Data is an extremely important factor when it comes to gaining insights about a specific topic, study, research, or even people. This is why it is regarded as a vital component of all of the systems that make up our world today.
In fact, data offers a broad range of applications and uses in the modern age. So whether or not you’re considering digital transformation, data collection is an aspect that you should never brush off, especially if you want to get insights, make forecasts, and manage your operations in a way that creates significant value.
However, many people still gravitate towards confusion when they come to terms with the idea of data collection.
In this article, we will help you understand:
- What is data collection
- Why collecting and acquiring data can be beneficial for your business
- What are the different methods of collecting data
- Modern tools for data collection
Need help collecting data for your business? We can help! At Iterators, we design, build and maintain custom software solutions that will help you achieve desired results.
Schedule a free consultation with Iterators today. We’d be happy to help you find the right software solution for your company.
What is Data Collection?
“Data is the competitive moat in today’s market. Companies that effectively collect and leverage data create a significant barrier for competitors, driving sustained growth and innovation.”
Jacek Głodek
Data collection is defined as a systematic method of obtaining, observing, measuring, and analyzing accurate information to support research conducted by groups of professionals regardless of the field where they belong.
While techniques and goals may vary per field, the general data collection methods used in the process are essentially the same. In other words, there are specific standards that need to be strictly followed and implemented to make sure that data is collected accurately.
Not to mention, if the appropriate procedures are not given importance, a variety of problems might arise and impact the study or research being conducted.
The most common risk is the inability to identify answers and draw correct conclusions for the study, as well as failure to validate if the results are correct. These risks may also result in questionable research, which can greatly affect your credibility.
So before you start collecting data, you have to rethink and review all of your research goals. Start by creating a checklist of your objectives. Here are some important questions to take into account:
- What is the goal of your research?
- What type of data are you collecting?
- What data collection methods and procedures will you utilize to acquire, store, and process the data you’ve gathered?
Take note that bad data can never be useful. This is why you have to ensure that you only collect high-quality ones. But to help you gain more confidence when it comes to collecting the data you need for your research, let’s go through each question presented above.
What is the Goal of your Research?
Identifying exactly what you want to achieve in your research can significantly help you collect the most relevant data you need. Besides, clear goals always provide clarity to what you are trying to accomplish. With clear objectives, you can easily identify what you need and determine what’s most useful to your research.
What Type of Data are you Collecting?
Data can be divided into two major categories: qualitative data and quantitative data. Qualitative data is the classification given to a set of data that refers to immeasurable attributes. Quantitative data, on the other hand, can be measured using numbers. Based on the goal of your research, you can either collect qualitative data or quantitative data; or a combination of both.
What Data Collection Methods will you use?
There are specific types of data collection methods that can be used to acquire, store, and process the data. If you’re not familiar with any of these methods, keep reading as we will tackle each of them in the latter part of this article. But to give you a quick overview, here are some of the most common data collection methods that you can utilize:
- Experiment
- Survey
- Observation
- Ethnography
- Secondary data collection
- Archival research
- Interview/focus group
Note: We will discuss these methods more in the Data Collection Methods + Examples section of this article.
Benefits of Collecting Data
Regardless of the field, data collection offers heaps of benefits. To help you become attuned to these advantages, we’ve listed some of the most notable ones below:
- Collecting good data is extremely helpful when it comes to identifying and verifying various problems, perceptions, theories, and other factors that can impact your business.
- It allows you to focus your time and attention on the most important aspects of your business.
- It helps you understand your customers better. Collecting data allows your company to truly understand what your consumers expect from you, the unique products or services they desire, and how they want to connect with your brand as a whole.
- Collecting data allows you to study and analyze trends better.
- Data collection enables you to make more effective decisions and come up with solutions to common industry problems.
- It allows you to resolve problems and improve your products or services based on data collected.
- Accurate data collection can help build trust, establish productive and professional discussions, and win the support of important decision-makers and investors.
- When engaging with key decision-makers, collecting, monitoring, and assessing data on a regular basis may offer businesses reliable, relevant information.
- Collecting relevant data can positively influence your marketing campaigns, which can help you develop new strategies in the future.
- Data collection enables you to satisfy customer expectations for personalized messages and recommendations.
These are just a few of the many benefits of data collection in general. In fact, there are still a lot of advantages when it comes to collecting consumer data that you can benefit from.
Data Collection Methods + Examples
As mentioned earlier, there are specific types of data collection methods that you can utilize when gathering data for your research. These data collection methods involve conventional, straightforward, and more advanced data gathering and analysis techniques.
Furthermore, it is important to remember that the data collection method being used will depend on the type of business you’re running. Therefore, not all types of data collection methods are appropriate for the study or research that you are conducting for your business. That is why being mindful of these methods can definitely help you find the best one for your needs.
Here are the top 5 data collection methods and examples that we’ve summarized for you:
1. Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires, in their most foundational sense, are a means of obtaining data from targeted respondents with the goal of generalizing the results to a broader public. Almost everyone involved in data collection, especially in the business and academic sector relies on surveys and questionnaires to obtain credible data and insights from their target audience.
Here are several key points to remember when utilizing this data collection method:
- Surveys can be easily done online and with ease. Fact that the digital landscape is constantly evolving, online surveys are becoming more and more prevalent every day.
- Online surveys can be accessed anytime and anywhere. The accessibility that online surveys and questionnaires provide is one of the most significant advantages that you can utilize to collect data from your target audience with ease.
- Low price method. Compared to the other data collection methods, creating surveys and questionnaires don’t require large spends.
- Offers a wide range of methods of data collection. When utilizing surveys and questionnaires, you will have the power to collect different data types such as opinions, values, preferences, etc.
- Flexibility when it comes to analyzing data. Surveys and questionnaires are easier to analyze compared to other methods.
Here is an example of an online survey/questionnaire:
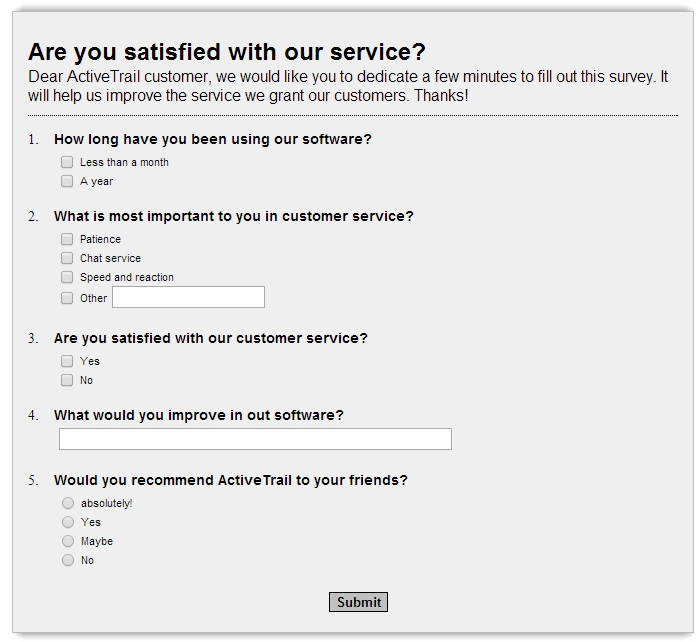
2. Interviews
An interview is accurately defined as a formal meeting between two individuals in which the interviewer asks the interviewee questions in order to gather information. An interview not only collects personal information from the interviewees, but it is also a way to acquire insights into people’s other skills.
Here is the summary of advantages you can gain from this data collection method:
- Conducting interviews can help reveal more data about the subject. Interviews can assist you in explaining, understanding, and exploring the perspectives, behavior, and experiences of participants.
- Interviews are more accurate. Since it is an interview, subjects won’t be able to falsify their identities such as lying about their age, gender, or race.
- An interview is a flowing and open-ended conversation. Unlike other methods, interviews enable interviewers to ask follow-up questions in order to better understand the subject.
Should you want to take advantage of this data collection method, you can refer to the table below for guidance:
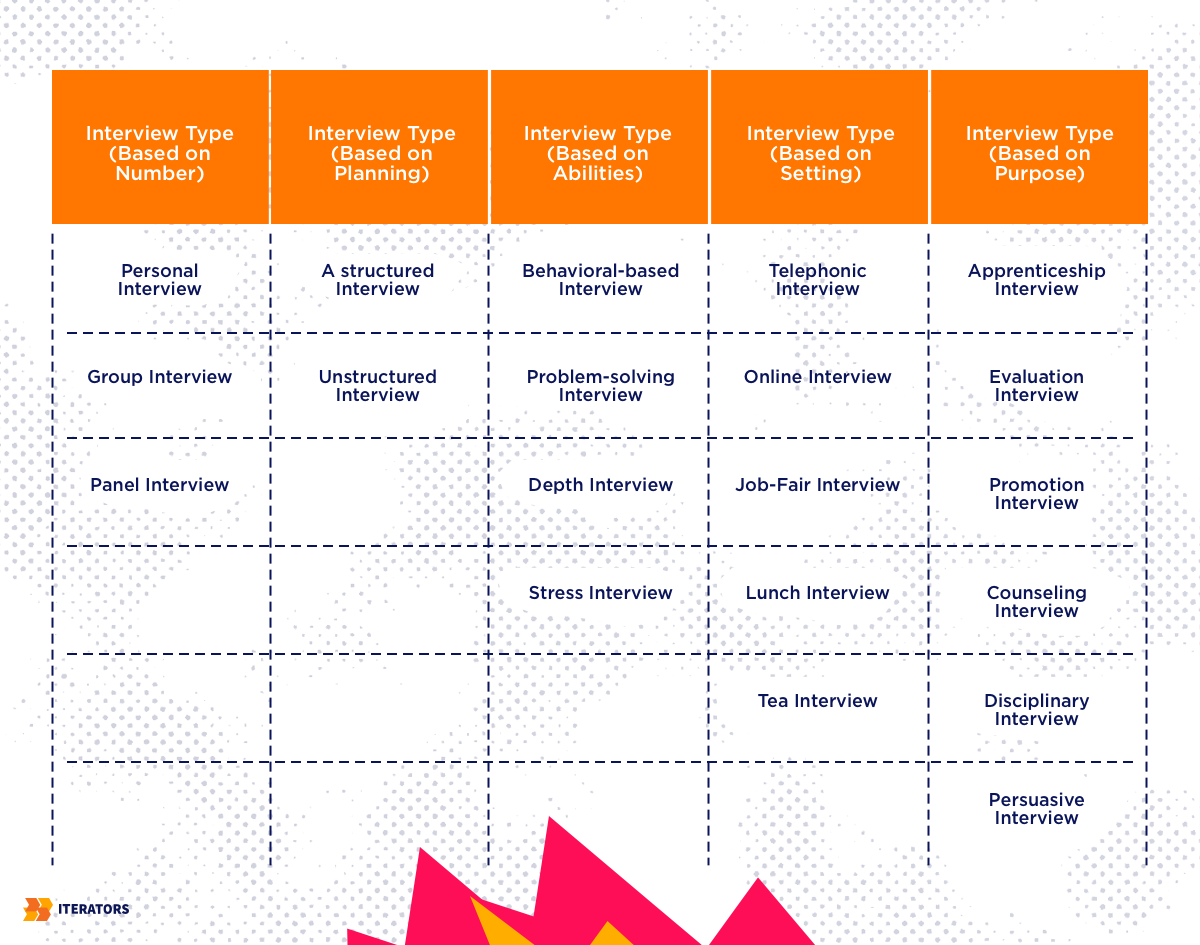
3. Observations
The observation method of data collection involves seeing people in a certain setting or place at a specific time and day. Essentially, researchers study the behavior of the individuals or surroundings in which they are analyzing. This can be controlled, spontaneous, or participant-based research.
Here are the advantages of Observation as a data collection method:
- Ease of data collection. This data collection method does not require researchers’ technical skills when it comes to data gathering.
- Offers detailed data collection. Observations give researchers the ability and freedom to be as detail-oriented as possible when it comes to describing or analyzing their subjects’ behaviors and actions.
- Not dependent on people’s proactive participation. The Observation method doesn’t require people to actively share about themselves, given the fact that some may not be comfortable with doing that.
When a researcher utilizes a defined procedure for observing individuals or the environment, this is known as structured observation. When individuals are observed in their natural environment, this is known as naturalistic observation. In participant observation, the researcher immerses himself or herself in the environment and becomes a member of the group being observed.
Here are relevant case studies and citations from PRESSBOOKS that provide in-depth examples of Observational research.
Structured Observation
“Researchers Robert Levine and Ara Norenzayan used structured observation to study differences in the “pace of life” across countries (Levine & Norenzayan, 1999). One of their measures involved observing pedestrians in a large city to see how long it took them to walk 60 feet. They found that people in some countries walked reliably faster than people in other countries. For example, people in Canada and Sweden covered 60 feet in just under 13 seconds on average, while people in Brazil and Romania took close to 17 seconds. When structured observation takes place in the complex and even chaotic “real world,” the questions of when, where, and under what conditions the observations will be made, and who exactly will be observed are important to consider.“
Naturalistic Observation
“Jane Goodall’s famous research on chimpanzees is a classic example of naturalistic observation. Dr. Goodall spent three decades observing chimpanzees in their natural environment in East Africa. She examined such things as chimpanzee’s social structure, mating patterns, gender roles, family structure, and care of offspring by observing them in the wild. However, naturalistic observation could more simply involve observing shoppers in a grocery store, children on a school playground, or psychiatric inpatients in their wards. Researchers engaged in naturalistic observation usually make their observations as unobtrusively as possible so that participants are not aware that they are being studied.ng that.”
Participant Observation
“Another example of participant observation comes from a study by sociologist Amy Wilkins (published in Social Psychology Quarterly) on a university-based religious organization that emphasized how happy its members were (Wilkins, 2008). Wilkins spent 12 months attending and participating in the group’s meetings and social events, and she interviewed several group members. In her study, Wilkins identified several ways in which the group “enforced” happiness—for example, by continually talking about happiness, discouraging the expression of negative emotions, and using happiness as a way to distinguish themselves from other groups.”
4. Records and Documents
This data collection method involves analyzing an organization’s existing records and documents to track or project substantial changes over a specific time period. The data may include the following:
- Email logs
- Staff reports
- Call logs
- Databases
- Information logs
- Minutes of meetings
Here are the significant advantages of using records and documents as a data collection method for your business:
- The data is already available. There is no need for you to conduct any active research because the information you need is already made available.
- Easy tracking of collected data. Records and documents will allow you to recheck the history of a specific event that can help you find answers to questions, such as why your supplies ran out way outside your projected schedule for example.
Examples of Records and Documents:
Customer Database
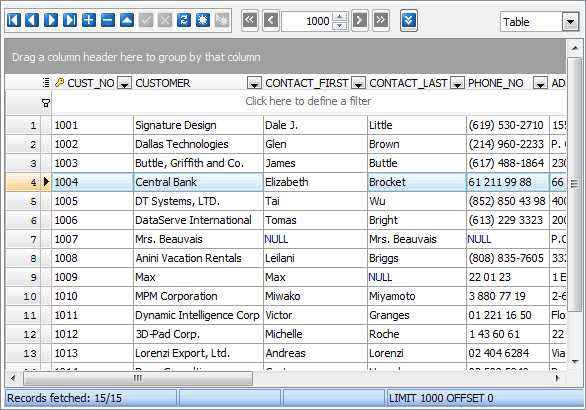
Email Logs
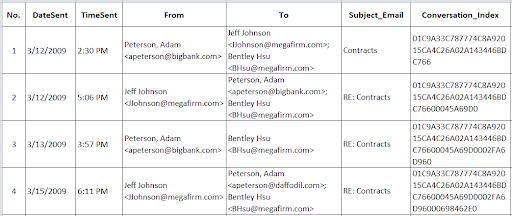
5. Focus Groups
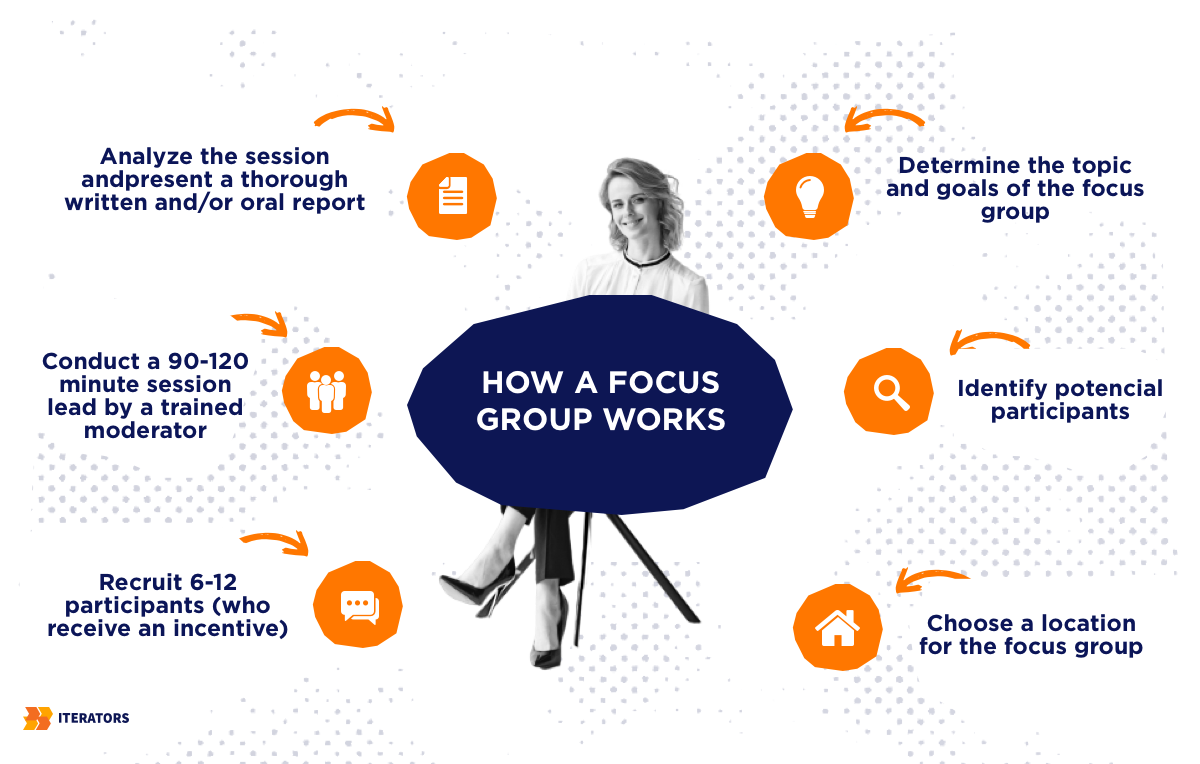
A focus group is a group interview of six to twelve persons with comparable qualities or shared interests. A moderator leads the group through a series of planned topics. The moderator creates an atmosphere that encourages people to discuss their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are a type of qualitative data collection in which the information is descriptive and cannot be quantified statistically.
Here are the advantages of Focus Groups as a data collection method:
- Easy collection of qualitative data. Focus groups can easily collect qualitative data since the moderator can ask questions to determine the respondents’ reactions.
- Non-verbal cues can be easily observed. The presence of the moderator is an essential part of the data collection. With the moderator around, it will be easier to obtain data from non-verbal responses from the participants.
Since Focus Groups are commonly carried out in person, there are no tangible examples to refer to. Moreover, here’s a diagram from QuestionPro to show how it works:
Quantitative Data vs. Qualitative Data
Data collection is comprehensive, analytical, and in some cases, extremely difficult. But when you categorize the data into the two categories we’ve mentioned earlier in this article, it becomes easy to deal with. To provide you with a brief understanding of qualitative data collection methods and quantitative data collection methods, we’ve outlined each of them below:
Quantitative Data
Quantitative data is numerical and is generally organized which means that it is more precise and definite. And because this method of data collection is measured in terms of numbers and values, it is a better choice for statistical analysis.
Here are some of the most popular quantitative data collection methods you can use to obtain concrete results:
- Surveys
- Experiments
- Tests
- Metrics
- Market reports
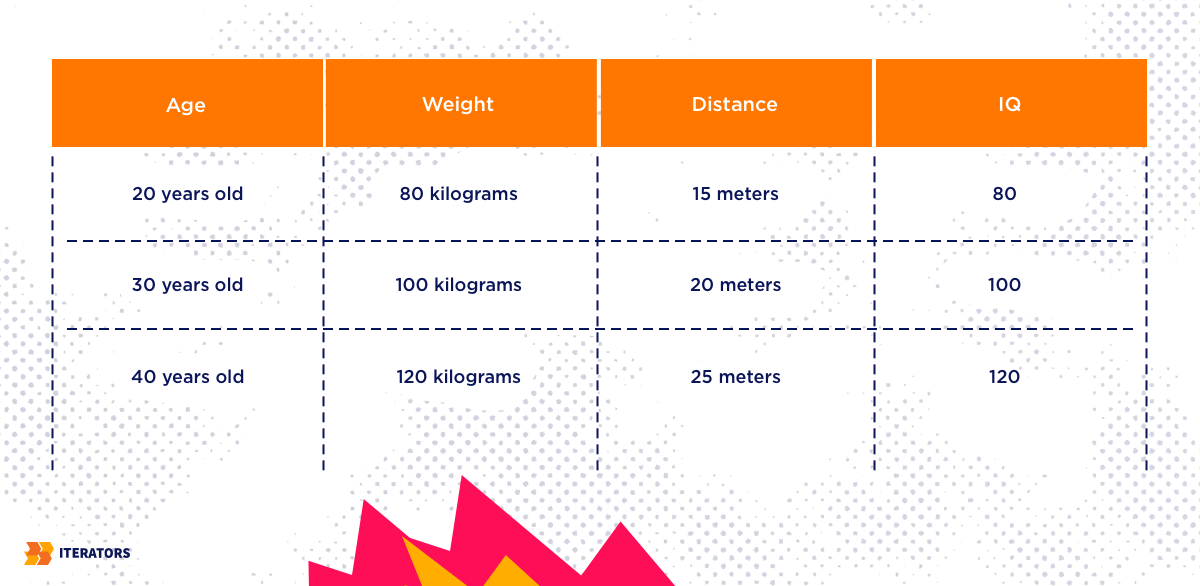
Quantitative data examples:
Qualitative Data
Unlike quantitative data, qualitative data is composed of non-statistical information that is commonly structured or unstructured. Qualitative data isn’t also measured based on concrete statistics that are used to create graphs and charts. They are classified according to characteristics, features, identities, and other categorizations.
Qualitative data is also exploratory in nature and is frequently left wide open until more study has been completed. Theorizations, assessments, hypotheses, and presumptions are all based on qualitative research data.
Here are some of the most commonly known qualitative data collection methods you can use to generate non-statistical results:
- Records and documents
- Interview transcripts
- Focus groups
- Observation research
Qualitative data examples:

Operationalization
Operationalization is the process of turning theoretical data into measurable observations. With the help of operationalization, you can effectively gather data on concepts that can’t be easily measured. This method converts a hypothetical, abstract variable into a collection of specific processes or procedures that determine the variable’s meaning in a given research. In a nutshell, operationalization serves as a link between hypothetically grounded ideas and the procedures employed to validate them.
Operationalization is a crucial element of empirically grounded research because it allows researchers to describe how a notion is analyzed or generated in a given study. There are three key phases in the operationalization process:
- Determine which of the major ideas or concepts you want to learn more about.
- Each idea should be represented by a different variable.
- For each of your variables, choose indicators.
To provide you with a clear guide on how operationalization works, let’s illustrate how the process is carried out based on the three key phases.
Please refer to the following:
1. Determine which of the major ideas or concepts you want to learn more about.
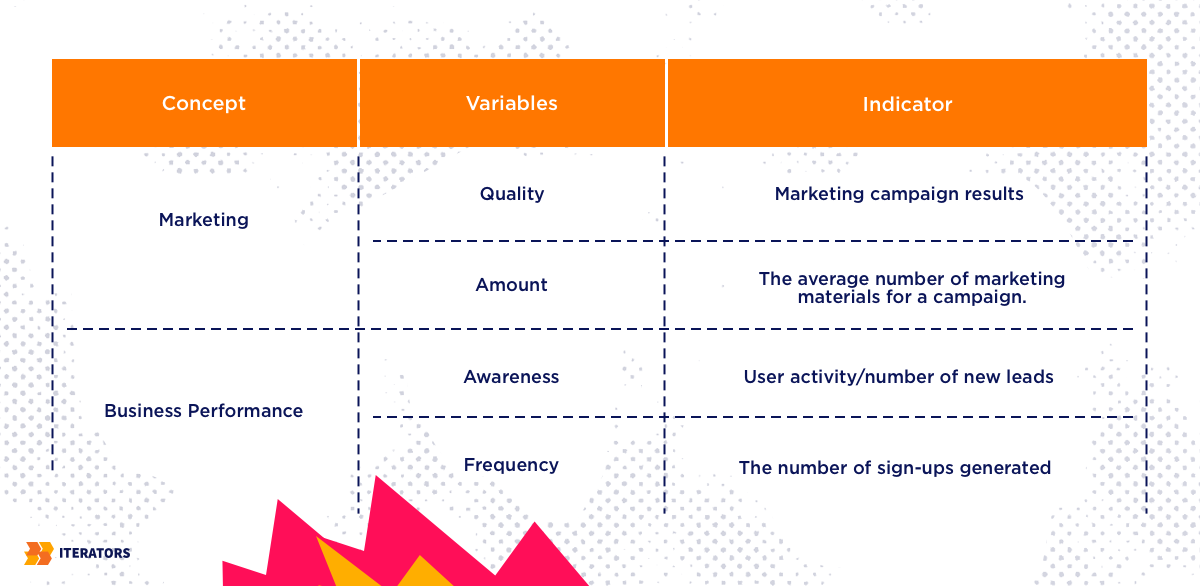
For example, the two main ideas you want to learn more about are the following:
- Marketing
- Business Performance
From the chosen concepts, formulate a question that will lead you to realize your research goal. Is there are correlation between marketing and business performance?
2. Each idea should be represented by a different variable.
Here is an illustration of the second phase of the operationalization process:
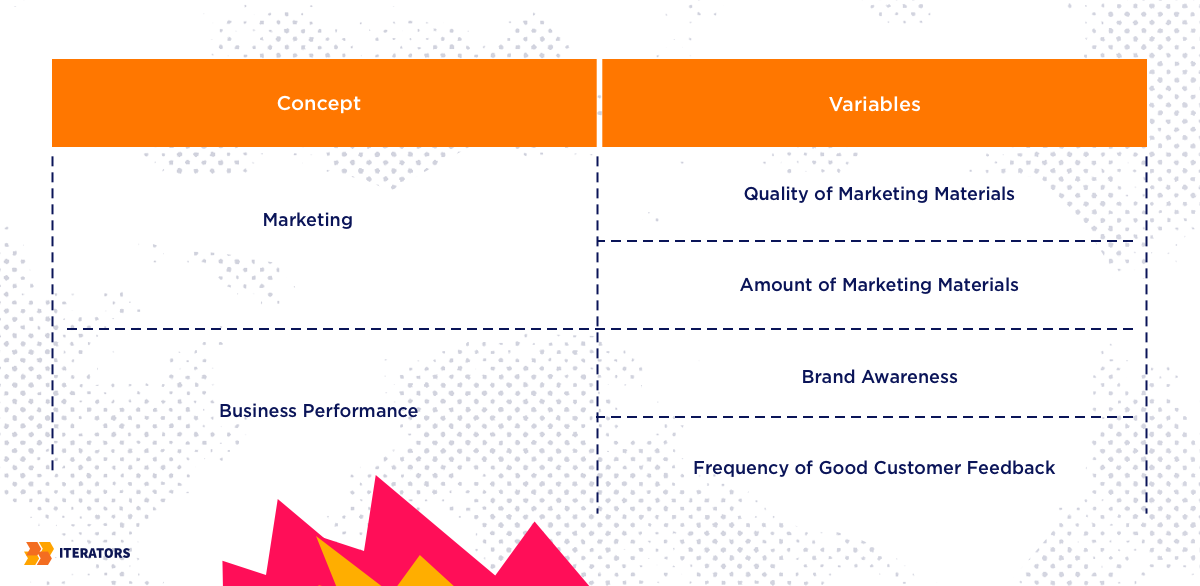
Take note that in order to find the alternate and null hypothesis of the following variables, utilizing the right data collection method is extremely important.
3. For each of your variables, choose indicators.
Your indicators will help you collect the necessary data that you need in order to arrive at the most credible conclusions.
Data Collection Tools
There are heaps of data collection tools that you can utilize to gather good data online. Some of these tools have already been discussed above such as interviews, surveys, focus groups, etc.
While most of the aforementioned methods of data collection are effective, there are other data collection tools that offer convenience to business researchers. Here are some of them:
Data Scraping
Data scraping is the process of collecting data from a website and saving it as a local file on a computer. It’s among the most effective data collection tools that you can use to gather information from the web.
Some of the most popular data scraping utilization includes the following:
- Locating sales leads
- Conducting market research
- Finding business intelligence
- Sending product data
You may customize your scraping criteria or parameters to selectively target a specific attribute, especially with the proper data scraping tool. You can easily collect qualitative and quantitative data in a manner that can be readily implemented into your study or business procedures.
Information Management Systems
Although these management systems are generally meant to manage and monitor your database, they may also assist you in collecting data, particularly internal data generated by your business. Some of the information management systems used by various businesses that you can collect data from can be found in the following areas or categories:
- Operations
- Sales and Marketing
- Research & Development
- Financial
- Human Resources
- Productivity
- Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Computing
- Business Intelligence
Data Collection Software
There is plenty of data collection software that can be used to acquire information from the internet. One of the best examples is Google Forms. It allows you to develop specific forms like job application forms, making it simple to collect information from applicants.
Here is some data collection software you can use:
- KoboToolbox
- REDcap
- JotForm
- Survey CTO
- CommCare
Conclusion
Data collection has become a crucial strategy for many professionals and businesses. While it might be a difficult task for tenderfoot researchers or business owners, understanding its methods can be contributory to collecting data in the most accurate way.


8 Comments
Well illustrated, clear and understandable. Thank you so much.
Thank you now have a picture of what i want to do
Good introduction Very useful.
thank you very much for the explanations
thanks alot.
you have really simplified my work
Great information. It is always a good reminder to ask ourselves what is our purpose of our intended data collection and how can we design a meaningful action plan to collect and utilize it.
I’m doing my bachelors level research in which I have one independent and two dependent variables. I’m seeing the impact of the independent variable on the two dependent variables separately. The two dependent variables have no connection with each other. The participants for the study are 60 and are not grouped.
Which test would be recommended for it?
Excellent!!!