaking that demands you understand and deliver user needs effectively. Usability testing and feedback are important components of this journey. In this article, we will explore why usability testing is crucial in UI development, the various methods for conducting usability tests, and how to collect and incorporate user feedback to drive UI improvements.
Importance of Usability Testing in UI Development
Usability testing serves as the compass that keeps UI development on the right course. Here’s why it’s vital:
- User-Centric Approach: Usability testing refocuses designers’ assumptions on users’ real experiences. It helps you identify pain points, preferences, and expectations, ensuring the product interface caters to user needs.
- Unveils Issues: Usability testing unveils hidden issues in the UI, such as navigation difficulties, confusing layouts, or unclear labels. These insights allow for early problem resolution.
- Validation of Design: The way to validate your design decisions is by testing them in production in real-world usage. It minimizes the risk of building a user interface that’s challenging or unappealing for customers.
- Cost-Efficiency: Identifying and rectifying usability issues during the development phase is far more cost-effective than extensive changes after the UI is available to the user.
- Enhanced User Satisfaction: A well-optimized user interface that has undergone usability testing will likely lead to improved user satisfaction, increased engagement, and potentially higher conversion rates.
Methods for Conducting Usability Tests
Depending on the goals, resources, and project timeline, various forms of usability testing exist. Here are some common methods to do this:
- Moderated Usability Testing: Here, a facilitator guides users through predefined tasks while observing their interactions. This method allows real-time feedback collection and probing for insights.
- Unmoderated Usability Testing: In this case, participants independently perform tasks on the UI and provide feedback through recorded sessions. This method is cost-effective and can involve a larger number of participants.
- Remote Usability Testing: Conducted online, remote usability testing lets participants access the UI from their own devices. It’s ideal for gathering feedback from users in diverse geographical locations.
- Hallway Testing: An informal usability testing method where individuals passing by are asked to interact with the UI. It’s quick and inexpensive, providing valuable insights to developers.
- Cognitive Walkthroughs: Evaluators simulate step-by-step user interactions, focusing on decision-making and thought processes. This method is useful for spotting potential usability issues.
Collecting and Incorporating User Feedback into UI Improvements
Collecting and incorporating user feedback is the core basis of effective UI development:
- A/B Testing: Implement A/B testing to compare the performance of different UI variations. Analyze user behavior and preferences to inform design decisions.
- Feedback Analysis: Systematically analyze all collected feedback, categorizing it based on common themes or issues. Prioritize identified problems based on their impact on user experience.
- Iterative Design: Implement iterative design cycles based on feedback. Make incremental improvements to the UI, testing each change with users to validate its effectiveness.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Use structured surveys or questionnaires to collect quantitative data on user preferences, satisfaction, and pain points. Analyze the results to identify trends and areas to improve your UI.
- User Interviews: Conduct in-depth interviews with users to gain qualitative insights into their experiences. Open-ended questions can reveal valuable details about user needs and frustrations.
- User Observations: Observe users as they interact with the UI during usability tests. Note their actions, comments, and expressions to identify usability issues and areas of confusion.
Ultimately, usability testing and feedback are pivotal in the evolution of user-friendly and effective user interfaces. A user-centric approach employs various usability testing methods, and by diligently collecting and incorporating user feedback, developers can create interfaces that culminate in higher user engagement and ultimately, a more successful digital product or service. Usability testing isn’t just a phase in user interface development; it’s an ongoing commitment to continually enhance the user experience and stay attuned to evolving user needs.
Designing UI for Different Platforms and Devices
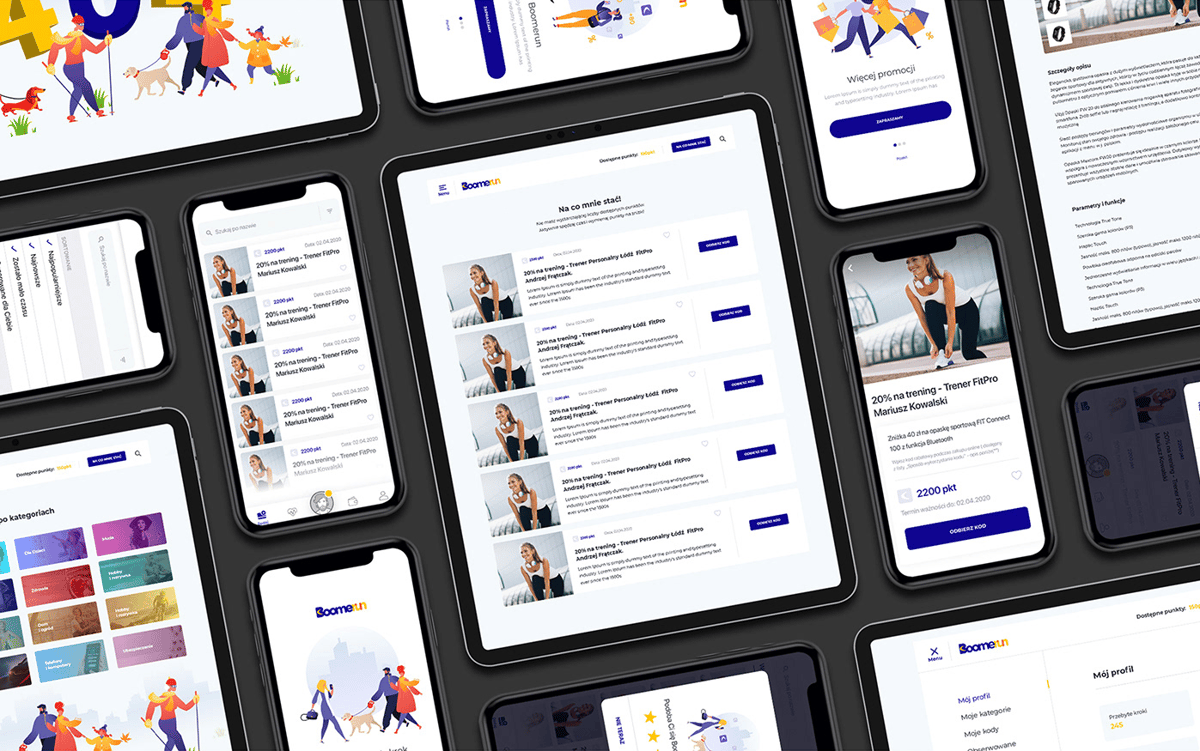
The digital landscape evolves fast. It would help if you designed your UI to adapt to various platforms and devices seamlessly. Users interact with software on a plethora of screens, from smartphones to desktops, and even emerging technologies like wearables and augmented reality (AR) devices. We should now explore the key considerations for responsive user interface design, strategies to adapt UI for mobile and desktop applications, and the challenges your designers face in creating UI for emerging technologies.
Responsive User Interface Design
Responsive UI design is the cornerstone of a user-friendly experience across diverse devices. It involves the following considerations:
- Screen Size and Orientation: Designers must account for varying screen sizes and orientations, ensuring content remains accessible and visually appealing. Media queries and flexible layouts help achieve this.
- Touch vs. Mouse Interactions: Different devices employ various input methods, such as touchscreens for mobile and tablets and mice or trackpads for desktops. Designers must optimize button sizes and interactive elements accordingly.
- Content Prioritization: On smaller screens, space constraints demand careful content prioritization. Key information should be prominently displayed, while non-essential elements may be hidden behind menus or accordions.
- Performance: Efficient UI design ensures that applications load quickly and run smoothly, regardless of the user’s device or internet connection speed.
Mobile and Desktop Applications UI Adaptation
Tailoring UI for both mobile and desktop applications requires a thoughtful approach:
- Mobile-First Design: Start with a mobile-first approach, designing for the smallest screens first. It ensures that the core functionality and content are well-defined before scaling for larger displays.
- Scalable Assets: Use scalable vector graphics (SVGs) and icon fonts to ensure that images and icons look sharp on all screen sizes. It’s best to avoid fixed-width elements.
- Responsive Layouts: Employ responsive design frameworks like Bootstrap or Flexbox to create layouts that adapt fluidly to various screen sizes and orientations.
- Navigation: On mobile, consider using a hamburger menu or bottom navigation for simplicity, while desktop applications may benefit from traditional menus and navigation bars.
- Testing and Iteration: Regularly test your UI on real devices to identify and rectify any issues. Continuous iteration is key to refining the user experience.
Challenges in UI Design
As technology continues to advance, designers encounter unique challenges when crafting UI for emerging platforms and devices:
- Limited Guidelines: Emerging technologies often need more established design guidelines, forcing designers to pioneer new UI principles. It necessitates extensive research and experimentation.
- Interaction Paradigms: Devices like AR glasses and virtual reality (VR) headsets introduce novel interaction paradigms, such as gesture controls and spatial interfaces. Crafting intuitive interactions is a complex undertaking.
- Performance Optimization: Emerging platforms may have limited processing power and memory compared to traditional devices. Optimizing UI for performance is paramount to ensure a seamless user experience.
- Accessibility: Ensuring accessibility for users with disabilities remains a challenge in emerging tech, as many accessibility standards and tools are designed for traditional platforms.
- Fragmentation: The diversity of emerging technologies, from smartwatches to mixed reality devices, leads to fragmentation in design. Each platform may require a unique UI adaptation.
Therefore, designing UI for different platforms and devices is a multifaceted task involving screen sizes, input methods, and performance optimization. Adapting UI for mobile and desktop applications requires a mobile-first approach, responsive layouts, and thorough testing. Your designers must deal with evolving guidelines, new interaction paradigms, and performance challenges. As technology continues to evolve, the art of user interface design must also evolve to meet the demands of a rapidly changing digital landscape.
UI Trends and Innovations
In the ever-evolving digital design landscape, User Interface (UI) trends and innovations are at the forefront of creating immersive and user-centric experiences. As technology advances at an unprecedented pace, designers and developers must stay on top of the latest trends to ensure their products remain relevant and engaging.
Now we’ll explore the latest UI design trends, the potential of emerging technologies in UI development, and some successful examples of innovative UI design.
Latest Trends in User Interface Design

In 2023, UI design embraces a range of exciting trends that enhance user experiences.
- Minimalistic Design: The “less is more” philosophy continues to thrive. Minimalistic design focuses on clean, uncluttered interfaces, emphasizing content and functionality. This trend simplifies navigation and ensures a seamless user journey. In creating the BBC iPlayer radio version, the designers appealed to older people. These folks knew little about tech and weren’t as fascinated about it, but the BBC needed them to listen to the shows. The simple and intuitive interface using a responsive scrolling dial that mimicked a traditional analog radio, complmented the array of 19 radio stations.
- Dark Mode: Dark mode is now a mainstream UI trend. It reduces eye strain and also adds a touch of sophistication to the app and web designs. Social media and productivity apps use dark mode as a way to have users focus and use the apps for longer times.
- Neumorphism: Another emerging trend in UI design, neumorphism is a fusion of skeuomorphism and flat design, neumorphism creates visually appealing and tactile interfaces by adding subtle shadows and highlights to elements. It provides a more immersive experience by simulating the interaction with real-world objects. Apple Inc. pushes the boundaries of neumorphic experiments in its hardware and software
- Microinteractions: These small, subtle animations and responses to user actions make UIs come alive. They provide feedback to guide users, providing a delightful experience overall.
Leveraging Emerging Technologies in UI Development
The rapid advancement of emerging technologies has opened up new horizons for UI development. Here are some ways you can harness these innovations:
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR transform UI through immersive experiences. Whereas AR overlays digital content on real-world elements, VR provides virtual environments. Industries such as e-commerce, gaming, and education leverage these technologies to enrich UX.
- Voice User Interfaces (VUIs): As smart speakers and virtual assistants become more mainstream, VUIs are increasingly prominent. Voice commands in your UI design can offer a convenient, hands-free interaction.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI-powered chatbots, recommendation engines, and predictive analytics enhance UX through content personalization and task automation. It saves time and boosts user engagement.
- 3D Graphics and Animation: 3D graphics and animations add depth and interactivity to UIs. They’re especially useful in product showcases, gaming, and storytelling, providing users with a more immersive and memorable experience.
Examples of Innovative UI Design
Several companies have embraced innovative UI design to create compelling user experiences:
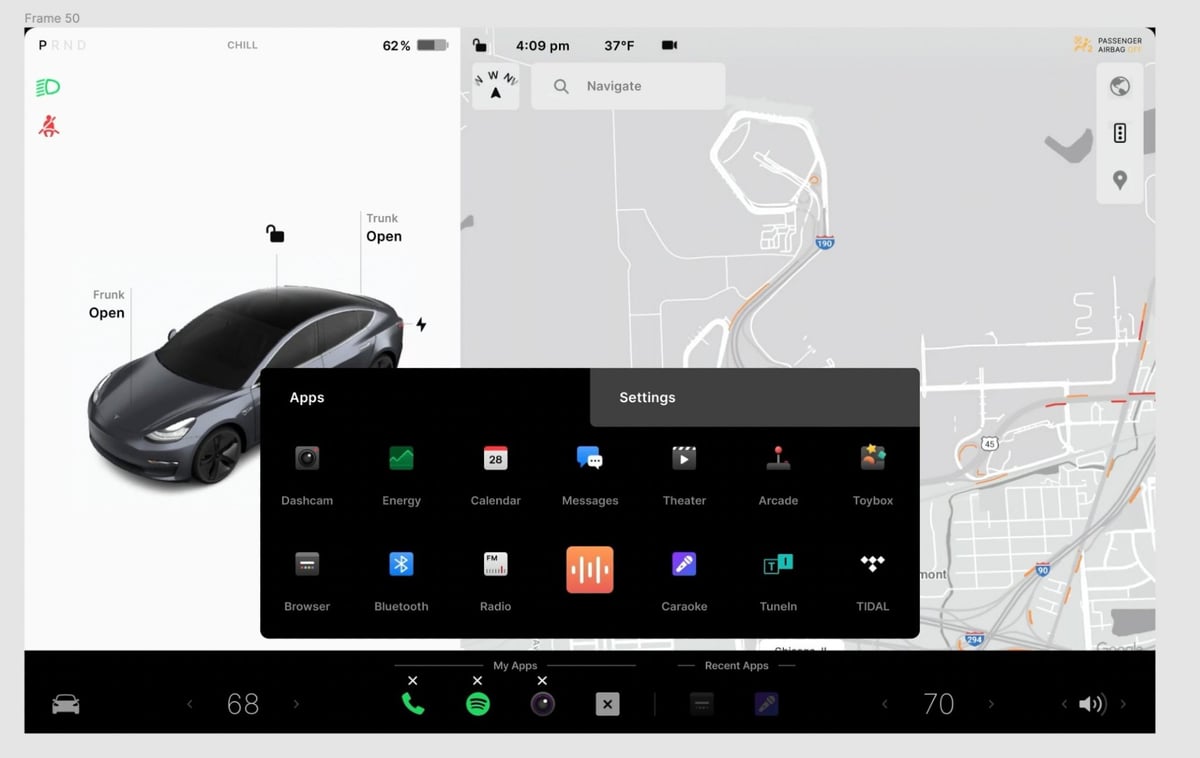
- Tesla’s In-Car UI: Tesla’s in-car UI is a prime example of blending innovation with functionality. With frequent software updates and a minimalist design, it offers users a futuristic experience while maintaining ease of use.
- Airbnb’s Lottie Animations: Airbnb uses Lottie, an open-source animation tool, to create engaging micro-interactions in their app. These animations add whimsy and feedback to user interactions, enhancing the overall experience.
- Duolingo’s Gamification: Duolingo’s UI transforms language learning into a game-like experience. Interactive lessons, rewards, and progress tracking keep users motivated and engaged.
- Apple’s ARKit: Apple’s ARKit empowers developers to create AR experiences within their apps. Apps like Ikea Place allow users to visualize furniture in their homes before making a purchase, offering a novel and practical UI solution.
UI trends and innovations are always evolving due to the forces of user expectations and technological advancements. Staying ahead in UI design requires a keen eye on the latest trends, an open mind to leverage emerging technologies, and inspiration from successful examples of innovative UI design. By embracing these principles, designers, and developers can create UIs that captivate users and shape the future of digital experiences.
The Takeaway
UIs are dynamic, continuously evolving, and essential to unlocking exceptional User Experiences (UX). Throughout this article, we’ve explored the crucial role of UI design in forging digital interactions, and you can harness it to improve how users engage with your digital products.
UI design is about aesthetics, usability, accessibility, and functionality. Your developers need a deep understanding of user behavior, needs, and preferences. Executing user interface design with precision and empathy allows them to transform otherwise ordinary applications into extraordinary experiences that users will find delightful and indispensable.
We’ve shared valuable principles, techniques, and practices that help us make the most of a complex and interconnected digital landscape. These are reminders that while pursuing exceptional User Experiences, the user should always define our design decisions. So, whether you are building a mobile app, website, or digital product, remember to craft experiences that inspire, inform, and empower. Knowing this and committing to excellence, you’ll be prepared to use User Interfaces as a driving force to continually improve and enhance User Experiences, helping users connect with your overall organizational objectives.


