[Originally Posted on January 21, 2019, last updated July 15 2025.]
Why are people so excited about blockchain applications?
Because they think blockchain technology has vast, untapped potential.
It’s one of those discoveries – like electricity or oil – that’s supposed to change the world.
Why? Because the application of blockchain technology seems endless. You could use it to manage your identity, feed green energy to a power grid, or trade stocks.
The best part?
It’s designed to be more secure, more efficient, faster, and cheaper than other solutions.
So, why isn’t everyone using it?
There are still many regulatory and political concerns. Not to mention the complexity of creating an infrastructure to integrate businesses with blockchain.
All that makes it difficult to know when and how to get on board. Yet, blockchain applications remain the darling of the tech industry.
“Blockchain holds immense potential for establishing trust in international affairs, especially when trust between parties is lacking. Its transparent, decentralized nature can ensure secure and verifiable transactions, making it a crucial tool for diplomacy, global trade, and conflict resolution where traditional trust mechanisms fall short.”
Jacek Głodek
That’s why this article will help you with:
- Knowing when a blockchain application could improve your business.
- Understanding blockchain applications and how they work.
- Finding out how blockchain strategies are being used today.
Already have a use case for a blockchain application? Need some help? At Iterators, we design, build, and maintain custom software for startups and enterprise businesses.
Schedule a free consultation today. We can leverage blockchain technology for you.
How Blockchain Applications Could Improve Your Business or Startup
So, what’s all the fuss? How big of a deal is blockchain technology?
At this point, it’s important to note that we’re not talking about Bitcoin.
Cryptocurrency is not blockchain, it is only one application of blockchain technology. So, Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency that uses blockchain technology to work. And yes, as the first application of blockchain technology, there is a lot of hype around the Bitcoin blockchain.
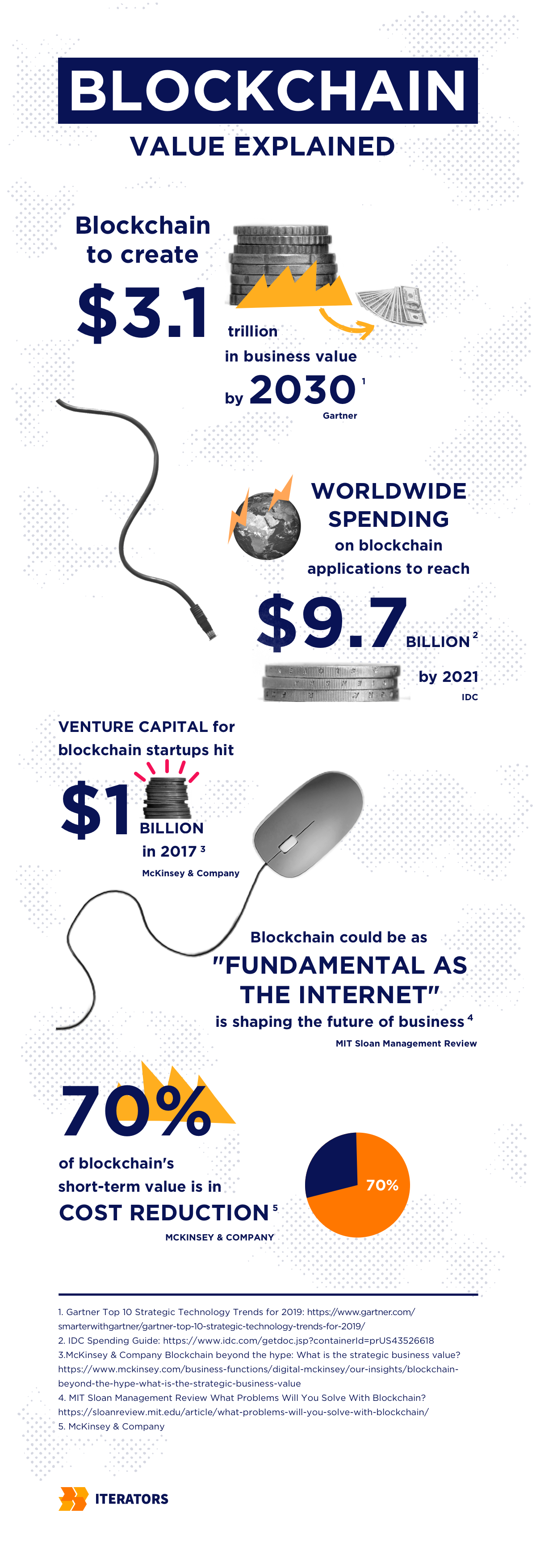
Yet, blockchain technology is garnering hype on its own. For starters, Grand View Research estimates the global blockchain technology market size was USD 31.28 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1,431.54 billion by 2030.
That’s a big deal. But wait, there’s more!
MarketsandMarkets expects the global blockchain market size to grow from USD 20.1 billion in 2024 to USD 248.9 billion by 2029 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 65%.
And over the past few years, PwC found that venture capital for blockchain startups has grown at a steady pace. Leading players are investing as well.
According to PwC, IBM has hired more than 1,000 employees to work on blockchain applications. They also invested $200 million in a blockchain-powered Internet of Things.
In the meantime, the MIT Sloan Management Review says that blockchain could be as “fundamental as the Internet” in shaping the future of business.
Let’s repeat that – as fundamental as the Internet.
Okay, so lots of money? Check. Lots of talk about blockchain being as important as the Internet? Check. So, why isn’t everyone using blockchain technology applications?
Well, the technology is maturing. That means it’s going to take quite a bit of innovation and application before blockchain becomes the norm. Regulation and standardization need to happen, not to mention adoption and returns on investment.
So, why should companies look at blockchain solutions now?
Most experts say it’s only a matter of time before blockchain becomes mainstream. It’s better to understand how it works now if you don’t want to risk being left behind.
Step 1: Understanding Blockchain
What are the real benefits of using a blockchain application?
Okay, so the technology is a big deal and you need to take it into consideration. But what is it actually going to do for your business? Who cares if everyone is excited about blockchain if it’s not going to impact your bottom line?
So, here’s a list of a few possible benefits for your company:
- Disrupting Business Operations
- Speeding up Business Processes
- Boosting ROI
- Cutting Costs
That’s right. The list contains all the usual suspects that justify any new undertaking. Blockchain technology can refine complicated processes that rely on traceability and visibility. And with the friction gone, you can save time and money.
In the short term, the main benefit is cost cutting.
Fortune Business Insights estimates that around 70% of blockchain’s short term value is in cost reduction. Blockchain applications reduce costs by removing the middlemen or the administrative effort of keeping records and managing transactions.
But the most important thing is not to think of blockchain as a technology that impacts your bottom line. Instead, think of it as a way to execute a business model, create a new market, or interact with markets.
Here are some key aspects of blockchain applications that can boost business processes:
- The Elimination of Human Error
- Secure Verification
- Democratization of Trust
- Permanent Recording
- Enhanced User Privacy
- Decentralization (Tamper-proof Ledger)
- The Efficiency of Verifications and Transfers
- Enhanced Transparency (Open Source Tech)
Now that you know the general benefits of a blockchain, the next step is finding out if a blockchain application will benefit you.
The ideal way to begin is to make a list of current pain points for your company, shareholders, and customers. Which business processes are slow? Which are causing friction? Which are causing the company to bleed money?
Once you’ve identified existing problems, you can investigate if a blockchain application will provide a unique fix. Ask yourself – would the key aspects of a blockchain improve any of my problematic business processes? If yes, it’s time to look more into what that process would look like if it ran on a blockchain.
The most important thing to remember is this:
Before deciding to use a blockchain technology application, you must have a use case.
You don’t want a solution without a problem to solve. Companies that don’t have a clear use case are less likely to reap the benefits of blockchain technology.
So, let’s take a look at what use cases other companies are finding for blockchain applications. A recent study by Deloitte asked companies how they plan to use blockchain applications. Here’s what they answered:
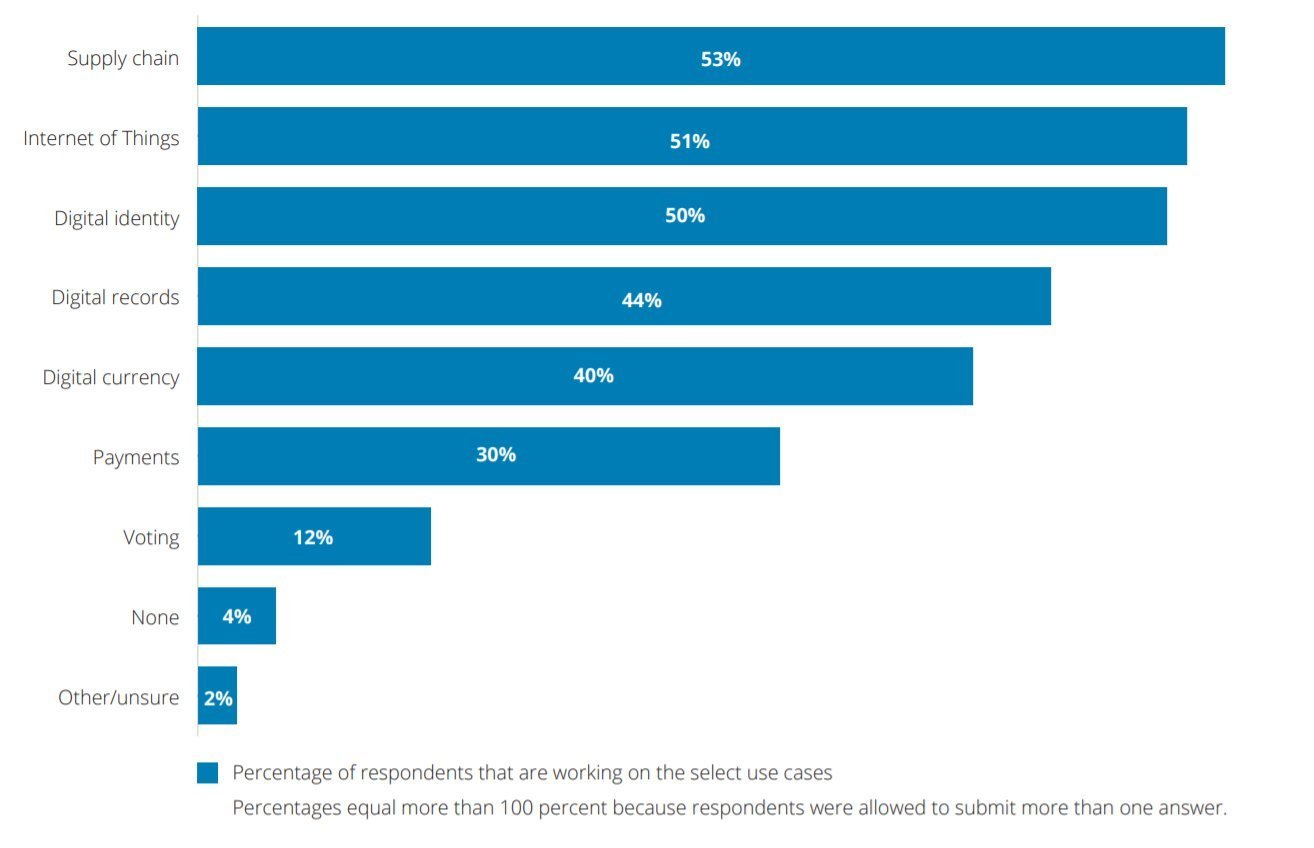
Because of the hype around cryptocurrencies, it’s often difficult to see the other applications for blockchain technology. We know that blocks can store information about monetary transactions. But they can also store data about any sort of transaction:
- Packages (Supply Chain)
- Personal Details (Medical Records)
- Assets (Real Estate / Luxury Items)
- Energy (Power Grids)
Notice that 53% of companies in the Deloitte study plan to use blockchain applications to handle their supply chain. Only 30% plan to use it for payments.
The bottom line? Blockchains can improve a variety of business processes. And implementing a blockchain application will change the way your business runs.
Step 2: Creating a Blockchain Strategy
Does your company have a use case for blockchain applications?
Let’s go deeper into identifying a use case for your business.
To make things simple, you can think of blockchain as a solution to two needs – record keeping and transactions. You can then address these needs with one of six use cases according to a report by McKinsey.
Check out the use case chart by McKinsey below:

Another way to look at things is to ask yourself if improving any of the following would solve the problems you’ve identified:
- Recording
- Tracking
- Verifying
- Aggregating
If you’re shaking your head no, then a blockchain application probably won’t solve that problem.
Additionally, you’ll want to ask yourself the following questions:
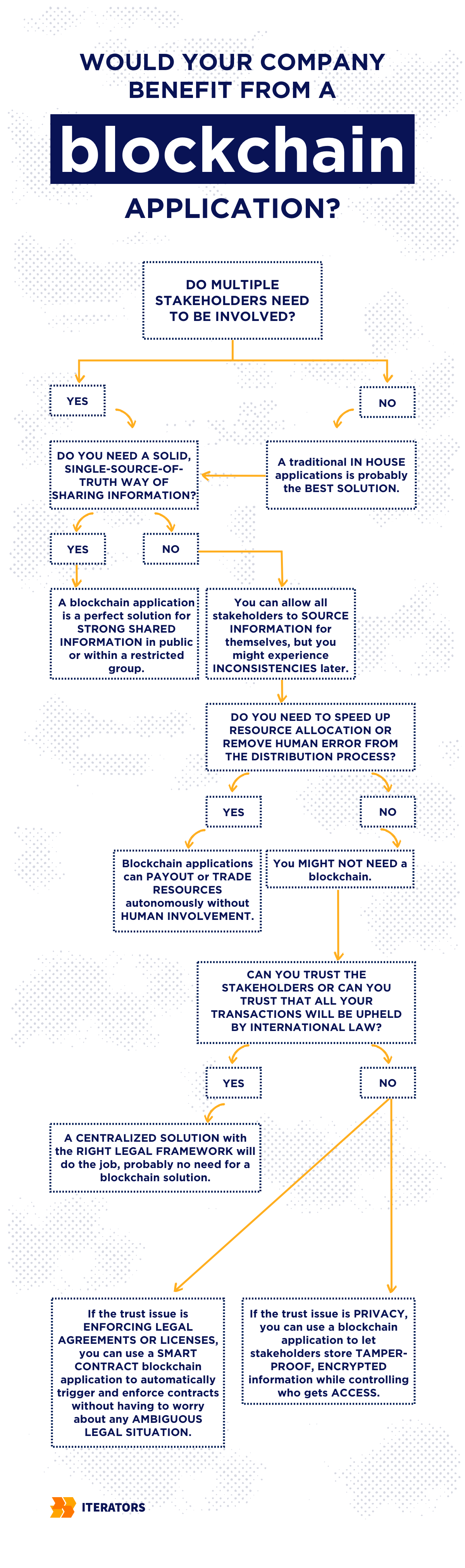
Step 3: Launching Your Blockchain Strategy
When should your company implement a blockchain application?
Let’s say you’ve gotten to the point where you’ve decided you definitely have a use case for a blockchain application. What’s next?
Well, it’s time to decide when to take action. And that’s when doubt might hit you. What if it’s all just hype after all? What if no one adopts blockchain in the long run? What if your investment amounts to nothing?
Maybe you should hold off and see how things develop, right?
These are all valid questions. But while cryptocurrencies boom and bust, blockchain remains a safe investment as long as you have a good use for it.
In fact, many experts say that it’s a bigger risk for companies to wait. Ignoring the blockchain trend for any reason is a “dangerous attitude” according to Gartner.
Why?
Let’s say MIT Sloan is right. Blockchain becomes as “fundamental as the Internet.” In that case, businesses who fail to adopt may end up as far behind as those who didn’t go digital.
The good news is that you won’t run the risk of getting left behind if you consider blockchain applications now. And you’re here, so you’re further ahead than most.
Gartner says 77% of CIOs still have no interest in blockchain and aren’t planning on investigating or implementing it.
The remaining problem is when to start using the technology. And for that, there is no single correct answer. You might decide to jump into the deep end or wait until you find a practical blockchain application that fits your needs.
It’s up to you, your business type, and your budget. Will it be better for you to be an adopter or a disrupter? The answer to that question also has a lot to do with your industry.
On that note, here are some stats about the future of blockchain applications:
In a 2024 survey, Deloitte said over 80% of financial executives believe blockchain technology is broadly scalable and will achieve mainstream adoption.
The trick is to start small. Don’t start by putting an entire system on a blockchain. PwC advises companies to start with individual processes. That way you can be sure that everything works.
Yet, PwC named blockchain as one of their “Essential Eight” emerging technologies. They believe that blockchain will be an essential technology in 3-5 years. And that’s true for all businesses across all industries.
There are others that are more conservative about the timeline for blockchain development. For example, HBR believes that we’re in for a long ride. But again, it’s never too early to look at possible applications for blockchain. The trick is to tie the technology to new business models.
The bottom line?
Companies are investing in blockchain applications. And that will continue until blockchain becomes an “essential” technology.
Step 4: Basic Blockchain Technical Details
Which architectural components should you consider?
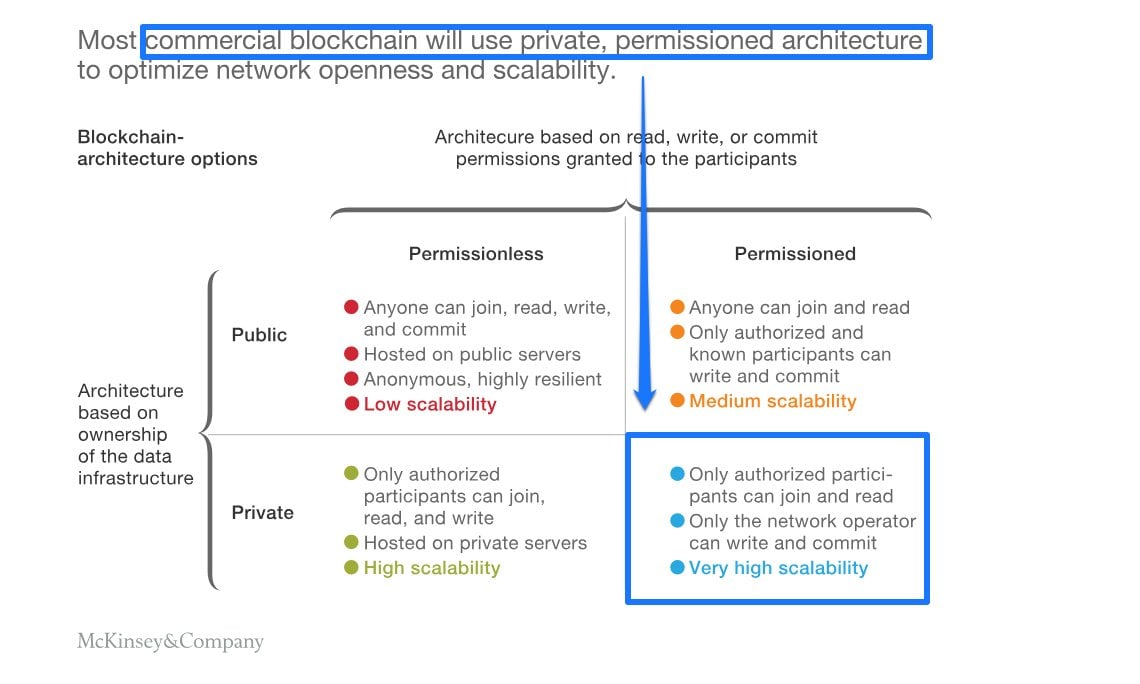
To help you answer the “when” question, it’s also a good idea to consider which architectural components will benefit your business most.
Do you need to build an in-house, private blockchain? Or can you tap into a public one? Or perhaps you need to join a blockchain with lots of other companies?
What type of blockchain will work best for you and your company? First, let’s look at the three types of blockchains:
- Public
- Private
- Consortium
Public blockchain examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum. Anyone can join the blockchain as a validator and send transactions.
Private blockchains are invite only. You might want to consider a private blockchain if you want to keep records of sensitive data or handle in-house accounting. You have the control because your blockchain is autonomous from the public Internet.
A consortium blockchain application comprises several companies running as nodes on the blockchain. You still need permission to join, but no single company controls the blockchain. Instead, administrators decide who can see what and who can execute consensus protocols.
Once you’ve decided which type of blockchain is best, you’ll need to research which blockchain code will fit your needs. Blockchain code differs depending on what you need to do. So, there is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to setting up a blockchain for your business.
Pro Tip: A good example of a consortium is R3. Comprising more than 70 global banks working together, R3 has developed the Corda blockchain platform. By working together, consortiums can create platforms that standardize blockchain applications.
Step 5: Implementing Your Blockchain Strategy
How would you go about implementing blockchain architecture?
After extensive research, you’ll want to invest in building blockchain architecture.
Without going into blockchain technical details, there are a couple of approaches you could consider. The first is to invest in people who know what they’re doing.
For the most part, blockchain code is open source and organization led. You can find it on Github and use it as the backbone of your projects. So, a simple approach would be to hire blockchain programmers for your project and build a solution in-house.
A second approach is to join an existing blockchain network like Quorum or Ethereum. Quorum is JP Morgan’s distributed ledger and smart contract platform. Built on Ethereum, Quorum is an “enterprise-focused” solution. Ethereum allows for a more individual, scaled approach.
Do make sure that any enterprise solution you choose has the blockchain components you need. There are five components of blockchain: encryption, immutability, distribution, decentralization, and tokenization.
A third solution is to outsource your project to a company that specializes in blockchain and can build a custom solution for you.
Your choice will rest on a few key aspects of your project:
- Do you want your blockchain application to be public, private, or part of a consortium?
- Do you want control over building a blockchain for your company?
- Do you have the budget and resources to hire a team or outsource your project?
Each solution has pros and cons, and your choice should reflect the individual needs of your business and your blockchain use case.
If you would benefit most from joining a consortium, you might have to wait longer to implement a blockchain until others are willing to join you. If you’re building an in-house solution your timeline is obviously up to you.
Pro Tip: If you need more help, there are templates for designing business use cases online. You can also use the tool to make spreadsheets of business processes. Add those that will speed up with the removal of a middleman or the creation of smart contracts.
Not sure how to decide if you need to hire a blockchain programmer or a company that specializes in blockchain applications? Do you struggle when it comes to tech staffing? Not to worry! Read our article: How to Hire a Programmer for a Startup in 6 Easy Steps
Blockchain Applications Explained – What is a Blockchain and How Does It Work?
Okay, so you know how a blockchain application could help your business. And you know the key aspects of a blockchain. But it’s also good to understand how blockchain works.
The good news – as a concept, blockchain is not impossible to understand.
The bad news – blockchain solutions (and code) differ depending on need. While core elements remain the same, others change.
Let’s take two different blockchain applications as examples – Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency blockchain application and Ethereum is a smart contract blockchain application with tokenization. Both are blockchain-based applications, but they have different structures, outcomes, and purposes.
That’s why it’s important to understand blockchain basics. You’ll have a better grasp on how to leverage the technology along with a broader idea of its possible applications.
What is a blockchain?
A blockchain is a form of distributed ledger technology. You can program it to become a growing record of anything of value. It has two parts – the block and the chain. The “chain” is a public database of blocks. A “block” is a chain link that contains information about transactions.
Let’s go into more detail.
A ledger is nothing more than a record of data or transactions. Ledgers date back to ancient times when they were nothing more than clay tablets that read:
“Joe bought two goats from Roger for 60 gold coins.” OR “Joe owns two goats.”
A distributed digital ledger is a shared record spread across a network (distributed). That means there are many copies of the ledger spread out across many computers. Imagine hundreds of copies of the same clay tablets – but on computers.
The system synchronizes the copies so that each one updates with each new transaction.
Because it is a distributed ledger, it is also decentralized as it has no single storage place. Also, there is no single ledger owner – like a bank or corporation.
Nodes – or computers in the network – verify the transactions. After, the blockchain ledgers update.
So, to repeat:
A blockchain is a distributed, decentralized ledger, allowing trade without a middleman. The blocks are individual records of data (ledger entries). The chain is the complete record of all the blocks (the full ledger).
What kind of information is stored on blocks?
It’s important to note that blocks can contain any type of data you need. Transactions do not have to be monetary. You can trade anything of value on a blockchain from data and storage to energy and assets.
In general, blocks contain four types of information:
- Transaction Data (e.g., Date, Timestamp, Dollar Amount)
- Personal Details of Transaction Participants
- A Unique ID Code for the Block (Hash)
- A Cryptographic Hash of the Previous Block
Let’s say you’re buying a house on a site that uses a blockchain application. The block would record the date, time, amount paid, and legal details. That’s straightforward.
Your personal information isn’t as straightforward. The block doesn’t record your real name. Instead, you use a “digital signature” that is unique to you. The same goes for the seller. That way your transactions are private and no one can identify you as the buyer.
At this point, it’s important to note that blocks can store more than one transaction. When it comes to the Bitcoin blockchain, a single block can store up to 1MB of data. That allows for thousands of transactions per block.
That being said, a block could store only one transaction. How much data goes on a block is dependent on the purpose of the blockchain application.
A block only receives its last bit of information when the nodes verify all its transactions. The final bit of information is the block signature, also known as a “hash.” A blockchain hash is a unique identifying code that helps people distinguish one block from another. Blocks also receive the hash of the block the came before it.
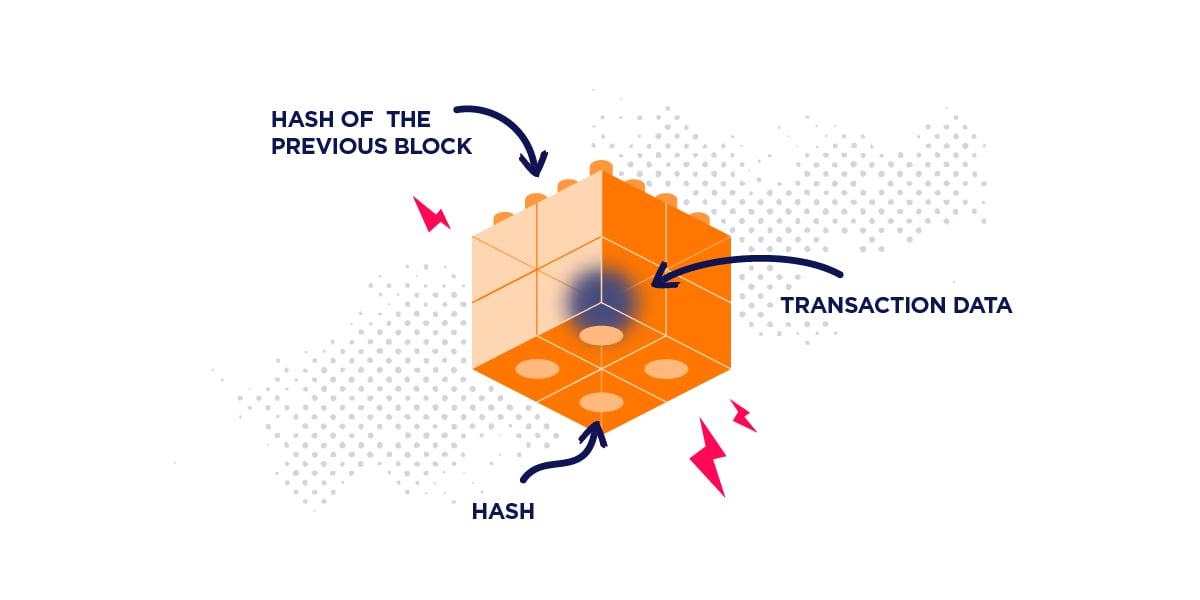
Once a block is created, it joins the chain. To recap, four things must happen for a new block to join the blockchain:
- Transactions
- Verification
- Storage in a Block
- Block Assigned a Hash
Once verified, the block joins the blockchain and becomes public. That means that everyone connected to the blockchain gets an updated copy of the database.
And what about the security of blockchain applications?
The nature of blockchain technology makes it one of the most secure ways to transfer money and data online. It also solves the “double spending” problem – spending the same money twice.
A blockchain is a growing list of records that cannot be edited or erased, which is why the technology is trustworthy. Here’s how:
First, the blocks themselves are virtually impossible to alter.
See, blocks join the chain in chronological order. As they join, they get a blockchain hash along with the hash of the preceding block. The first block in the chain is the “Genesis” block. It does not have the hash of a preceding block as it’s the first one.

Now, if a hacker wanted to alter information on a block, the hash would change. That means that the block no longer matches its old hash on the next block. So, the hacker would have to change that hash as well. And so on and so forth until all the following blocks are up to date.
But aren’t computers sophisticated and fast enough to recalculate the invalid hashes?
Well, that’s where proof of work and other consensus algorithms come into play. They work as added safety measures to make sure hackers can’t change blockchain hashes.
See, these algorithms slow down the creation of new blocks. With Bitcoin, it takes about 10 minutes for a computer to create a proof of work and add a new block to the chain. A hacker would need to recalculate the proof of work for all the following blocks. And that takes time.
When combined, hashing and consensus algorithms effectively stop tampering.
Finally, the fact that a blockchain is distributed also puts a stop to hacking. When a new block is created, every node in the network gets a copy for verification. At this point, everything needs to be correct for the network to accept it.
To get the network to accept an altered block, a hacker would have to take control of more than 50% of the network. Good luck with that.
That means a hacker needs to change the hashes, solve the proofs, and take over more than 50% of the computer network to alter a transaction. And that’s virtually impossible.
Different Uses for Blockchain Applications and Why They Work
So, how do you know if your use case is going to work? A good way to answer that question is to look at existing blockchain applications.
For starters, here is a shortlist of blockchain applications now in use:
- Cryptocurrency (Bitcoin)
- Smart Contracts (Ethereum)
- Cross-border Payments (Ripple)
- Supply Chain Management (IBM Food Trust)
- Prediction Markets (Augur)
- Royalties/ Intellectual Property (Mycelia)
- Provenance Tracking and Verification of Luxury Goods (Everledger)
- Global Shipping (Maersk and IBM)
- Supply Chain Management (Walmart)
Of course, the list is not exhaustive. UPS, FedEx, and DHL are all using blockchain applications. Plus, there are many startups investing in blockchain and big players are teaming up to shape solutions together. For example, Walmart uses IBM’s blockchain and Augur uses Ethereum.
Meanwhile, Microsoft has teamed up with Ernst & Young to create a blockchain for the gaming industry that will make it easier to manage royalties and rights.
Pro Tip: Joint efforts are a great approach to blockchain applications. When companies like Maersk and IBM or Microsoft and Ernst & Young team up, each brings unique resources to the table. In the end, they can do more together than they could alone.
A Closer Look at Smart Contract Blockchain Applications
It’s worth it to take a closer look at smart contract blockchain applications.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that run on blockchain technology. One current example of the technology in action is the Ethereum blockchain.
Ethereum allows users to:
- Create and Use Smart Contracts
- Create Cryptocurrencies or Tokens
- Store and Manage Cryptoassests
Smart contracts are much the same as regular contracts. The main difference? Smart contracts make automatic payouts when relevant parties meet the conditions of the contract.
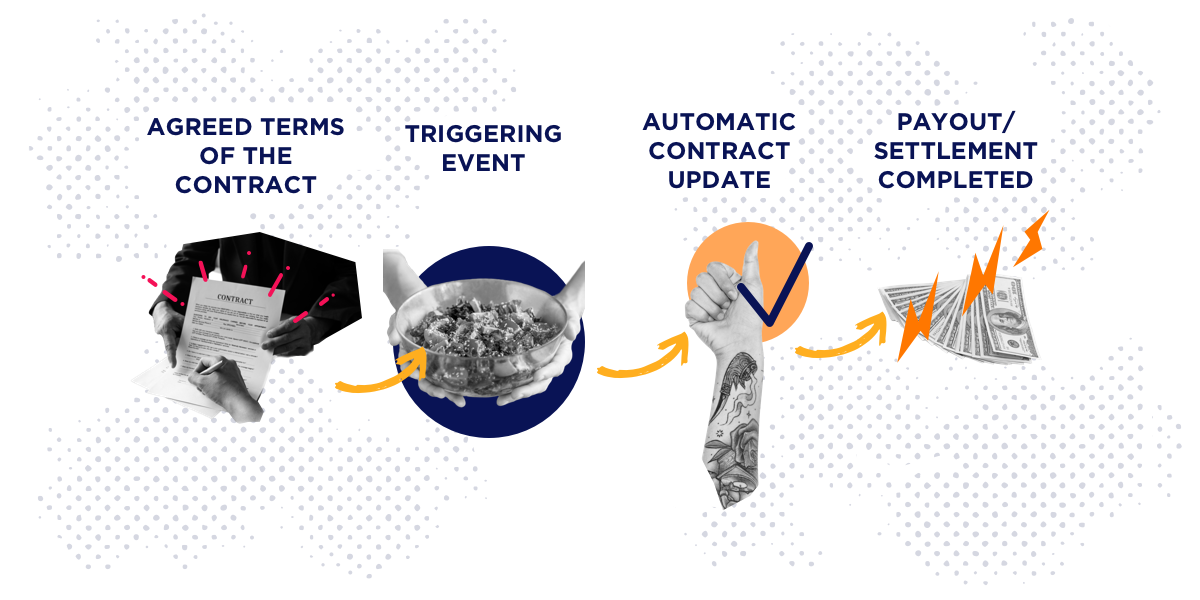
When combined, smart contracts and cryptocurrencies have the power to create new markets. And smart contracts alone could disrupt every industry. Supply chain management, prediction markets, and royalty management are only a few examples.
But let’s take a look at the financial industry. You may find it surprising, but banks and financial institutions are blockchain leaders. Despite being the middlemen, financial institutions have many use cases for blockchain applications. And according to Deloitte, over 80% of financial executives believe blockchain technology is broadly scalable and will achieve mainstream adoption.
When it comes to smart contracts, banks can use them to grant personal loans and mortgages with massive cost savings. A study by Capgemini shows that smart contracts can save consumers between $480 and $960 on average.
Banks will also have the potential to cut processing costs between $3 and $11 billion annually in the US and the EU. Everyone saves money on mortgages and loans with the implementation of smart contracts.
Beyond personal loans and mortgages, banks can use blockchain and smart contracts to:
- Process Insurance Claims
- Speed up Investment Banking Procedures
- Handle Payment Processing
For banks, smart contracts speed up all core business process while cutting costs.
A Closer Look at Supply Chain Management Blockchain Applications
Remember how more than 50% of the participants in Deloitte’s survey were using blockchain applications to handle aspects of their supply chain?
That’s because it’s one of the most likely use cases for blockchain technology. Why? Supply chains rely on transparency, trust, and efficiency to work. And blockchain applications enhance all three of these qualities.
Here’s how it might work:
Let’s say that you sell salads. Do keep in mind that Walmart uses a blockchain to track mangos. But let’s stick to salads.
To make your salads, you need lettuce. You get that lettuce from various suppliers. You send the lettuce to various vendors. So, using a blockchain application would allow you to track your salad and the lettuce in it from farm to table.
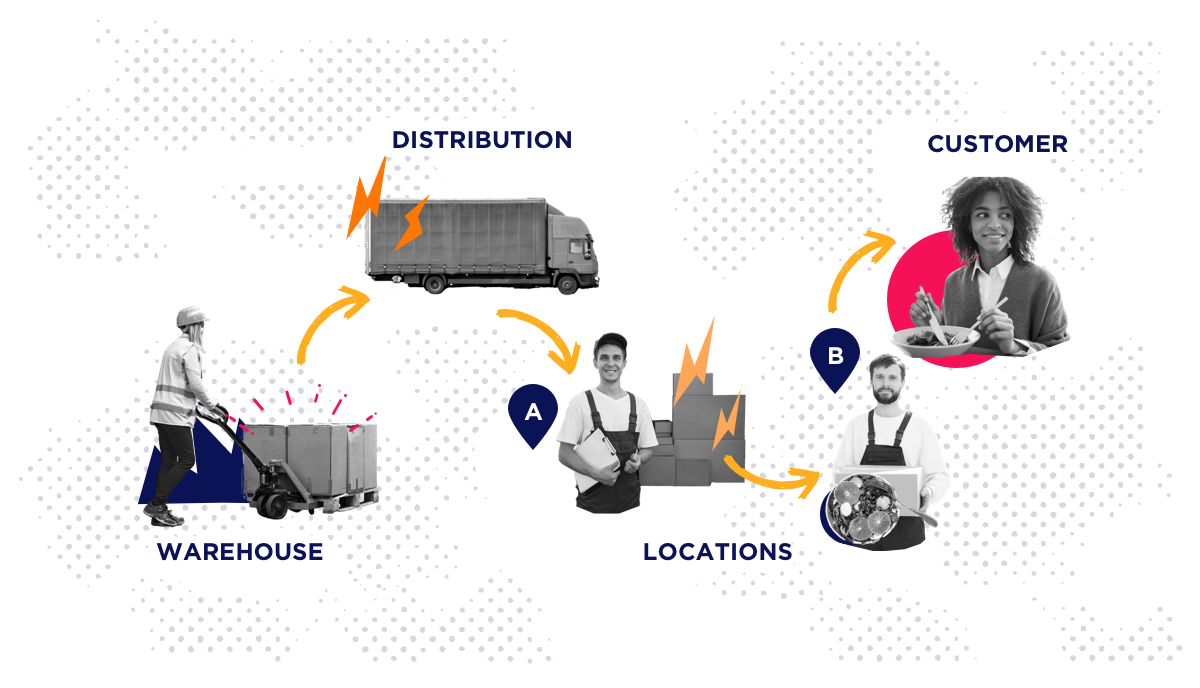
You could know where your lettuce is at any point, who handles it, and if it’s are in good condition. You can keep track of payments and deliveries. And in the case of contaminated lettuce, you can trace the product back to the source without accruing significant losses.
Having that kind of control over a supply chain is game-changing.
Future Applications of Blockchain: Disrupting Every Industry
But what about the future of blockchain? Here is a list of blockchain applications that could change the way we make digital transactions online:
- Asset Management
- Charity
- Cybersecurity
- Data Backup
- Data Sharing
- File Storage/ Cloud Storage
- Food Tracking
- Gift Cards and Loyalty Programs
- Governance (Voting, Polling, Passports)
- Identity Management
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Land Title Registration/ Property Records
- Medical Records
- Neighborhood Microgrids (Energy)
- Notary
- Personal Data Management
- Prescription Drug Tracking
- Sharing Economy
- Smart Property/ Ownership
- Stock Trading
- Tax Regulations and Compliance
- Weapons Tracking
- Wills and Inheritance
- Worker Rights
Of course, the list is not exhaustive. Blockchain applications have the ability to disrupt business processes across every industry.
It’s only a waiting game to see where and how blockchain applications will manifest.
Two interesting applications include identity management and smart property.
A Closer Look at Identity Management as a Blockchain Application
Almost all the applications listed above would benefit from blockchain ID management. That’s because online transactions can’t happen without identity verification.
Blockchains could control personal data for passports, medical records, tax compliance, and voting. To be more precise, you would control digital identification documents.
You could grant access to personal details while controlling who sees what. Only need to prove your age? Blockchain technology could make that happen. Want to change your doctor? Give them access to your medical records via a secure blockchain.
Plus, your data would be safer – in theory. Ideally, blockchain technology would make it harder for hackers to steal your identity or personal data.
Many institutions are already researching how to use blockchain applications for identification.
According to McKinsey, more than 25 governments are already running blockchain pilots. Once implemented, blockchain applications would create a wider economy and make things simpler and more secure for citizens.
A Closer Look at Smart Property as a Blockchain Application
Smart property is a blockchain application that could allow you to prove you own something and to manage and trade your assets easier.
Let’s take a closer look at proof of ownership. Right now, you can’t prove that you own things like your TV or your dishwasher. But with blockchain, you could prove that. You could also prove that you own digital property. A good example is Cryptokitties – digital kittens that you can buy with Ether tokens.
These kittens are stored in the blockchain as your property. That means you can trade and sell your kitties, and you have complete proof of ownership. Here’s a video:
You could also use blockchain applications to register land and create property titles. Legal procedures for documents are often lengthy, expensive, and susceptible to human error. The idea is that blockchain would make paperwork unnecessary.
Imagine having a digital wallet that contains the proof of ownership for all your stuff. From your house and car to your TV and Cryptokitties. To create proof you would only need to make one transaction on a blockchain. No more paperwork. No more middlemen. No receipts. Nothing.
That’s more or less what the future that blockchain-based smart property promises.
Are you a game developer or a business person interested in digital property? Want to find out how blockchain technology is being applied to the gaming industry? Check out our article: Blockchain Games: Take Your Game to the Next Level
Conclusion
When it comes to blockchain applications, it’s no longer a matter of “if” but “when,” and when is coming soon. More companies are investing in and finding use cases for blockchain technology.
Why?
They understand that blockchain applications have the ability to disrupt outdated business processes. They also understand the benefits – greater transparency, trust, and efficiency. Not to mention a cut in costs and an increase in consumer privacy.
All signs point to blockchain applications as the future. Are you ready to jump on board?