Ever feel like your business is running a marathon, but everyone’s on different tracks? That’s where a great product roadmap template comes in! It’s your secret weapon for steering through the chaos, keeping your team aligned, and ensuring that every step you take leads you closer to your big goals.
In a world where speed and innovation are everything, having a clear roadmap can make all the difference. In this guide, we’ll explore why product roadmaps are essential, the benefits of using templates, and some handy tips for crafting a roadmap that really drives your business forward.
The Power of a Roadmap
A product roadmap is a strategic tool that is vital for businesses of all sizes. It offers a detailed overview of the product’s journey from concept to market and serves as a guiding framework for the entire organization. More than just a plan, a product roadmap encapsulates the vision and direction of the product, ensuring that all teams and stakeholders are aligned around a common objective. By providing this clarity, it helps to coordinate efforts, prioritize tasks, and allocate resources effectively, making sure that everyone is working towards the same end goal.
Need help with roadmapping your product? At Iterators we can help design, build, and maintain custom software solutions for both startups and enterprise businesses.
Schedule a free consultation with Iterators today. We’d be happy to help you find the right software solution to help your company.
Establishing Clear Vision
A well-crafted product roadmap sets a clear direction for your team, outlining the long-term vision and the steps to get there. To establish this vision, start by involving your team in brainstorming sessions to gather diverse insights and foster ownership. Next, break down your goals into key milestones—this makes big projects feel more manageable and achievable.
Prioritize tasks by aligning them with your overall strategy; use techniques like the Eisenhower Matrix to determine what’s urgent versus important. Establish timelines that are realistic, allowing for flexibility as needed.
Finally, communicate regularly—use visual aids like Gantt charts or Kanban boards to keep everyone on track. This clarity not only boosts efficiency but also motivates employees, as they can see how their contributions drive the company’s success. Your roadmap ultimately becomes a vital tool for reducing ambiguity and harmonizing efforts toward your strategic objectives.
Alignment with Stakeholders
Getting buy-in from key stakeholders is vital for any product’s success, and your product roadmap is essential in this process. Start by clearly communicating the roadmap’s strategic direction and how it aligns with broader business goals. Use visuals like infographics to make the information more digestible.
Involve stakeholders early in the planning phase—hold workshops or brainstorming sessions to gather their input. This not only helps them feel valued but also ensures their concerns are addressed from the start.
Regularly update stakeholders on progress and any changes to the roadmap. This transparency builds trust and confidence, making it easier to secure the necessary resources and approvals.
Lastly, highlight the benefits of the product to different stakeholders, showing how it meets their specific needs. By fostering a collaborative environment, you’ll enhance support and collaboration throughout the development process, paving the way for a successful product launch and long-term sustainability.
Adaptability in Dynamic Markets
In today’s rapidly evolving markets, flexibility is key to staying competitive. A product roadmap serves as a structured yet adaptable framework that can be adjusted as market conditions change. By regularly reviewing and updating the roadmap, businesses can remain agile, pivoting when necessary to seize new opportunities while maintaining focus on their long-term goals.
The Risks of On-the-Fly Product Development

Operating without a clear product roadmap exposes businesses to significant risks and uncertainties. Without a strategic plan, companies can end up navigating aimlessly, reacting to short-term challenges instead of proactively pursuing long-term goals. This lack of foresight can lead to costly missteps, such as missed market opportunities, wasted resources, and, ultimately, a product that fails to meet customer expectations.
Missed Opportunities
For instance, without a roadmap, a tech startup might overlook emerging trends like AI integration, missing the chance to enhance their product’s capabilities and attract a wider audience.
This reactive approach often results in shifting priorities—imagine a team pivoting to address immediate customer complaints instead of investing in features that could significantly increase market share.
In a competitive landscape, the ability to act strategically is crucial. A roadmap enables companies to identify and seize opportunities, keeping their products relevant and competitive.
Resource Misallocation
One of the biggest risks in product development is misallocating resources. Without a clear plan, teams may waste time on low-impact tasks, such as minor design tweaks, while overlooking critical initiatives like market research or user testing. This can drain both time and budget, especially if investments are made in features that don’t align with customer needs.
To allocate resources effectively with a roadmap, start by prioritizing tasks using a scoring system that evaluates impact, urgency, and alignment with strategic goals. Set clear milestones to create a timeline for resource allocation, ensuring teams know when to shift focus. Regular check-ins help reassess priorities and allow for quick pivots based on new insights.
Encourage cross-functional collaboration to share insights and feedback, and leverage project management tools for transparency. By following these strategies, you can mitigate resource misallocation risks and keep your team aligned toward product success.
Benefits of Using a Template

Creating a product roadmap from scratch can be an intimidating task, especially for those new to product management. However, using a pre-designed template offers numerous advantages that can significantly streamline the process and enhance the overall quality of the final roadmap.
Time-Saving
One of the primary benefits of using a template is the substantial time savings it offers in the planning process. Templates provide a ready-made structure, allowing teams to focus on content rather than format. This efficiency enables faster decision-making, quicker alignment, and helps businesses maintain momentum throughout the product development lifecycle.
Professional Structure
A well-designed template ensures that the roadmap is both organized and professional in appearance. It provides a cohesive layout that guides the inclusion of essential elements, such as goals, timelines, and milestones. This professional structure not only enhances internal communication but also makes a strong impression on external stakeholders, such as investors or partners, reinforcing the credibility and seriousness of the product strategy.
Flexibility and Customization
Despite being pre-designed, templates offer a high degree of flexibility and customization to meet the specific needs of a business. Teams can easily adapt the template to reflect their unique goals, priorities, and timelines. This customization ensures that the roadmap isn’t only visually appealing but also highly relevant and aligned with the company’s strategic objectives, making it a powerful tool for guiding the product’s development and success.
Understanding Product Roadmaps
It’s essential to present a proper background of what product roadmaps are and how they impact business growth. Let’s start with the following:
Key Components of a Product Roadmap
A product roadmap is composed of several key components that work together to provide a comprehensive view of the product’s development journey. These components include:
- Goals: The overarching objectives that the product aims to achieve. These can be both short-term and long-term, providing direction for the product’s development.
- Features: The specific functionalities or enhancements that will be included in the product. Features are typically prioritized based on their value to the customer and their alignment with the product’s goals.
- Timelines: The schedule for when different features or milestones will be completed. Timelines help set expectations and ensure that the product development process stays on track.
- Milestones: Significant points in the product’s development, such as the completion of a major feature, the release of a new version, or the achievement of a key performance indicator (KPI). Milestones help teams measure progress and celebrate achievements.
Together, these components provide a structured approach to product development, ensuring that every step taken is purposeful and aligned with the product’s strategic objectives.
Example of a Product Roadmap
To help you understand the components of a product roadmap and its effectiveness, here’s a simple example for a fictional mobile app called “FitTrack,” which focuses on fitness tracking and community engagement:
FitTrack Product Roadmap
Timeframe: Q1 2024 – Q4 2024
Q1 2024: Planning and Research
- Goals: Define target audience and key user needs.
- Features:
- User surveys and interviews.
- Competitive analysis report.
- Milestones:
- Complete user persona documentation.
- Present findings to stakeholders by the end of March.
Q2 2024: MVP Development
- Goals: Launch a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to gather initial user feedback.
- Features:
- Basic fitness tracking (steps, calories burned).
- Community forum for user interaction.
- Timelines:
- Development phase: April – June.
- Beta launch scheduled for June 30.
- Milestones:
- Achieve 100 beta users by July 15.
Q3 2024: User Feedback and Iteration
- Goals: Improve the app based on user feedback.
- Features:
- Introduce personalized workout plans.
- Add social sharing capabilities.
- Timelines:
- Iteration phase: July – September.
- Milestones:
- Release updated version by September 30.
- Reach 500 active users by the end of September.
Q4 2024: Growth and Marketing
- Goals: Increase user acquisition and engagement.
- Features:
- Launch referral program.
- Implement gamification elements (badges, challenges).
- Timelines:
- Marketing campaigns to begin in October.
- Milestones:
- Achieve 1,000 downloads by December 15.
- Conduct user engagement survey by December 31.
This roadmap provides a clear structure for the FitTrack app’s development journey. It outlines goals, features, timelines, and milestones to ensure alignment and focused progress.
The Value of a Well-Structured Roadmap

1. Improved Decision-Making
A well-structured product roadmap is an invaluable tool for making informed decisions throughout the product development process. By clearly outlining goals, priorities, and timelines, it provides a framework for evaluating potential initiatives and determining which ones align best with the product’s strategic objectives.
This structured approach helps avoid knee-jerk reactions to market pressures or internal demands, ensuring that every decision is made with the long-term vision in mind.
Additionally, a roadmap facilitates scenario planning, allowing teams to assess the potential impact of different decisions and choose the path that offers the greatest benefits with the least risk.
2. Enhanced Communication
Clear and consistent communication is essential for the success of any product development effort, and a well-structured roadmap plays a pivotal role in facilitating this.
Providing a visual representation of the product’s strategy and progress, the roadmap serves as a single source of truth for all stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is aligned and informed. It helps bridge the communication gap between different teams—such as engineering, marketing, and sales—by providing a shared understanding of priorities and timelines. This alignment reduces misunderstandings and conflicts, enabling more efficient collaboration and ensuring that all efforts are directed towards the same goals.
3. Better Resource Allocation
Efficient resource allocation is critical to the success of any product development effort, and a well-structured roadmap provides the necessary guidance for making these decisions. By clearly prioritizing features and initiatives based on their strategic importance, the roadmap helps teams allocate resources—such as time, budget, and personnel—where they will have the most significant impact.
This focused approach minimizes waste and ensures that critical tasks are completed on time and within budget. Additionally, by providing a long-term view of the product’s development, the roadmap helps identify potential resource bottlenecks and plan accordingly, reducing the risk of delays and cost overruns.
4. Alignment with Business Objectives
A well-structured product roadmap ensures that all efforts within the product development process are aligned with the company’s overarching business objectives. By clearly articulating how each feature, milestone, and initiative contributes to these objectives, the roadmap provides a direct link between the day-to-day work of the product team and the broader strategic goals of the organization.
Alignment not only ensures that resources are used effectively but also helps maintain focus on the company’s long-term vision. As a result, the product roadmap becomes a powerful tool for driving business success, ensuring that every decision and action taken is aligned with the company’s strategic priorities.
Common Types of Product Roadmaps
1. Feature Roadmaps
Feature roadmaps are one of the most commonly used types of product roadmaps, focusing primarily on the specific features and functionalities that will be included in a product. These roadmaps provide a detailed view of the development and release of individual features, allowing teams to prioritize based on customer needs, business value, and technical feasibility.
Feature roadmaps are particularly useful for guiding the work of development teams, as they provide clear and actionable guidance on what needs to be built and when. However, their narrow focus on features can sometimes lead to challenges in aligning with broader strategic goals, making it essential to balance feature priorities with long-term objectives.
These roadmaps are best suited for products in the development phase, where the focus is on delivering tangible functionality to users. They’re also beneficial in scenarios where the product’s success is heavily dependent on the timely delivery of specific features that address customer pain points or market demands.
2. Release Roadmaps
Release roadmaps focus on the timing and coordination of product releases, detailing what will be delivered and when. These roadmaps are particularly valuable for planning and managing the expectations of both internal teams and external stakeholders.
Release roadmaps typically include information on the scope of each release, the features that will be included, and the timeline for delivery. They help ensure that all teams—from development to marketing—are aligned on the release schedule, enabling coordinated efforts to prepare for product launches. Release roadmaps are especially useful for organizations that operate in fast-paced environments, where frequent updates and new releases are critical to maintaining competitive advantage.
However, they require careful management to avoid the risk of overcommitting to timelines or features that may not be feasible. In addition, they help manage customer expectations by clearly communicating when new features or updates will be available, thereby building trust and anticipation among users.
3. Strategic Roadmaps
Strategic roadmaps provide a high-level view of how a product’s development aligns with the company’s long-term business goals. These roadmaps focus on the broader vision, outlining how the product will evolve over time to meet market needs and achieve strategic objectives.
Strategic roadmaps are particularly useful for communicating with executive leadership, investors, and other high-level stakeholders, as they provide a clear picture of the product’s future direction and how it supports the company’s overall strategy. Unlike feature or release roadmaps, which focus on specific deliverables, strategic roadmaps emphasize the product’s role in achieving business outcomes, such as market expansion, revenue growth, or customer retention.
This broader perspective helps ensure that the product remains aligned with the company’s strategic priorities, even as market conditions and customer needs change. Strategic roadmaps are essential for long-term planning and for making high-level decisions about the product’s future.
4. Other Types
In addition to feature, release, and strategic roadmaps, there are several other types of roadmaps that can be valuable depending on the specific needs of a business. These include technology roadmaps, which focus on the evolution of technical infrastructure; market roadmaps, which outline market trends and competitive positioning; and portfolio roadmaps, which provide an overview of multiple products within a company’s portfolio, highlighting how they interact and contribute to the overall business strategy.
Each of these roadmaps serves a unique purpose, helping organizations plan and execute their product strategies more effectively.
Creating Your Own Product Roadmap
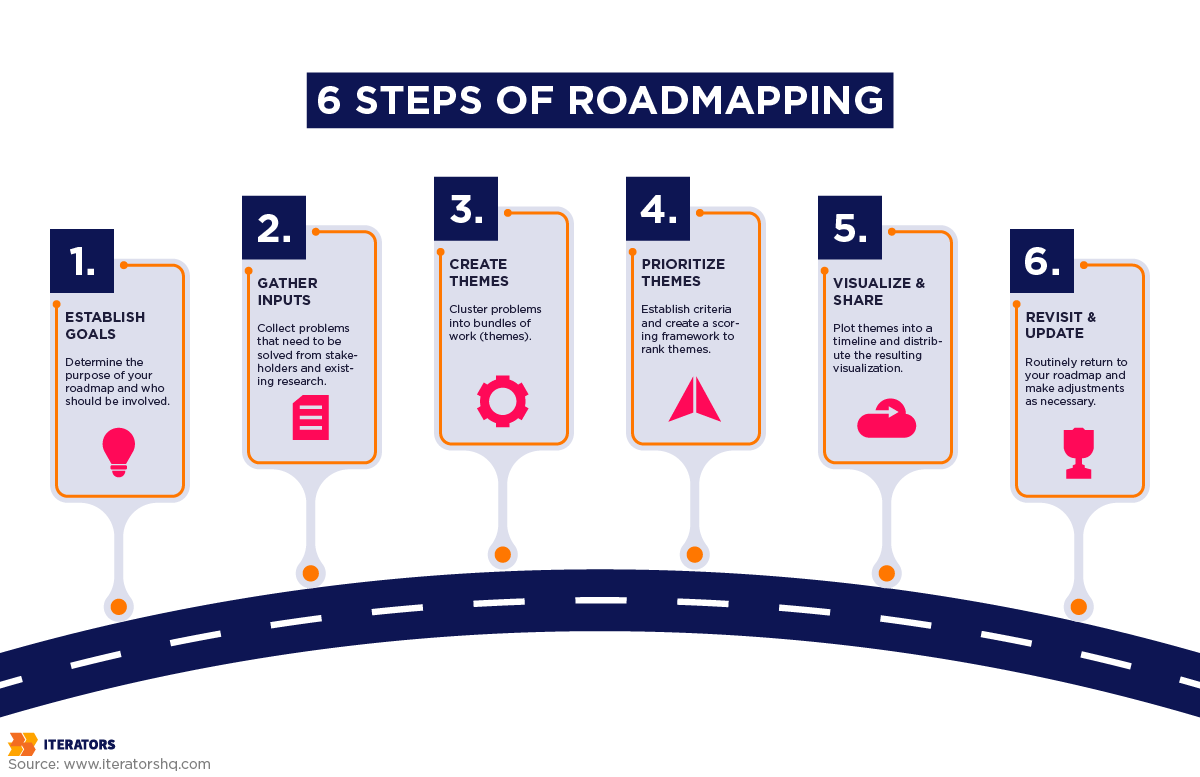
Defining Your Goals and Objectives
Setting clear, achievable goals is fundamental to the success of any product roadmap. Clear goals provide direction and purpose, ensuring that every effort is aligned with the overall vision of the product. They help teams understand what needs to be accomplished and why it matters, creating a sense of focus and motivation.
Well-defined goals also enable better prioritization and decision-making, as they offer a benchmark against which progress can be measured. By setting clear goals, teams can avoid ambiguity and ensure that all stakeholders are aligned around the same objectives. This alignment is crucial for maintaining momentum and achieving successful outcomes, as it helps to coordinate efforts, allocate resources effectively, and navigate challenges more efficiently.
Clear goals facilitate effective communication and transparency. They provide a basis for tracking progress and evaluating success, allowing teams to celebrate achievements and identify areas for improvement. In essence, clear goals serve as a roadmap for the roadmap, guiding the development process and ensuring that every step taken is purposeful and aligned with the product’s strategic vision.
Effective Goal-Setting Techniques
Effective goal-setting techniques are essential for creating a product roadmap that drives success. Two widely recognized methodologies for setting clear and actionable goals are SMART goals and OKRs.
1. SMART Goals
This technique emphasizes the importance of setting goals that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. SMART goals ensure that objectives are well-defined and attainable within a set timeframe.
For example, instead of setting a vague goal like “improve user engagement,” a SMART goal would be “increase user engagement by 20% over the next six months through targeted feature enhancements and marketing campaigns.”
2. OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
OKRs are a framework for defining and tracking objectives and their outcomes. An objective is a clearly defined goal, while key results are specific, measurable outcomes that indicate progress towards that goal.
For instance, an objective might be “launch a new feature,” with key results such as “complete development within three months,” “achieve a 90% satisfaction rate from beta testers,” and “increase user adoption by 15% within the first quarter of release.”
Both methodologies help ensure that goals are not only ambitious but also practical and aligned with the broader business strategy. They provide a structured approach to goal-setting, making it easier to track progress and make data-driven decisions.
Identifying Key Features and Initiatives
1. Prioritization
Identifying and prioritizing key features and initiatives is a critical component of developing an effective product roadmap. The process begins by evaluating features and initiatives based on their business value and customer needs. Several techniques can aid in this prioritization:
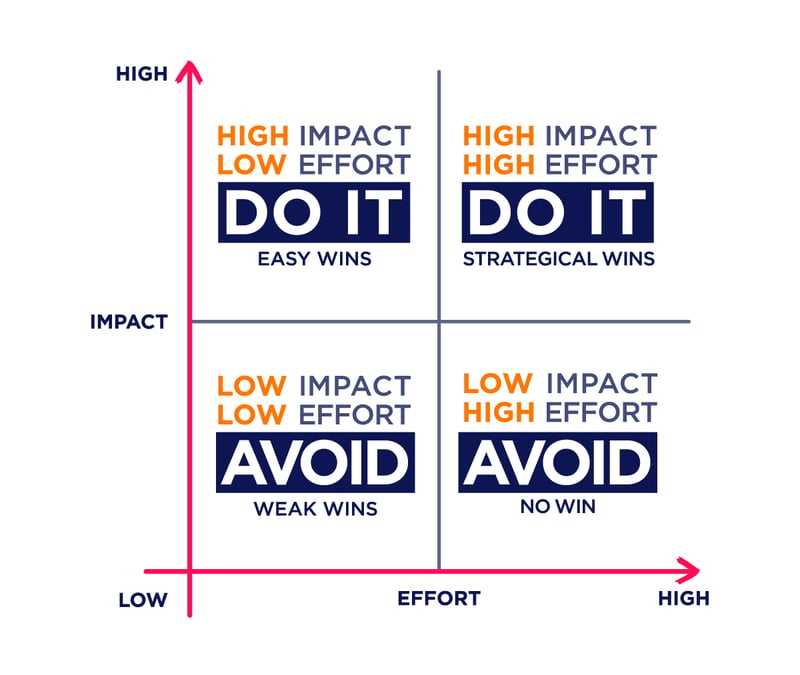
- Impact vs. Effort Matrix: This method involves plotting features on a matrix where one axis represents the potential value to the business or customer, and the other axis represents the effort required to implement them. Features that offer high impact with low effort should be prioritized, while those that require significant effort for minimal impact may be deferred.
- Customer Feedback and Market Research: Gathering insights from customers through surveys, interviews, and usage data helps identify features that address their pain points and needs. Market research also provides information on competitive offerings and industry trends, helping to prioritize features that can differentiate the product and provide a competitive edge.
- Value vs. Effort Scoring: This technique involves scoring features based on their potential value to the business and the effort required to develop them. Features with high value and low effort are prioritized, while those with lower value and higher effort are considered for later phases.
2. Breaking Down Large Projects
Managing complex projects can be challenging, but breaking them down into smaller, manageable tasks is a key strategy for success. This approach involves decomposing large projects into smaller components that are easier to plan, execute, and track. Several methods can be used to achieve this:
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): WBS is a hierarchical decomposition of the project into smaller, more manageable work packages. Each work package represents a distinct deliverable or component of the project, making it easier to assign responsibilities, estimate effort, and track progress.
- Agile Sprints: In agile methodologies, large projects are divided into iterative cycles called sprints. Each sprint focuses on delivering a specific set of features or tasks, allowing teams to make incremental progress and adapt to changes based on feedback and evolving requirements.
- Task Decomposition: Breaking down large tasks into smaller, actionable steps helps to identify dependencies, allocate resources, and track progress more effectively. Each step should be clear, achievable, and directly contribute to the completion of the larger project.
Setting Realistic Timelines and Milestones
Setting realistic timelines is essential for successful product development. Realistic timelines balance ambition with feasibility, ensuring that goals are achievable within the given timeframe.
Overly ambitious timelines can lead to project delays, resource strain, and compromised quality, while overly conservative timelines may result in missed opportunities and slower time-to-market.
To establish realistic timelines, it’s important to consider several factors:
- Historical Data: Reviewing past projects and their timelines can provide valuable insights into how long similar tasks or features took to complete. This data helps set more accurate expectations and identify potential challenges.
- Resource Availability: Assessing the availability and capacity of team members and other resources helps determine how much work can be realistically accomplished within a given timeframe.
- Complexity and Dependencies: Understanding the complexity of tasks and their dependencies is crucial for setting realistic timelines. Tasks with high complexity or significant dependencies may require more time to complete, affecting the overall timeline.
Tips for Estimating Development Time
Accurate time estimation is critical for effective project management and successful product delivery. Several best practices can improve the accuracy of time estimates:
- Use Historical Data: Analyze data from previous projects to inform estimates. Historical data provides a benchmark for how long similar tasks or features took to complete, helping to create more realistic timelines.
- Involve the Team: Engage team members in the estimation process, as they have hands-on experience with the tasks and can provide valuable input on the time required. Techniques such as Planning Poker or Delphi Method can facilitate collaborative estimation.
- Break Down Tasks: Decompose large tasks into smaller, more manageable components. Estimating the time required for each component individually can improve accuracy and identify potential challenges early.
- Factor in Buffers: Include contingency buffers in the timeline to account for uncertainties and unexpected issues. This helps to mitigate the impact of unforeseen delays and ensures that the project stays on track.
- Continuous Review: Regularly review and adjust estimates as the project progresses. This iterative approach helps address any discrepancies and adapt to changes in scope or requirements.
Managing Dependencies and Risks

Dependencies refer to the relationships between tasks or features where one task relies on the completion of another. Understanding these dependencies is crucial for effective project management, as they can impact the sequence and timing of activities. Dependencies can be classified into several types, including:
- Finish-to-Start: Task A must be completed before Task B can begin. For example, development must be completed before testing can start.
- Start-to-Start: Task B cannot start until Task A has started. For instance, design work and development might need to start simultaneously.
- Finish-to-Finish: Task B cannot finish until Task A is finished. For example, documentation cannot be completed until the final version of the software is ready.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks
Risk management is a key aspect of creating a successful product roadmap. Identifying potential risks early and developing contingency plans helps mitigate their impact and ensure project success. Effective strategies for risk mitigation include:
- Risk Identification: Conduct risk assessments to identify potential issues that could impact the project. Common risks include technical challenges, resource constraints, and market changes.
- Risk Analysis: Evaluate the likelihood and impact of identified risks to prioritize them. This analysis helps determine which risks require immediate attention and which can be monitored.
- Develop Contingency Plans: Create contingency plans to address high-priority risks. These plans outline steps to take if risks materialize, helping to minimize disruption and maintain progress.
- Monitor and Review: Continuously monitor risks throughout the project lifecycle and review contingency plans regularly. This proactive approach helps address emerging risks promptly and adapt to changing conditions.
Choosing the Right Product Roadmap Template

Key Factors to Consider
1. Scalability and Flexibility
When selecting a product roadmap template, scalability and flexibility are crucial factors to consider. A scalable template should accommodate the growth of your product, allowing for the addition of new features, initiatives, and timelines as the product evolves. It should be adaptable to different stages of development, from initial planning to post-launch adjustments. Flexibility ensures that the template can be modified to reflect changes in strategy, priorities, or market conditions without requiring a complete overhaul.
Choose a template that offers customizable sections and fields, enabling you to tailor it to your specific needs. This adaptability is essential for maintaining alignment with your product’s evolving goals and for managing complex projects with multiple phases or teams. A flexible template will help you stay organized and responsive to changes, ensuring that your roadmap remains relevant and effective throughout the product life cycle.
2. Ease of Use
Ease of use is another critical factor when choosing a product roadmap template. A user-friendly template simplifies the planning and management process, reducing the time and effort required to create and maintain your roadmap. Look for templates with intuitive interfaces, clear instructions, and straightforward navigation to ensure a smooth implementation.
Templates that are easy to use help facilitate adoption across your team, enabling everyone to contribute and access the roadmap without extensive training. A well-designed template should also support collaboration, allowing multiple users to update and view the roadmap seamlessly. Features such as drag-and-drop functionality, pre-built sections, and customizable views enhance usability and streamline the roadmap creation process. Selecting a template that balances functionality with ease of use ensures that your roadmap remains a valuable tool for managing product development.
Customizing a Template to Your Needs
Customizing a product roadmap template to fit your specific business requirements is essential for creating a roadmap that truly reflects your product’s goals and challenges. Start by assessing your unique needs and objectives, such as project scope, team structure, and strategic priorities. Choose a template that allows you to modify sections, add custom fields, and adjust timelines to align with your specific requirements.
Consider the following when adapting a template:
- Integration with Existing Tools: Ensure that the template integrates with tools and systems already in use within your organization. This compatibility can streamline data sharing and improve workflow efficiency.
- Customization Options: Look for templates that offer flexible customization options, such as adjustable timelines, milestones, and feature prioritization. This flexibility allows you to tailor the roadmap to your specific project phases and goals.
- Visual Representation: Choose a template that supports various visual representations, such as Gantt charts, Kanban boards, or timelines. Customizing the visual format helps convey information in a way that best suits your team’s preferences and needs.
Incorporating Team Feedback
Engaging your team in the customization process is crucial for creating a product roadmap that is both relevant and effective. Involving team members ensures that the roadmap reflects their insights, addresses their needs, and gains their buy-in. Here’s how to incorporate team feedback into the customization process:
- Solicit Input: Gather feedback from team members who will use the roadmap, including developers, project managers, and other stakeholders. Understanding their perspectives and needs helps tailor the template to support their workflows and responsibilities.
- Collaborative Customization: Involve team members in the customization process by allowing them to contribute to the template design and configuration. This collaboration helps ensure that the roadmap meets the practical needs of those who will interact with it regularly.
- Iterative Reviews: Regularly review and refine the customized template based on ongoing feedback. Encourage team members to provide input on how well the template supports their tasks and make adjustments as needed to improve usability and effectiveness.
Best Practices for Implementing and Maintaining a Roadmap
Communicating the Roadmap to Your Team
Effective communication of the product roadmap is crucial for ensuring that all team members understand the vision, goals, and specific actions required. Clear communication helps align the team with the roadmap’s objectives, fosters transparency, and sets expectations. Strategies for effective communication include:
- Detailed Presentations: Use presentations to explain the roadmap’s key elements, including goals, timelines, and major milestones. Visual aids such as charts and diagrams can enhance understanding and retention.
- Regular Updates: Schedule regular meetings to review progress, address questions, and discuss any changes to the roadmap. This ongoing communication keeps everyone informed and engaged.
- Written Documentation: Provide written summaries of the roadmap and updates for reference. This documentation can be shared through internal communication channels, ensuring that team members have access to the roadmap details at all times.
Involving Your Team
Fostering collaboration and ownership among team members enhances the effectiveness of the roadmap and promotes a sense of shared responsibility. Techniques for involving your team include:
- Collaborative Workshops: Conduct workshops where team members can provide input on the roadmap’s content and structure. This collaborative approach encourages buy-in and ensures that the roadmap reflects diverse perspectives.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Create channels for team members to give feedback on the roadmap and its implementation. Regularly solicit their opinions and suggestions to make improvements and address concerns.
- Ownership and Accountability: Assign specific roles and responsibilities related to the roadmap’s execution. By involving team members in these roles, you empower them to take ownership of their contributions and drive progress.
Regularly Reviewing and Updating the Roadmap
Establishing a regular review process is essential for maintaining the relevance and accuracy of the product roadmap. Set up a cadence for reviews that aligns with the product development cycle, such as monthly or quarterly check-ins. During these reviews:
- Evaluate Progress: Assess the progress of ongoing initiatives and compare it against the roadmap’s milestones and timelines. Identify any deviations from the plan and address them promptly.
- Adjust Priorities: Re-evaluate priorities based on changes in market conditions, business objectives, or resource availability. Adjust the roadmap to reflect these changes and ensure that it continues to align with the overall strategy.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Include key stakeholders in the review process to gather their input and ensure that the roadmap remains aligned with their expectations and requirements.
Adjusting Based on Feedback
Incorporating feedback from stakeholders is crucial for maintaining the roadmap’s relevance and effectiveness. To adjust the roadmap based on feedback:
- Collect Feedback: Gather feedback from team members, customers, and other stakeholders through surveys, interviews, and meetings. Focus on their insights regarding the roadmap’s priorities, timelines, and overall direction.
- Analyze Feedback: Evaluate the feedback to identify common themes, concerns, and suggestions. Determine which aspects of the roadmap need to be adjusted based on this analysis.
- Implement Changes: Make necessary adjustments to the roadmap based on the feedback. This may involve revising timelines, re-prioritizing features, or modifying goals to better align with stakeholder expectations.
- Communicate Updates: Inform the team and stakeholders about any changes made to the roadmap. Clearly explain the reasons for the adjustments and how they will impact the product development process.
Measuring Success and Tracking Progress
Identifying and tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for measuring the success of your roadmap. KPIs provide quantitative metrics that reflect the performance and effectiveness of the roadmap. Consider the following KPIs:
- Achievement of Milestones: Measure the percentage of roadmap milestones completed on time. This KPI helps assess how well the product development is adhering to the planned schedule.
- Feature Adoption: Track the adoption rates of new features or functionalities introduced according to the roadmap. High adoption rates indicate that the features are meeting customer needs and providing value.
- Customer Satisfaction: Use customer feedback and satisfaction scores to evaluate the impact of the roadmap’s deliverables. Positive feedback and high satisfaction levels suggest that the roadmap is addressing key user needs.
- Resource Utilization: Assess how effectively resources are being allocated and utilized in relation to the roadmap. Efficient resource utilization reflects well on the planning and execution process.
Tracking Progress

To monitor the progress of your roadmap and identify potential bottlenecks, use the following tools and techniques:
- Project Management Software: Utilize project management tools such as Jira, Asana, or Trello to track the status of tasks, milestones, and deadlines. These tools provide visibility into progress and help manage dependencies.
- Progress Dashboards: Create dashboards that visualize key business metrics and progress against roadmap objectives. Dashboards offer a real-time view of how the roadmap is performing and highlight areas that may need attention.
- Regular Status Updates: Conduct regular status meetings or check-ins to review progress, discuss challenges, and identify any issues that may be impacting the roadmap. Use these meetings to adjust plans and address any obstacles.
- Issue Tracking: Implement a system for tracking and managing issues that arise during the roadmap execution. Addressing these issues promptly helps to keep the project on track and minimizes delays.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Common pitfalls in roadmap implementation include:
- Lack of Clear Goals: Roadmaps without well-defined goals can lead to misaligned efforts and confusion.
- Inadequate Communication: Poor communication can result in misunderstandings and lack of buy-in from the team.
- Rigid Planning: Overly rigid roadmaps that do not allow for flexibility can become obsolete as market conditions change.
To overcome challenges, consider these tips:
- Foster a Collaborative Environment: Engage your team and stakeholders in the roadmap process to gain valuable insights and support.
- Maintain Flexibility: Be prepared to adapt the roadmap in response to changing conditions and feedback.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: Establish a routine for reviewing and updating the roadmap to address any issues and keep it aligned with your goals.
Key Takeaways
A well-constructed product roadmap is a vital tool for guiding product development and ensuring alignment with strategic objectives. Here are the key takeaways from the discussion:
- Strategic Importance: A product roadmap provides a clear vision and direction, helping teams stay focused on achieving business goals. It aligns all stakeholders by defining the roadmap’s objectives, timelines, and key milestones.
- Planning and Prioritization: Effective roadmaps require careful planning and prioritization. Defining clear goals, identifying key features, setting realistic timelines, and managing dependencies are crucial steps in creating a roadmap that drives successful product development.
- Communication and Collaboration: Regular communication and involvement of the team are essential for successful roadmap implementation. Keeping team members informed and engaged fosters collaboration and ensures that everyone is aligned with the roadmap’s goals.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Roadmaps must be flexible to accommodate changes in market conditions, customer feedback, and business priorities. Regular reviews and updates are necessary to keep the roadmap relevant and effective.
- Measuring Success: Tracking progress and measuring success through key performance indicators (KPIs) helps in assessing the effectiveness of the roadmap and making data-driven adjustments.
Understanding and implementing these principles has enabled Iterators to create product roadmaps that guide development and adapt to evolving business needs and drive long-term success.
