Every day, businesses generate a staggering amount of data and users continue to spark internet growth by discovering new methods to consume information. While users generate 64.2 ZB (zettabytes) of data in 2020, data creation could top 147 ZB by the end of 2024 and 180 ZB in 2025. This is far more than the number of detectable stars in the cosmos.
The pandemic accelerated demand for data as more people worked and learned from home, using home entertainment options more than before. This data explosion offers a goldmine of insights, but businesses need big data applications to crack the code and unlock its true value.
This article will introduce you to the power of big data applications. We’ll equip you with the knowledge to leverage big data for significant business success.
What are Big Data Applications
Big data applications are the tools and technologies businesses use to analyze, process, and extract insights from massive datasets that traditional data processing methods can’t handle.
Here’s one way to think of it: If you had a giant warehouse overflowing with boxes of information, big data applications are like the specialized equipment and strategies needed to efficiently sort through these boxes, identify valuable items, and ultimately make sense of everything stored inside.
Need help implementing big data applications into your project? The Iterators team can help design, build, and maintain custom software solutions for both startups and enterprise businesses.
Schedule a free consultation with Iterators today. We’d be happy to help you find the right software solution to help your company.
Analyzing Large Datasets
The digital age enables businesses to generate a colossal amount of data every day. This data comes from various sources, including:
- Customer transactions (online purchases, loyalty programs)
- Social media interactions (posts, comments, reviews)
- Machine-generated data (sensor readings, logs from applications)
- Financial transactions
- Clickstream data (website visits, user behavior)
The volume, variety, and velocity of this data make it challenging to analyze using traditional data processing methods. This is where big data applications become necessary.
The Three Vs of Big Data
In describing the concept of big data, we usually refer to the three Vs: Volume, Variety, and Velocity.
These characteristics define the challenges and unique aspects of handling big data compared to traditional datasets.
- Volume: This refers to the sheer amount of data generated by businesses today. Measured in terabytes, petabytes, and even exabytes, the volume of big data is constantly growing, posing a storage and processing challenge.
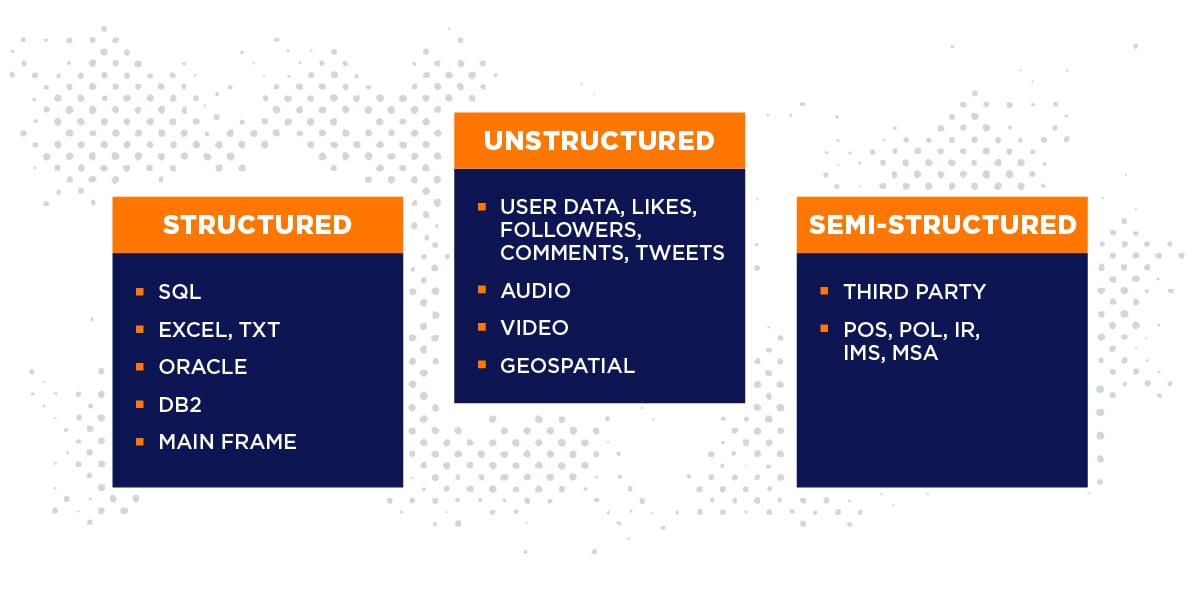
- Variety: Big data comes in many forms, not just the neat rows and columns of traditional databases. It can include structured data (like sales figures), semi-structured data (like log files), and unstructured data (like social media posts and emails). This variety requires flexible data management tools.
- Velocity: The speed at which data is generated and needs to be processed is another defining characteristic. Big data can be generated in real-time (think stock market feeds) or near real-time (like website clickstream data). This velocity necessitates tools that can handle high-speed data ingestion and analysis.
The three Vs, working together, are what make big data so complex to manage and analyze using traditional methods. Big data applications are specifically designed to address these challenges and unlock the potential hidden within these massive and diverse datasets.
Big Data Applications in Practice
As specialized software tools designed to manage, analyze, and extract valuable insights from these massive and complex datasets, big data applications are useful in combating information overload.
Here’s how they work:
- Data Ingestion: Big data applications first ingest data from various sources, often in real-time. This data can be structured (e.g., customer names in a database) or unstructured (e.g., social media posts).
- Data Storage: Once ingested, the data is stored in specialized data warehouses or distributed file systems designed to handle massive amounts of information.
- Data Processing: The applications then process the data, cleaning it for inconsistencies and transforming it into a format suitable for analysis.
- Data Analysis: Powerful analytics tools within the applications are used to identify patterns, trends, and correlations within the data. This could involve statistical analysis, machine learning algorithms, or other techniques.
- Insight Generation: Finally, big data applications translate the raw data into actionable insights businesses can use to make informed decisions.
The Role of Big Data Applications
By unlocking the hidden potential within massive data sets, big data applications empower businesses to:
- Improve decision-making: Data-driven insights can guide strategic choices, product development, and marketing campaigns.
- Optimize operations: Identifying trends in customer behavior or operational inefficiencies can lead to process improvements and cost savings.
- Boost revenue generation: Understanding customer preferences and market trends helps businesses personalize offerings and identify new revenue streams.
- Enhance customer experience: Utilizing customer data allows businesses to personalize interactions and provide a more satisfying customer journey.
- Gain a competitive edge: By leveraging big data for deeper market understanding and innovation, businesses can stay ahead of the curve.
In a nutshell, big data applications are essential tools for businesses navigating the ever-growing sea of data. They play a crucial role in transforming raw data into valuable insights, ultimately leading to better decision-making and a competitive advantage.
Importance of Big Data Applications

In today’s data-driven world, information is king. Businesses generate a wealth of data from customer interactions, operations, and the market. But this data is only as valuable as the tools used to analyze it. Traditional data processing methods often struggle with the sheer volume, variety, and velocity of big data. This is where big data applications come in, acting as the key that unlocks the immense potential hidden within massive datasets.
Managing and Analyzing Big Data
The explosion of big data presents businesses with a double-edged sword. On one hand, it offers a treasure trove of insights for improved decision-making and competitive advantage. On the other hand, managing and analyzing this vast and ever-growing data comes with significant challenges.
Challenges
- Data Deluge: The sheer volume, variety, and velocity of big data can overwhelm traditional data storage and processing systems. This necessitates specialized big data infrastructure and expertise to handle the data effectively.
- Data Quality and Integration: Data quality issues like inconsistencies, inaccuracies, and missing values can plague big data projects. Integrating data from diverse sources further complicates the process, requiring robust data cleansing and transformation techniques.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: Protecting sensitive customer information within massive datasets becomes a top priority with big data. Robust security measures and adherence to data privacy regulations are essential.
- Skill Gap: The growing demand for data scientists and analysts with big data expertise creates a skills gap in the workforce. Finding and retaining qualified professionals is crucial for successful big data adoption.
Opportunities
- Data-Driven Decisions: Big data empowers businesses to make informed decisions based on real-time insights extracted from vast datasets. This can lead to improved product development, resource allocation, and marketing strategies.
- Operational Efficiency: Big data analytics can help identify inefficiencies in operations, leading to cost savings and improved resource utilization. Streamlining processes and predicting potential issues become possible with real-time data analysis.
- Personalized Customer Experience: By analyzing customer data, businesses can personalize interactions, recommend relevant products, and anticipate customer needs. This translates to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty, driving brand advocacy.
- Innovation and Competitive Advantage: Big data analysis can uncover hidden trends and patterns that inform innovative product development and targeted marketing strategies. Businesses that leverage big data effectively gain a significant edge over competitors by anticipating market shifts and customer preferences.
Big data presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses. Investing in the right tools and expertise will help your business unlock the immense potential of big data, transforming information into strategic advantages that drive growth and success.
Why Big Data Matters for All Businesses

Information is the new currency in today’s data-driven world. Businesses of all sizes, from established giants to nimble startups, are generating a wealth of data from customer interactions, operations, and the market. However, this data remains a dormant resource without the tools to unlock its potential. Traditional data processing methods often struggle with the sheer volume, variety, and velocity of big data. This is where big data applications come in, acting as the key that unlocks the treasure trove of insights hidden within massive datasets.
While big data might seem like the domain of large corporations with vast resources, big data applications are particularly crucial for startups and growing companies. Here’s why:
- Early Adoption Advantage: Startups have a unique opportunity to build a data-driven culture from the ground up. By integrating big data insights seamlessly into their operations from the start, startups can accelerate growth and establish a competitive edge early on. Imagine launching with a product or service that perfectly resonates with your target market because you have data-driven insights into their needs and preferences. That’s the power of big data for startups.
- Leveling the Playing Field: The big data landscape is evolving rapidly. Cloud-based solutions are making powerful big data tools more accessible and affordable for startups with limited IT resources. This allows them to compete with established players who may have traditionally held an advantage in data analysis capabilities.
- Data as a Foundation for Growth: Startups can leverage big data to guide product development efforts. Analyzing customer data allows them to ensure features and functionalities resonate with the target market, leading to a higher chance of product success. Big data can also help identify new market opportunities and inform future product iterations.
Beyond Startups
While startups stand to gain significant advantages from early adoption, big data applications are no longer a luxury for established businesses either. They have become a strategic necessity for companies of all sizes. Here’s why:
- Stay Ahead of the Curve: Big data empowers businesses to monitor market trends in real-time, identify emerging customer preferences, and adapt their strategies accordingly. This agility allows them to stay ahead of the curve and capitalize on new opportunities before competitors.
- Optimize Operations and Boost Revenue: By analyzing operational data, businesses can identify inefficiencies, streamline processes, and improve resource allocation. Big data also helps personalize customer experiences, leading to higher satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, increased revenue.
Big data applications are a game-changer for businesses of all sizes. By harnessing the power of big data, companies can gain a deeper understanding of their customers, optimize their operations, and make data-driven decisions that fuel growth and success. Regardless of your company’s size or stage, embracing big data applications is an investment in your future.
The Potential of ROI in Big Data Adoption
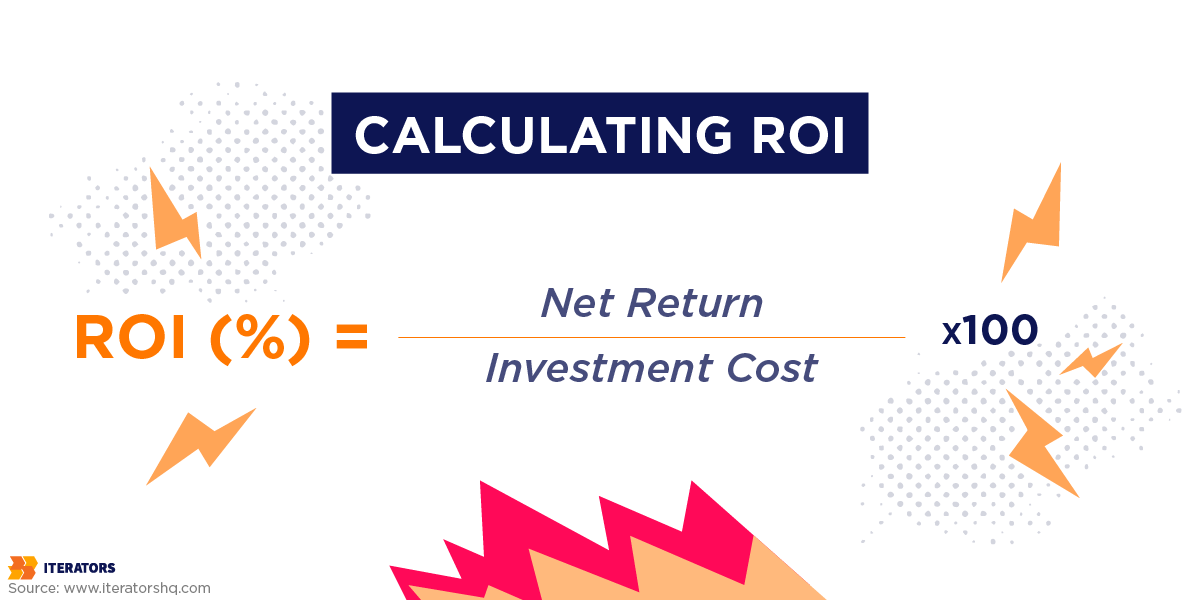
The potential return on investment (ROI) from big data adoption is undeniable. Here are some statistics that showcase the power of big data:
- Increased Revenue: According to a study by McKinsey, companies that leverage big data are 23 times more likely to acquire customers and 6 times more likely to retain customers. This translates to significant revenue growth.
- Cost Savings: A study by IDC estimates that big data adoption can lead to cost savings of up to 10% through improved operational efficiency and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: A study by Forbes Insights revealed that 89% of executives believe that big data has a significant or very significant impact on their ability to make data-driven decisions.
Real-World Examples
These statistics paint a clear picture: big data adoption can lead to substantial financial benefits. Let’s look at some real-world examples:
- Walmart: By analyzing customer purchase data, Walmart can identify trends and predict future demand. This allows them to optimize inventory management, reduce costs, and personalize product recommendations for each customer, leading to increased sales.
- Amazon: Amazon is a leader in big data analytics. They leverage customer data to personalize product recommendations, improve search results, and predict customer needs. This data-driven approach has been a key factor in their continued growth and success.
- Netflix: Netflix uses big data to analyze viewing habits and preferences. This allows them to produce personalized content recommendations, predict the success of new shows, and optimize their content library. This data-driven strategy has helped them build a loyal subscriber base.
These statistics and real-world examples showcase the undeniable ROI of big data adoption. Big data applications are a game-changer for businesses of all sizes. By harnessing the power of big data, companies can gain a deeper understanding of their customers, optimize their operations, and make data-driven decisions that fuel growth and success. Embrace big data applications and unlock the potential for significant financial benefits and a competitive edge.
Demystifying Big Data Applications
Though it’s easy to feel lost in the big data buzz, this section unveils the power behind big data applications. We’ll show you how your business – no matter the size – can leverage this technology to gain insights, boost efficiency, and make smarter decisions.
How Big Data Applications Leverage Data
Big data isn’t just about massive datasets. It’s about unlocking the hidden potential within that information. This section dives into the fundamental principles behind big data applications, revealing how they transform raw data into actionable insights that fuel smarter decisions, improved efficiency, and ultimately, business success.
Despite holding immense power, how exactly do they extract valuable insights from massive datasets? It all boils down to the ability to identify patterns and trends hidden within the vast amount of information. Here’s a breakdown of the key principles:
- Volume, Variety, and Velocity: Big data applications are built to handle not just a large quantity of data (volume), but also a wide range of data types (variety), such as text, images, sensor readings, and social media posts. Additionally, these applications can process data at an incredibly fast pace (velocity), allowing for real-time analysis.
- Statistical Analysis: Big data applications leverage powerful statistical techniques to identify patterns and trends within datasets. These techniques can detect correlations between seemingly unrelated pieces of data, revealing hidden connections and insights.
- Machine Learning and AI: Advanced algorithms powered by machine learning and artificial intelligence play a crucial role in big data analysis. These algorithms can sift through massive datasets, identifying complex patterns and relationships that might escape traditional statistical methods. They can also learn and improve over time, becoming more adept at uncovering hidden insights as they are exposed to more data.
- Data Visualization: Once patterns and trends are identified, big data applications employ data visualization tools to present the information in clear and compelling ways. Charts, graphs, and interactive dashboards allow stakeholders to easily understand the insights and make informed decisions based on the data.

If a retailer analyzes customer purchase history data, by looking at volume (quantity of purchases), variety (types of products bought), and velocity (buying frequency), they can identify patterns. They might discover that customers who buy product A are also likely to buy product B. This trend allows them to personalize product recommendations, leading to increased sales.
Big data applications are like powerful search engines for hidden patterns. They allow businesses to transform raw data into a treasure trove of insights, ultimately driving innovation, improving efficiency, and achieving success.
Big Data Architecture
Big data architecture refers to the framework that supports the collection, storage, processing, analysis, and visualization of massive datasets. It’s a complex ecosystem with various components working together to unlock the power of big data. Here are the key components of a big data architecture:
- Data Sources: This is the starting point, where the vast data originates. It can come from various sources, including:
- Traditional Databases: Relational databases that store structured data used in business operations (e.g., customer information, sales data)
- Social Media: Publicly available data from social media platforms like Twitter and Facebook
- Machine-Generated Data: Data collected from sensors, IoT devices, and other automated systems
- Log Files: Server logs, web logs, and application logs that capture user activity and system events
- Data Ingestion: This component focuses on how data enters the big data system. Techniques include:
- Batch Processing: Data is collected and transferred in large batches at regular intervals.
- Stream Processing: Data is ingested and processed continuously in real-time.
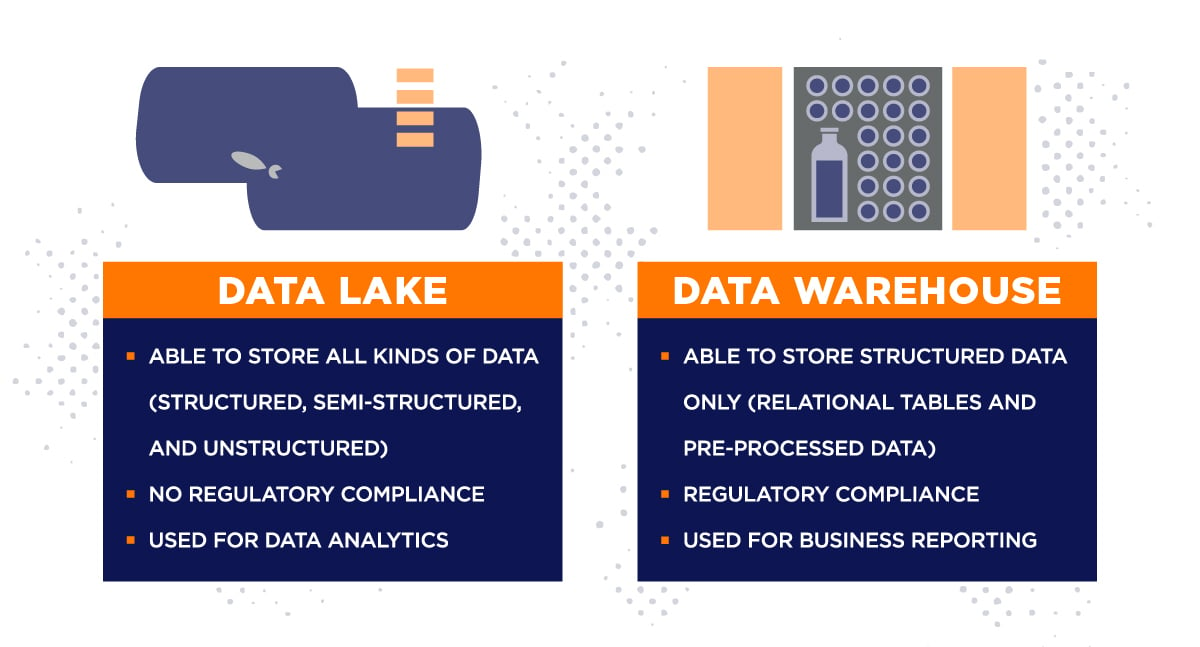
- Data Storage: Big data requires robust storage solutions to handle the massive volume and variety of data. Common options include:
- Data Warehouses: Centralized repositories designed for storing historical data and facilitating data analysis.
- Data Lakes: Scalable storage solutions that hold raw data in its original format, allowing for flexible analysis later.
- NoSQL Databases: These databases offer flexibility in handling unstructured and semi-structured data.
- Data Processing: Once data is ingested and stored, it needs to be processed for analysis. This involves techniques like:
- Data Cleaning: Removing errors, inconsistencies, and duplicate data to ensure accuracy.
- Data Transformation: Converting data into a format suitable for analysis.
- Data Integration: Combining data from various sources to create a unified view.
- Data Management: This component ensures the data within the big data architecture is secure, reliable, and accessible. Key aspects include:
- Data Governance: Establishing policies and procedures for data access, usage, and security.
- Data Security: Implementing measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Data Analytics and Processing Engines: These are the tools that analyze the processed data to extract insights. Popular options include:
- Hadoop: Open-source framework for distributed processing of large datasets across clusters of computers.
- Spark: Framework built on top of Hadoop, known for its speed and efficiency in real-time data processing.
- Data Visualization: After analysis, insights need to be communicated effectively. Data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI translate complex data into clear and compelling visuals, enabling stakeholders to understand the information and make data-driven decisions.
- Orchestration and Workflow Management: This component ensures the various components of the big data architecture work together seamlessly. It automates data pipelines and workflows for efficient data movement and processing.
By working together, these key components create a robust big data architecture that empowers businesses to leverage the vast potential of their data and unlock valuable insights for success. It’s important to note that the specific components and their configuration will vary depending on the specific needs and goals of each organization.
Benefits of Big Data Applications

Your organization can gain a significant competitive edge by taking advantage of the power of massive datasets. Here’s a closer look at some ways big data applications can help you with this:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Data-driven insights extracted from big data empower businesses to make informed decisions based on facts and trends, not just intuition. This leads to improved strategic planning, resource allocation, and overall business performance.
- Increased Efficiency and Optimization: Big data applications can analyze operational data to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in processes. Businesses can then optimize workflows, reduce waste, and streamline operations for greater efficiency and cost savings.
- Improved Customer Experience: By analyzing customer data and behavior, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their customers’ needs and preferences. This allows for personalization of marketing campaigns, product recommendations, and customer service interactions, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Innovation and New Product Development: Big data can reveal hidden patterns and trends in customer behavior, market demands, and competitor strategies. This valuable information can fuel innovation and the development of new products and services that cater to evolving customer needs.
- Risk Management and Fraud Detection: Big data analytics can be used to identify potential risks and fraudulent activities in real-time. This allows businesses to take proactive measures to mitigate risks, prevent financial losses, and protect sensitive information.
- Real-Time Insights and Agility: Big data applications can process data streams in real-time, providing businesses with immediate insights into customer behavior, market fluctuations, and operational performance. This real-time decision-making capability allows businesses to be more agile and adaptable to changing market dynamics.
- Competitive Advantage: By leveraging big data effectively, businesses can gain valuable insights that their competitors might miss. This can lead to a significant advantage in terms of market positioning, product development, and overall business success.
These are just a few of the many benefits big data applications offer. As technology continues to evolve and data becomes even more abundant, the potential applications of big data will continue to expand. Businesses that embrace big data and invest in data analytics capabilities will be well-positioned to thrive in the ever-growing data-driven world.
Industry Examples

The transformative power of big data applications extends across various industries. Here, we’ll delve into how big data is revolutionizing specific sectors, showcasing real-world examples and the quantifiable benefits companies have achieved.
- Retail and E-commerce:
- Challenge: Understanding customer preferences and purchase behavior across multiple channels (online, stores) to personalize the shopping experience and drive sales.
- Solution: Retailers leverage big data to analyze customer purchase history, browsing behavior, and social media interactions. This allows them to create targeted marketing campaigns, recommend relevant products, and optimize pricing strategies.
- Benefits: A study by Accenture found that companies using big data personalization techniques have seen a 10% to 30% increase in sales. Additionally, big data can help optimize inventory management, reducing stock outs and lost sales.
- Example: Amazon, a leader in big data and e-commerce, uses customer data to personalize product recommendations, predict demand, and optimize product placement on their website. This data-driven approach has been a significant factor in their continued growth and success.
- Marketing and Advertising:
- Challenge: Reaching the right audience with the right message at the right time in a crowded digital landscape.
- Solution: Marketers use big data to analyze customer demographics, interests, and online behavior. This allows them to create highly targeted advertising campaigns that resonate with specific audiences, leading to higher conversion rates.
- Benefits: A study by Teradata revealed that companies using big data for marketing purposes experience a 15% increase in marketing ROI. Additionally, big data helps measure campaign effectiveness and optimize marketing budgets for better results.
- Example: Starbucks leverages big data to personalize its mobile app experience. By analyzing customer purchase history and location data, they send targeted offers and promotions, increasing customer engagement and loyalty.
- Finance and Banking:
- Challenge: Managing risk, detecting fraudulent activities, and offering personalized financial products to customers.
- Solution: Financial institutions use big data to analyze customer financial data, transaction history, and creditworthiness. This allows them to detect fraudulent activities in real-time, personalize loan offers, and offer tailored financial products based on individual customer needs.
- Benefits: A study by Capgemini found that banks using big data for fraud detection can achieve a 20% reduction in false positives. Additionally, big data helps personalize financial products and services, leading to increased customer satisfaction and retention.
- Example: JPMorgan Chase utilizes big data to analyze customer financial data and identify potential fraud attempts. This proactive approach protects customers and minimizes financial losses.
These are just a few examples, and the potential applications of big data continue to evolve across various industries. Healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics are also embracing big data to improve efficiency, gain valuable insights, and ultimately achieve significant business outcomes.
Remember, big data isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The specific applications and benefits will vary depending on the industry and the unique challenges faced by each company.
Big Data Technologies
Your big data journey will see you deploy a variety of technologies designed to handle the storage, processing, and analysis of massive datasets. Here’s a glimpse into some of the commonly used tools:
- Apache Hadoop: An open-source software framework that allows distributed processing of large datasets across clusters of computers. It’s a foundational technology for big data storage and processing.
- Apache Spark: Another open-source framework built on top of Hadoop, known for its speed and efficiency in processing large datasets in real-time or near real-time. It’s ideal for tasks requiring faster processing than traditional Hadoop MapReduce.
- NoSQL Databases: Traditional relational databases can struggle with big data’s variety and volume. NoSQL databases offer flexible schema designs that can handle different data types and structures, making them well-suited for storing and managing big data. Popular NoSQL options include MongoDB and Cassandra.
- Cloud-based Big Data Solutions: Cloud platforms like Google Cloud Platform, Amazon Web Services, and Microsoft Azure offer scalable and cost-effective solutions for big data storage, processing, and analytics. These platforms provide a range of big data services that can simplify data management for businesses.
- Data Visualization Tools: Once you’ve analyzed your data, you need to communicate insights effectively. Data visualization tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Metabase help translate complex data into clear and compelling visuals, making it easier for stakeholders to understand the information and make data-driven decisions.
Challenges of Big Data Applications

Big data’s potential is undeniable, but it’s not without its challenges. Here are some key hurdles businesses face when implementing big data applications:
- Data Silos and Integration: Data often resides in isolated systems across different departments. Integrating this data into a unified platform for analysis can be complex and expensive.
- Data Quality and Management: Big data can be messy, containing errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates. Ensuring data quality requires robust cleansing processes and ongoing data management practices.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: Big data often contains sensitive customer information. Businesses must implement robust security measures to protect data from breaches and ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: Extracting value from big data requires skilled data scientists, analysts, and engineers. Finding and retaining these professionals can be challenging for many businesses.
- Scalability and Infrastructure Costs: Storing and processing massive datasets requires robust infrastructure. Scaling this infrastructure to accommodate growing data volumes can be expensive.
- Real-time Processing Hurdles: While real-time analytics offer immense benefits, processing massive data streams in real-time can require significant computing power and specialized infrastructure.
Despite these challenges, the potential rewards of big data are substantial. Businesses that can overcome these hurdles will be well-positioned to unlock valuable insights, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge in the data-driven world.
The Future of Big Data Applications
Big data’s potential is just beginning to unfold. As technology advances, we’ll see even more powerful applications emerge. This section explores the exciting trends shaping the future of big data, from AI integration to real-time insights, revealing how businesses can leverage these advancements for even greater success.
AI and Machine Learning Integration

Extracting the most valuable insights can be a complex task. Here’s where artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) come in as powerful allies. By integrating AI and ML with big data applications, businesses can unlock a new level of intelligence and automation.
AI algorithms sifting through massive datasets, identifying hidden patterns, and predicting future trends with remarkable accuracy. This is the future of big data analysis. Machine learning can automate repetitive tasks like data cleansing and anomaly detection, freeing up human analysts to focus on higher-level cognitive tasks.
The synergy between big data and AI/ML goes beyond efficiency. AI can uncover complex relationships within data that might escape traditional statistical methods. This leads to more accurate forecasts, risk assessments, and even the ability to develop AI-powered chatbots for personalized customer service.
The future is bright for businesses that embrace this powerful combination. AI and ML will supercharge big data applications, transforming them from data analysis tools into intelligent decision-making engines that drive innovation and growth.
Advanced Big Data Analytics
Big data holds immense potential, but its vastness can be overwhelming. Traditional data analysis methods often struggle to keep pace with the volume, variety, and velocity of big data. This is where artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) step in as game-changers, transforming big data applications with advanced analytics capabilities. Here’s how:
- Unlocking Hidden Patterns: Big data may contain complex relationships and patterns that are invisible to the human eye. AI algorithms, powered by techniques like deep learning, can analyze massive datasets and identify these hidden patterns. This can lead to breakthrough insights in areas like customer behavior prediction, product development, and market forecasting.
- Advanced Automation: Machine learning automates repetitive tasks involved in big data analysis, such as data cleaning, anomaly detection, and data preparation. This frees up valuable time for data scientists to focus on more strategic tasks – interpreting AI outputs, building predictive models, and developing data-driven strategies.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Predictions: AI and ML algorithms can analyze historical data and identify trends to make more accurate predictions about future events. This can be invaluable for businesses in various sectors. For example, retailers can use AI to predict customer demand and optimize inventory management, while financial institutions can leverage ML to detect fraudulent transactions and improve risk assessment.
- Real-time Analytics: The ability to analyze data in real-time is crucial in today’s fast-paced business environment. AI and ML algorithms can process data streams in real-time, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions instantly. Imagine receiving real-time customer sentiment analysis on social media or identifying potential equipment failures before they occur in a manufacturing setting.
- Hyper-personalization: Combining big data with AI allows for highly personalized experiences. AI can analyze customer data to anticipate needs and preferences, enabling businesses to personalize marketing campaigns, product recommendations, and customer service interactions. This leads to higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, increased revenue.
- Continuous Improvement: AI and ML models are constantly learning and evolving. As they are exposed to more data, they become more accurate and sophisticated in their analysis. This continuous improvement ensures that businesses stay ahead of the curve and leverage the latest advancements in big data analytics.
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing big data applications by providing advanced analytics capabilities. By unlocking hidden patterns, automating tasks, and enabling real-time insights, AI and ML empower businesses to make smarter decisions, optimize operations, and gain a significant competitive edge in the data-driven world.
Edge Computing
The power of big data applications is undeniable, but processing massive datasets in the cloud can introduce limitations. Latency issues, bandwidth constraints, and security concerns can arise when data needs to travel long distances to central servers for analysis. This is where edge computing emerges as a crucial partner in the big data ecosystem.
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data closer to where it’s generated, at the “edge” of the network, on devices like sensors, smart machines, or local servers. Here’s how edge computing complements big data applications:
- Reduced Latency: By processing data locally, edge computing eliminates the need for lengthy data transfers to the cloud. This significantly reduces latency, allowing for real-time insights and faster decision-making. Imagine a factory where sensors on equipment can analyze data locally to predict potential failures and trigger preventative maintenance before downtime occurs.
- Improved Efficiency: Edge computing reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud. This frees up bandwidth and reduces processing load on central servers, leading to improved overall efficiency and cost savings.
- Enhanced Security: Certain types of data may be sensitive or subject to regulations. Processing data locally on edge devices can improve data security by minimizing data transmission and potential vulnerabilities associated with cloud storage.
- Offline Functionality: Edge computing enables data processing and analysis to continue even when internet connectivity is unstable or unavailable. This ensures uninterrupted operations in scenarios where real-time decision-making is critical.
While edge computing doesn’t replace big data applications in the cloud, it acts as a powerful extension. The data processed at the edge can be aggregated and sent to the cloud for further analysis and storage. This two-tiered approach unlocks the benefits of both centralized and decentralized processing, leading to a more robust and efficient big data architecture.
A Collaborative Approach
The future of big data analytics lies in a collaborative approach where edge computing and cloud-based applications work together seamlessly. By leveraging the strengths of both, businesses can gain real-time insights from edge data, coupled with the broader historical and contextual analysis offered by cloud-based big data applications. This synergy will ultimately empower businesses to make smarter data-driven decisions and achieve greater success in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Real-time Analytics

Traditional data analysis, which often relies on historical data, can leave businesses lagging behind. This is where real-time analytics comes in, providing game-changing capabilities for big data applications.
Real-time analytics refers to the process of analyzing and extracting insights from data as it’s generated. Imagine a constant stream of data flowing in – customer clicks on a website, sensor readings from a machine, social media mentions of your brand. Real-time analytics tools can analyze this data stream instantaneously, providing businesses with valuable insights and enabling them to make data-driven decisions in real-time.
Here’s how real-time analytics transforms big data applications:
- Faster Response Times: Real-time insights allow businesses to react to situations immediately. For example, a surge in website traffic can trigger automatic scaling to prevent crashes, or negative customer sentiment on social media can be addressed before it escalates.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: By analyzing real-time data on equipment performance or production lines, businesses can identify and address issues as they occur, minimizing downtime and optimizing operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Real-time customer data allows businesses to personalize interactions and provide more relevant support. Imagine a customer service agent receiving real-time purchase history while chatting with a customer, enabling them to offer personalized recommendations or troubleshoot issues more effectively.
- Fraud Detection and Risk Management: Real-time analysis of financial transactions can help identify fraudulent activities in real-time, minimizing financial losses. Similarly, real-time sensor data from critical infrastructure can be used to predict and prevent potential failures.
- Dynamic Decision-Making: Real-time insights empower businesses to make informed decisions based on the latest data. Imagine a retailer dynamically adjusting prices based on real-time demand or a stock exchange making investment decisions based on real-time market fluctuations.
Challenges and Considerations
While real-time analytics offers significant benefits, there are challenges to consider. Processing massive amounts of data in real-time requires robust infrastructure and powerful computing resources. Additionally, ensuring data quality and security in a high-velocity environment is crucial.
The Future of Real-time Analytics
The future of real-time analytics is bright. Advancements in technologies like edge computing, AI, and machine learning will further enhance real-time capabilities. We can expect faster processing, improved data quality, and the ability to derive even deeper insights from real-time data streams. This will empower businesses to make truly real-time, data-driven decisions that lead to a significant competitive advantage.
Real-time analytics is a powerful tool that transforms big data applications from historical analysis platforms to real-time decision engines. By embracing real-time analytics, businesses gain the agility and responsiveness needed to thrive in today’s dynamic market landscape.
The Synergy Effect
These trends aren’t isolated advancements; they work together to create a powerful synergy. Imagine AI algorithms analyzing real-time data processed at the edge, providing businesses with immediate, actionable insights. This is the future of big data – a future where businesses can leverage these trends to unlock the true potential of their data and achieve remarkable results.
By embracing these advancements, businesses can:
- Gain a competitive advantage: Make smarter data-driven decisions, optimize operations, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
- Drive innovation: Uncover new opportunities and develop innovative products and services based on real-time customer insights.
- Increase revenue and profitability: Improve operational efficiency, personalize marketing strategies, and optimize pricing for maximum profitability.
- Future-proof their business: Stay ahead of the curve by leveraging the latest advancements in big data analytics.
The future of big data is intelligent, automated, and real-time. By understanding and adopting these trends, businesses can unlock the key to unlocking valuable insights, making informed decisions, and achieving sustainable success in the data-driven era.
Getting Started with Big Data Applications
The world of big data can seem overwhelming at first, but the potential benefits are undeniable. Here are some steps to get you started on your journey towards leveraging big data applications in your business:
- Define Your Goals and Challenges:
- What business problems are you hoping to solve with big data? Identify your specific goals, whether it’s improving customer experience, optimizing marketing campaigns, or streamlining operations.
- What challenges are you currently facing with data management and analysis? Understanding your limitations will help you choose the right big data solutions.
- Assess Your Data Landscape:
- What type of data do you currently collect (customer data, financial data, operational data, etc.)?
- Where is this data stored? Is it siloed in different systems, or is it centralized in a data warehouse?
- What is the quality of your data? Ensure your data is accurate, complete, and consistent for effective analysis.
- Develop a Big Data Strategy:
- Based on your goals and data landscape, develop a roadmap for big data adoption. This might involve investing in new data storage solutions, exploring cloud-based big data tools, or hiring data analytics professionals.
- Consider starting small with a pilot project focused on a specific business challenge. This allows you to test the waters, identify potential hurdles, and refine your approach before a full-scale implementation.
- Prioritize Data Security and Governance:
- Big data comes with big responsibility. Ensure you have robust data security measures in place to protect sensitive customer information.
- Implement data governance policies to ensure data quality, compliance with regulations, and ethical data usage.
- Invest in Your People:
- Building a skilled workforce is crucial for success. Consider training existing employees on big data concepts or hiring data scientists and analysts with the expertise to manage and analyze your data effectively.
- Additional Resources:
- Numerous online courses and tutorials are available to teach you about big data fundamentals, big data tools, and data analysis techniques.
- Industry associations and big data software companies often offer valuable resources, including whitepapers, case studies, and webinars.
Remember, big data adoption is a journey, not a destination. By taking these initial steps, you can position your business to unlock the immense potential of big data and gain a significant competitive edge in the years to come.
Your Move
With such a vital transformative force, you can harness the potential of massive datasets to gain deeper customer insights, optimize operations, and power data-driven decisions for innovation and success. From AI integration to real-time analytics, the future of big data is replete with possibilities.
However, navigating the big data landscape can be complex. Here at Iterators, we understand the challenges and opportunities that big data presents. We offer a comprehensive suite of big data solutions and services, from data strategy consulting to implementation and ongoing support.
If you’re ready to unlock the potential of big data and build a better business, we invite you to partner with Iterators. Let’s work together to transform your data into actionable insights and propel your business towards a data-driven future.

1 Comment
Great post!