Corporate dashboards, IT dashboards, or simply dashboards are standard in modern workplace communication. These single screens of critical information come arranged as panels. Like your car’s dashboard, they offer a comprehensive view of the data and information pertinent to business growth.
The dashboard marketplace offers many tools that support KPI and metrics visualization. Some free options include Dasheroo, Databox, Datapad, FineReport, Google Data Studio, Grafana, Inetsoft, Matomo, and Tableau.
In this guide, we’ll reveal the power of dashboards and everything else you need to use them effectively in your organization.
What is Dashboarding and how does it fit into the realm of Business Intelligence?
A dashboard is a visual representation of organizational data for effective decision-making.
In simple terms, dashboarding is a way to display critical business information. Getting these benchmarks helps to keep track of progress relative to goals. It applies to any aspect of your business or organization and uses visual elements to be more relatable.
Dashboarding software tools support simplified data management. They collect, display, monitor, and visualize business health while providing data-driven insights.
Businesses would often deliberate on whether they need a centralized dashboarding tool. The decision lies in the fact that modern enterprises make critical decisions based on data. The latter comes in massive volumes, with much of it needing to be more obvious.
Therefore, your business’s competitive edge lies in surfacing and exploiting less obvious data points. You may hear folks refer to dashboarding as Business Intelligence dashboarding. That’s because it enables the user to circumvent the difficult task of wading through raw data or curated reports to discover insights quickly and clearly. In turn, they can focus on taking effective action when necessary.
Dashboarding tools are excellent for gleaning, analyzing, and monitoring data from various sources. They also perform key performance indicators (KPI) measurements and save resources in business intelligence (BI) operations. In addition, they present data in an intuitive format, enabling executives to make improved and timely data-backed decisions.
BI Dashboards display the current status of metrics and KPIs. We find consolidated and arranged numbers, metrics, and performance scorecards on a single screen. These may be role-specific and display metrics for a single department or perspective.
A business intelligence dashboard typically includes a customizable interface and lets you get real-time data from multiple sources. The most effective dashboards consolidate critical and actionable data, including KPIs, sales metrics, employee turnover metrics, project metrics, trends and outliers, and everything else we can visualize.
You’ll be surprised at how well dashboarding platforms adapt to business intelligence needs. Besides, the learning curve is less steep.
Why Do You Need Dashboarding and Reporting?
Today’s competitive market has defined analytics as an essential commodity for optimizing decisions. Of course, you need some experience and intuition to make optimized decisions. Yet, analytics remains critical to business success.
To ensure effective and efficient use of data, your management team needs to easily visualize data in a format that makes it easy to glean critical insights.
Business intelligence dashboards and reports combine several data views, highlighting and filtering them to display vital relationships and integrating groups of insights to create a “guided story” to understand why your data appears the way it does.
It helps key stakeholders develop a strategic outlook for their organization. Organizations that find success at leveraging analytics and dashboarding experience gains in efficiency. These businesses also become more competitive in their industries by tapping into a mostly underused resource.
We will now review why organizations are spending more on dashboards and dashboarding.

Access to actionable data
A dashboard enables identifying both positive and negative trends, delayed KPIs, or operational bottlenecks. More importantly, it allows teams to quickly take action when something appears to be going off-course.
Ample time savings
Web-based BI dashboards are a huge convenience. When the underlying data changes, they automatically update.
When a web-based dashboard is available on mobile, as soon as you connect your data source and build your dashboard content, it automatically updates depending on your preferred schedule.
Improved clarity
The idea behind dashboarding is to present data visually or graphically, and it’s different from displaying a non-intuitive list of facts and figures.
As such, a period-over-period line or bar graph of sales is more intuitive than tens of rows of sales totals.
Improved agility
Dashboarding platforms offer simple tools that enable you to visualize and comprehend trends in data. Some offer upwards of 200 chart types, including core maps. They also allow unlimited expansion via extensive customization.
Users may also use an alerts feature for reminders through email, SMS, or push notifications. It’s essential when you have preset the levels of critical metrics.
Better security
As businesses increasingly adopt IT solutions, the security component of their strategy and budget follows suit. Secure web-based dashboarding platforms provide customizable data permissions. You can limit the data from each of your users and safely share new data and insights. It’s preferable to send sensitive information through email.
How Does Dashboarding Help with the Analysis and Visualization of Business Metrics?
The terms “data dashboard” and “data visualization” are pretty standard but different in analytics and reporting. Data visualization presents data in graphic or visual form, making it easier to understand and analyze.
However, data visualization is usually employed to support data dashboarding through standard tools like charts, graphs, and tables. Data dashboards summarize different but related datasets, presenting the corresponding information in a way that’s easy to understand.
Whether you’re an analyst, business leader, marketer, or sales rep, a dashboard helps to make the most of customer metrics and financial information, human resources data, logistics information, manufacturing information, marketing performance, and web analytics.
How to use dashboards to monitor and track KPIs and metrics
Data dashboards aggregate data from various sources to help non-technical folks understand it.
The interactive elements on a data dashboard make it easier to understand critical points, explore areas of interest, and raise questions to clarify concepts and develop insights to make crucial decisions.
A dashboard displays a comprehensive view of data from many sources, and they utilize raw data from these sources through monitoring, measuring, and analyzing relevant areas. More importantly, these metrics are monitored suitably for the viewer’s needs.
Professionals and subject matter experts use dashboards to reveal what matters to executives and other stakeholders. It helps the latter better to appreciate challenges, opportunities, and growth potential and identify opportunities for change.
How to pick crucial metrics and KPIs on a dashboard

A dashboard is a beautiful pool of data. However, only some pieces of data will be equally relevant to everyone. Therefore, knowing how to choose the metrics and KPIs you need to do your work effectively is essential. It isn’t rocket science, however.
Marketing agencies aim to solve the perennial problems of increasing sales revenue or growing customer retention. However, this is only possible if the agency understands the specific audience and users. Let’s see two scenarios to guide you in choosing critical metrics and KPIs for your role.
Customer support
Let’s look at web behavior data, for example. It provides insights into how users interact with your website. The crucial KPIs to track include:
- Average time on page
- Bounce rate
- Pages viewed per session
- Unique website visitors
Sales support
Sales are inevitable in any business. As such, a sales team will pay attention to the following KPIs captured on a dashboard:
- Cost per acquisition
- Gross profit
- Purchase returns
- Sales conversion rate
- Time spent on each purchase
- Total sales
Choosing relevant metrics and KPIs is a mix of science and art that could provide a competitive edge for your business.
What Tools and Technologies Can Be Used to Create and Implement Dashboarding?
Dashboarding software tools simplify data management. They collect, display, and monitor complex data through interactive, customizable dashboards and reports.
When you use a dashboarding tool, consider whether it’ll be compelling enough for your team. Only some dashboard tools are robust enough to meet your business needs, and in many cases, the product might even be overkill for your operations.
Here are five factors to consider when choosing the best dashboard tool for your team:
1. Ease of setup
You need to be able to set up your dashboarding tool quickly and easily. This is a crucial productivity point.
The dashboard software you choose should be easy to set up. Of course, every vendor says their product is easy to set up, yet your team remains the best judge of what an easy setup means for them.
You should choose a tool that enables you to set up dashboards using mouse clicks, which takes only a few minutes. Find out if the tool provides free setup resources, including guides, tutorial videos, and good customer support.
2. Quick dashboard access
Some tools only allow you to access your dashboard sometime after you’ve set it up. Slow loading time or processing of loaded databases are possible reasons for this.
Your ideal dashboard tool gives you instant data visualization capabilities, allowing you to maximize your time for your bottom line. Therefore, your dashboard should be accessible with just one click.
3. Accessible on mobile
Most dashboarding tools offer desktop-only features. However, you’ll need mobile access when you’re away from the office and your desktop computer.
Therefore, your dashboarding tool should offer a mobile application or a mobile-optimized web app.
4. Easy to use for the entire team
Many dashboarding tasks require collaboration. Thus, dashboarding tools with easier learning curves are more likely preferable for teams.
Two things to look out for include how long it’d take and how much training is necessary to use your software.
5. The price
One of the cool parts of exploring dashboarding tools is the pricing question. Even though most devices present a competitive pricing policy, it’s still complicated for the uninitiated.
Some platforms offer a free plan but make users put up with limited features. Others do it somewhat differently, only making full features available for a limited time. This freemium model attracts users long enough to get them hooked, but they’re different from the 100 percent free products.
Yet, other tools like Datapad do not have such complex pricing. They’re entirely free for all users, without any restricting policies.
If you’re trying out a dashboarding product with a free plan or freemium, it’s best to compare them based on your context.
The best dashboarding tools you should use
Now, we present five dashboarding solutions that are excellent choices for individual and enterprise users.
Metabase
Metabase has built a top-quality reputation among open-source BI and data viz tools. It’s excellent at helping users weave relevant stories from data.
Interactive dashboards in Metabase present data in an intuitive format for business stakeholders. They improve the probability of making successful decisions.
Metabase works best for small teams, growing businesses, and big enterprises, and the free plan is most suitable for small teams and startups. Here’s a round-up of Metabase’s features:
- User-friendly UI with an embedded visual query builder that allows advanced users to probe data for hidden insights.
- More than 20 integrated data sources and over 15 built-in visualizations to build eye-popping live charts and dashboards.
- Share dashboards easily using smart links; schedule automated reports through email or Slack for prompt notification; integrate dashboards in web pages, presentations, etc.
- Enable management by role to control how and when anyone can access dashboards.
Pros:
- Quick and easy setup (5 minutes)
- Unlimited dashboards and charts
- Access to friendly forums
- Free community edition remains usable long after trial period
Cons:
- Too dependent on SQL
- No formatting flexibility
Google Data Studio
Sometimes, users want a dashboarding tool that lets them collect raw data from diverse sources. They also want to transform the data into attractive and interactive dashboards and reports. A fantastic means to do both of these is Google Data Studio.
One of the excellent parts of Google Data Studio dashboards is that they’re fully customizable and easy to share with teams and stakeholders.
Google Data Studio is a superb dashboarding tool choice if you want to use data better without the significant overhead or the risk of data mishandling.
Features:
- Extensive dashboards and reports gallery for creating breathtaking visuals quickly and easily.
- More than 800 data sources and 650 connectors to collect and import data from multiple sources with a single click.
- A collection of visualization tools, including the Gantt chart, Gauge, and Waterfall. You can also create custom visualizations.
- Share dashboards and reports with individuals or teams; collaborate in real-time and use simple code snippets to apply reports on a webpage.
Pros:
- Excellent integration with Google’s software ecosystem
- Fine-grained access and sharing mechanisms
- Price is $0 – free forever
Cons:
- No real-time updates
- No support for Microsoft Excel
- May have trouble performing complex visualizations
Microsoft BI
Microsoft’s robust dashboard solution is a popular choice among those using it in business settings. Power BI is available for an affordable $10 per user per month. Bundling it in the Office 365 software suite means it’s inevitable that enterprise users have it.
Regarding functionality, Power BI is a dashboarding heavyweight with convenient advantages for analytics. Therefore, it’s excellent for tracking KPIs and metrics of all descriptions – a key reason many users love it.
Power BI also offers automated artificial intelligence (AI)-powered functionality and machine learning (ML) tools. It can create and analyze visual narratives around text and image data.
Microsoft’s long experience in designing and delivering enterprise software has served it right concerning Power BI dashboarding. Users consider it one of the best dashboarding tools on the market. The user experience is top-notch, and it ships with documentation that supports user training and development in using the software.
Features:
- Sensitivity labels
- It contains privacy and regulatory requirements
- Offers data governance and loss prevention with report sharing
Pros:
- DAX data analytics
- Flexible tiles
- Q&A question box
Cons:
- Bulky user interface
- Hard to customize
- Limited storage on the free version
Tableau
Tableau Public is a free dashboarding platform for organizing, visualizing, and sharing important data with the public. It features an extensive library of data visualization tools that you can use to structure unorganized datasets.
Data professionals, businesses, and tech teams will find Tableau Public valuable. It can help them to make sense of raw data, seek support from the open-source community, and contribute valuable data.
Features:
- Broad application in business, the economy, investing, and sports.
- Faster visualization than other tools with presets and representation libraries for accommodating all sizes of data heaps.
- Active global community to share knowledge and interpret data. The community is free to join, participate and promote in.
- Create seamless interactive charts, graphs, and other representations without knowing the nitty-gritty of coding or plotting.
- Allows easy export and sharing of dashboards in multiple formats, including CSV (comma-separated values), Microsoft Excel, and spreadsheets.
Pros:
- Completely free libraries you can access and use.
- Supports all kinds of data sources, whether online or in local storage.
- Mobile-friendly platform.
- Highly intuitive platform for anyone to use
Cons:
- Storing data publicly means personal security is absent
- Users can only access 10 million records per data source and 10 GB of overall content for every account
Databox
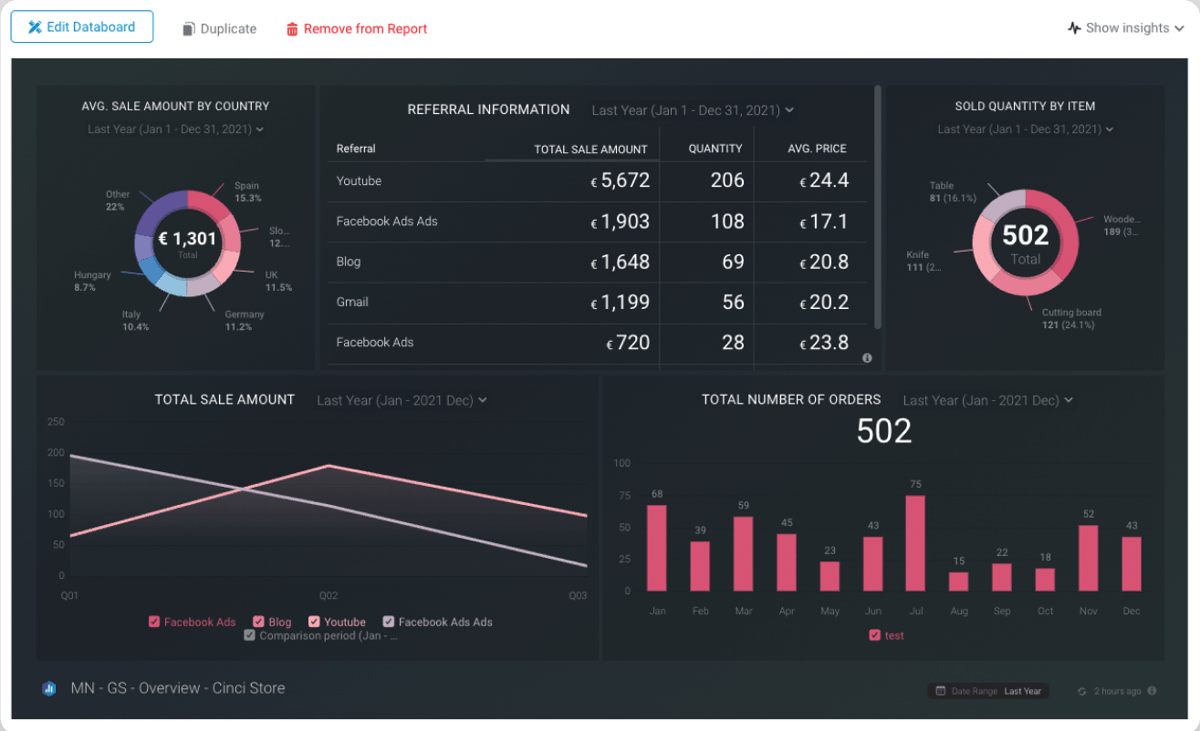
As a top-rated business analytics dashboard, Databox helps you to connect data from any tool, and it also helps in measuring business performance from any location.
Tens of thousands of businesses use Databox to track and visualize their business data and make improved data-powered decisions.
Databox is suitable for analysts and data-driven marketers and equally useful for CEOs and decision-makers. It’s a platform capable of meeting the needs of businesses regardless of their size.
Features:
- Gallery of over 200 proven dashboard and report templates tailored to specific departments. Domain experts build these templates.
- Drag-and-drop interface builder to easily calculate new metrics and create custom ones from multiple data sources.
- Intuitive dashboard designer to support customization and visualization of KPIs without coding or designing anything.
- Automated alerts feature when specific metrics trend up or down from a predefined threshold point. You can also schedule performance reports using email, Slack, and so forth.
- More than 60 one-click integrations to quickly connect data. Users can integrate custom data through APIs, Google Sheets, SQL databases, or Zapier.
Pros:
- Quick and easy setup
- A friendly UI (user interface)
- Ample number of integration
Cons:
- Presents a steep learning curve for beginners
- One limited data source connection and one dashboard for free plan
How to Incorporate Dashboarding in Your Team’s Process

Here are the key steps your team can take to begin dashboarding:
Identify insights that will make you more effective
Every dashboard needs to have only one focus: digital marketing, finance, inventory, project management, ROI, or sales. Before creating dashboards, list your core business measurements and prioritize them.
List out your requirements
Identifying the data that support your key metrics, their location, and how you prefer to visualize them is essential.
Choose the right platform for dashboarding
Many organizations immediately consider Microsoft Excel and other desktop software options when building dashboards. However, web-based [cloud-native] platforms are more comprehensive options.
Cloud-based web dashboards are accessible from anywhere, feature secure sharing, and allow all users to see the most up-to-date dashboard version in real-time. Any trade-offs made in building these platforms sacrifice power and flexibility.
Connect your data
Modern dashboarding tools enable scheduled updates to your data directly from the source. Many offer hundreds of pre-built connectors for the most common business systems.
Secure the data
Depending on your specific business needs, you must implement security options that work for you. The best cloud-native, web-based dashboarding platforms offer appropriate customization options to preserve data integrity and its users.
Build the dashboard
Once your infrastructure is in place, you can take it on a test drive. After building one or two dashboards and becoming comfortable with the process, users can test it and provide you with critical feedback.
If you’re a big enterprise with complex needs, consider engaging a professional firm specializing in implementing dashboarding platforms.
Revise your implementation
After experimenting with various graph types and formats, and collecting user feedback, try to make your dashboard more specific. Ask yourself if there are other metrics you need to visualize. Also, make it easier to understand.
One popular method for making dashboards more interactive and customizable by users is to include variables.
Expand it. Iterate it.
As your dashboard comes alive, you must also answer more questions. For instance, with what you now know about your sales data, what new insight will your marketing dashboard enable you to learn?
This process is highly iterative – as people see the visualization of their data, they start to see and understand more efficient ways to get insights from data. Many customizable capabilities in web-based dashboarding platforms enable users to make dashboards on their own, which helps to reduce the expectations of your IT team significantly.
Benefits of Dashboarding for Your Business

Using business intelligence dashboards can bring about a significant business impact. They support end-users, managers, and decision-makers to take data-led action and find opportunities for business growth.
Understanding how customers interact with your business can help you improve customer service and drive revenue growth beyond a gut feeling, intuition, or copying the competition.
Some other vital ways that dashboarding will benefit your business include:
Dashboarding communicates critical business information quickly
You can quickly and easily access critical data from dashboards. It helps you make informed decisions from the revealed trends and patterns, allocate resources efficiently, and make the appropriate changes accordingly.
Dashboards enable businesses to monitor performance in real time and make the necessary adjustments. It is a reliable hack to stay ahead of the competition and control your growth.
Everyone can access information on time
Dashboard data is rich in insights, but those needing critical information will most likely benefit. Such people can access essential information quickly and easily.
Finance staff, marketing people, and your customers are among the stakeholders who may find dashboard data beneficial. Centralized dashboards allow anyone to access the necessary information, providing actionable insights as and when due.
Data-driven decisions create a data culture
Dashboards help everyone to make data-driven decisions. Doing this long enough creates a data culture, and data points can help businesses to make informed decisions.
Understanding what’s going on in data makes it easier to make strategic decisions and optimize your operations.
BI dashboard reports make it possible to identify where more input is necessary and identify potential risks. It helps you optimize your business for growth and stay ahead of the competition.
Improved precision in forecasting
Applying predictive modeling and other forecasting methods ensures that your business is future-proof.
BI dashboards save you resources, making you more responsive than reactive when unexpected events may affect the business. You have a summary of your most important reports and business metrics.
Self-service BI platforms can help in automating forecasting processes. It lets you focus on crucial business tasks while accessing data quickly.
Better than traditional charts and reports
In business intelligence and data analytics, dashboard and reports are often mistaken to be the same. They are both tools to present operational data visually for data-based decision-making. However, they have telling differences.
- Purpose: A dashboard provides a visual overview of business-critical data on one screen, while a report is a static snapshot of business performance at a specific time.
- Design: Dashboard information is available in one screen pane, while a report is as brief or detailed as necessary. Reports may connect to dashboards.
- Interactivity: Dashboards are web-based, whereas reports may be available online or offline (PDF). Dashboard users can click on metrics for dynamic behavior, while reports only contain what they have when created.
- Granularity: Dashboards offer a broad summary of data in visualization and tables, and reports, on the other hand, may only feature a data set segment. Therefore, dashboards are better for a summary performance overview, while reports provide more detail per focus.
- Timeliness: Dashboard data is updated live so that you can trace real-time performance. Reports are static snapshots, so they don’t offer a reflection of dynamic data. So, dashboards work better for constant monitoring and tracking of data.
Examples of Companies Using Dashboarding to Improve Performance
As companies increasingly embrace digital transformation, dashboarding has become a dependable tool for fine-tuning business processes for efficiency and profit. A few examples of companies that have used dashboarding to achieve repeatable outcomes are as follows:
Case study #1 – Intenda
Multinational software enterprise, Intends, operates in the UK, EU, USA, and South Africa. It provides data consulting services and custom data solutions development services to clients. It also maintains a flagship product, Fraxses, a distributed data platform.
Intenda’s customer base cuts across several industries: banking, health, insurance, logistics, medical, retail, and even the public sector.
Earlier versions of Fraxses featured a data visualization module that allowed users to connect to third-party BI tools, but this needed more functionality. Building Fraxses as the total package for all data needs was important. It meant embedding an analytics module offering actionable insights and enabling users to visualize and interact with data.
To make this happen, Intends partnered with a BI software vendor to include contextual analytics in its product. Embedded reports and dashboards become part of the application’s workflow at this embedded analytics maturity curve level.
Therefore, without leaving the software, the user can capture data, analyze data, and update dashboards and visualizations automatically. Despite what’s happening under the hood, the application looks like a single component to the user, effectively creating a BI ecosystem in which data is meaningful and actionable.
Case study #2 – the telecommunications industry
Few industries are more dynamic than telecommunications. New technologies, competitors, changing economic conditions, regulations, and ever-shifting consumer sentiment are perennial factors that affect the business.
However, the adoption of new and disruptive technology, competitive pricing, and a challenging business environment means there’s a need for cost-effective and highly scalable business intelligence tools to control and analyze spending and investment.
One company, Yellowfin, offers personalized dashboards that enable companies to build a competitive advantage in the telecommunications industry. The solution has helped AT&T, Celcom, Sensis, Vodafone, and Telstra, among others, to monitor, track, analyze, and manage vital metric scopes captured in the chart below:
| Metrics Scope | Details |
| Customer relationship management | – Customer affinity – Customer attrition and churn rates – Customer lifetime value – Customer relationship management – Multi-channel customer engagement – Real-time call trends and dynamics |
| Finance and asset management | – Product profitability analysis – Services profitability analysis – Asset liability management – Billing Reporting – Budgeting – Actual performance and forecast performance – Statutory reporting |
| Human resources management | – Performance and benchmarking – Attrition and absenteeism – Training and workforce allocation |
| Marketing | – Customer segmentation – Campaign analytics – Identifying cross-sell opportunities – Marketing effectiveness and revenue |
| Operations and budgets | – Development of a unified view of revenues and expenses – Targeted performance and budget analysis – Network performance – Revenue performance – Loss Prevention |
| Product development | – Service design and delivery – Service usage and charging – Service fulfillment |
Dashboards have become indispensable in the telecommunications industry.
Case study #3 – BGL Life achieves complete performance visibility and improvements
BGL Life offers life insurance through brands such as Beagle Street, Budget Insurance, Dial Direct, and FiftyLife. The company also sells white-labeled insurance solutions.
While BGL had its enterprise data warehouse (EDW) solution to collect information from various systems, it needed to be more agile since daily data extraction took two hours to deliver the Management Information (MI) the company needed.
Deploying a dashboard allowed BGL to have end-to-end performance visibility. They can pick up issues immediately, work into the details, and make changes instead of waiting until you do a complete manual analysis.
BGL Life’s affinity partners have found this dashboard-based service to be an invaluable benefit.
There’s massive potential in using dashboards for all types of businesses.
What are the Most Common Dashboard Mistakes That You Should Avoid?
While we’ve established that dashboards benefit businesses in all industries, it’s important to highlight common mistakes companies make when implementing dashboarding solutions.
- Not keeping it simple – using different colors and styles – can clutter and overwhelm your dashboard.
- Not choosing appropriate visualization options. It may not represent your data best, and you may include too much information.
- Not double-checking data will leave you with messy data that makes your insights and solutions wrong.
- Using irrelevant data that may not be relevant to your audience and overwhelm them.
- Not defining your audience and goals at the outset might lead you to build solutions your audience does not understand. You’ll also not be able to offer adequate answers to their questions.
- Not using templates to save time or using one that doesn’t work with the data you have.
- Not iterating and improving your dashboard regularly. A rapidly evolving business environment means you need specific feedback all the time from stakeholders, and such feedback helps to improve the dashboard, insights, and decisions from it.
Conclusion
Data is a goldmine of significant value for any enterprise. Data dashboarding initiatives can help by making the inherent value accessible to business users whose responsibility is to make the organization succeed.
Dashboarding offers a business’s key information and trends in an easily accessible and digestible format. It ensures that no one worries about studying data, and a greater focus is on taking action.
