The relationship between corporations and innovation is an important one.
On one hand, corporations need innovation to stay relevant and keep the competitive edge.
On the other hand, innovation needs funding and resources to grow and become a functional standard.
Between these two interests lies a whole spectrum of potential conflicts and immense potential for cooperation and symbiosis.
When the relationship is good – it brings significant benefits to all parties involved.
When it’s bad – it can be a source of financial failure and public embarrassment.
Without a doubt, the stakes are high.
So how does one leverage the value of innovation in a corporate setting and live to tell about it?
The Corporate Innovation Handbook series aims to answer that question and many more.
In this article you’ll find useful information about:
- Why innovation is the future of corporations
- The current landscape of corporate innovation
- Technologies behind corporate innovation
- Reasons behind corporate innovation initiatives failing
- Common strategies for corporate innovation implementation
At Iterators, we know firsthand what successful corporate innovation looks like. We designed, built, and maintained custom software solutions for both startups and enterprise businesses.

Schedule a free consultation with Iterators today! We’d be happy to help you design and build your innovative product.
Why Innovation Is the Future of Corporations
Let’s start with some hard facts.
Harvard Business Review reports that since 2000, 52% of enterprises in the Fortune 500 “have either gone bankrupt, been acquired, or ceased to exist” due to digital transformation.
On top of that HBR anticipates that 75% of S&P companies will be replaced by 2027.
Corporate innovation isn’t a voluntary investment anymore. It’s a necessity.
How so?
Most corporations are built around a unique set of products. That’s why at a certain point, they reach a point of saturation, where their product line has been upgraded/extended to the maximum. The profit margins stop growing so dynamically. When they reach that moment, they need to innovate to keep growing.
Corporate innovation has become the price of longevity – if you don’t disrupt your own business and get in front of the competition, someone else will likely overtake you.
Imagine corporations are like the giant passenger ships in the early 1900s, and start-ups are the icebergs – technological disruption can come out of nowhere and upturn whole industries.
We can see it happening all time, for example:
- Taxi vs Uber – the Taxi business got upturned completely by on-demand apps like Uber, Lyft, and car sharing applications like Sixt or Car2go which forced the change of an entire industry.
- Cell phones vs Smartphones – iPhone completely dominated the mobile phone industry, effectively rendering usual cell phones irrelevant. Industry leaders like Nokia missed the beat on the big transformation and eventually got pushed back and overtaken.
- Streaming Platforms vs TV – The rise of the streaming platforms is a topic that deserves a separate article or 10, but the point is – Netflix, Youtube, Hulu are now the most common way to get your entertainment and information. Youtube channels with millions of subscribers have more views than huge media moguls like Fox News.
Summarizing, because of their size, corporations require more time for an organizational shift and are slower to adapt, due to their size. Start-ups, on the other hand, are way more agile, and quicker to adjust but are limited in terms of resources.
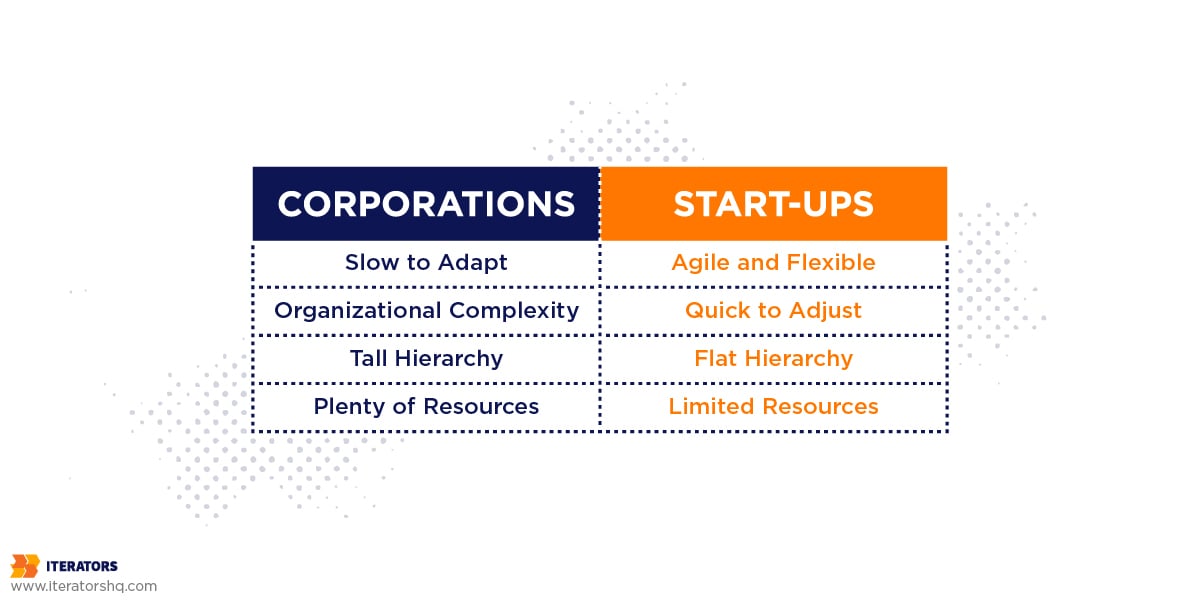
There is a clear potential for cooperation between start-ups and corporations and the common denominator is innovation.
That’s why corporate innovation is the only way forward for huge enterprises and frequently start-ups play a big part in making that transformation happen.
But let’s stop here for a moment and define what corporate innovation actually is.
What is Corporate Innovation?
Corporate innovation is the process of introducing new technological solutions to the already existing business structure. This process usually involves working with start-ups, creating accelerator programs, and funding internal innovation projects. We can distinguish product innovation, division innovation, and business model innovation.
- Product Innovation refers to upgrading your product portfolio by developing a new product or upgrading an existing one. It can happen through emerging technologies like: AI, blockchain, machine learning, or nanotechnology.
- Process Innovation refers to the optimization of different business processes through the implementation of new equipment and technology during the development stage. This type of innovation, albeit not visible to the customers, can significantly increase productivity and reduce costs.
- Business Model Innovation refers to an improvement of the core business strategy and the way a product or service is presented to the market. This is the most challenging type of innovation, as it can upturn and transform both the product and processes behind it.

Knowing there are many corporate innovation approaches and many areas to innovate – how do you choose the one that fits you best?
After all, every company offers a product or a service, and all of them have their processes and business models.
So can you innovate it all?
Not advisable. If you’re a big company, you have to choose your battles. Due to organizational complexity changing your business model or even innovating, your product can be a big challenge.
That’s probably why process innovation is often the easiest choice for corporations willing to stick to their will to innovate. It is considerably less risky and less expensive to innovate a process within your business structure than to upturn your main product or a business model.
The Importance of Corporate Innovation
As mentioned above, corporate innovation is of paramount importance and frequently – the only way forward for giant enterprises.
NFTS are already radically transforming the advertising industry and helping turn large corporates’ customers into fans. They change the incentive structure in profound ways as they bring the customer on an exciting and engaging journey. Instead of being forced to watch something consumers are being given something they can actually use. Brands such as Budweiser, Burger King, Coke, Disney, Visa, Verizon, and the NBA, are already experimenting with this new asset class.
But let’s leave the threats of business fiasco behind for a moment and focus on the positives. Corporate innovation may be a necessity, but if done right, it can be a good thing that brings meaningful change. Not only to those who govern the enterprises but also to society as a whole.
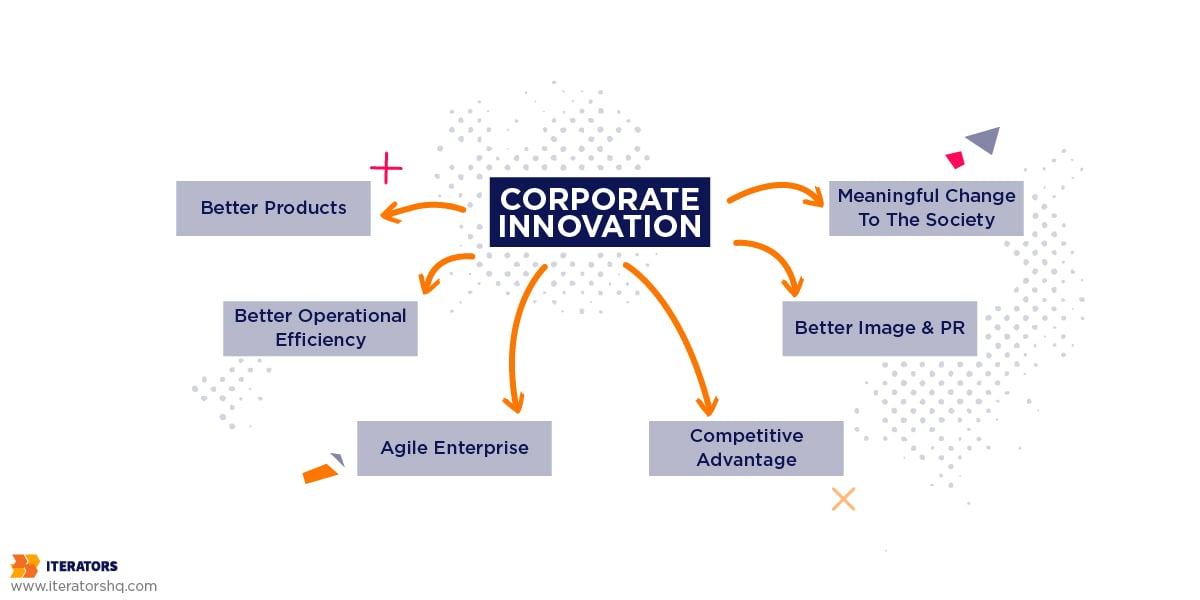
Let’s take a look at the range of potential benefits that corporate innovation programs bring to the table.
Benefits of Corporate Innovation
- Better Products. Corporate innovation often results in products that are better suited to the evolving business environment and ever-changing needs of the customers. One could even argue that truly innovative products should anticipate the needs that are not yet apparent.
- Better Operational Efficiency. Corporate innovation that is focused on process optimization can boost your bottom line in a significant way. Many processes can be optimized through digital transformation, and we can see it happening across all kinds of industries. Better productivity and reduced costs are some of the direct results of that change.
- Agile Enterprise. Investing in corporate innovation is investing in out-of-the-box strategies related to all facets of your business. Companies that managed to develop an innovation culture have better chances to adapt to unusual and unpredictable circumstances.
- Competitive Advantage. One of the biggest benefits of being truly innovative is that you’re the first one to leverage it. The history of corporate innovation shows that the companies that stayed on top of the innovation trends gained a huge edge over their competitors.
- Better Image & PR. As mentioned above, everybody wants to look innovative, and “innovation” has gotta be the buzzword of the decade. Still, those who can genuinely innovate can share their success with a pure conscience and reap the PR benefits. In this day and age, this can translate to better sales, etc.
- Meaningful change to society. Enacting change can be the most significant benefit that corporate innovation brings to all of us. Let’s think about all the inventions that came out of that: electric cars, smartphones, social media, and countless smaller improvements to our life. While one could argue the ethical limitations of those inventions, they sure made our lives easier in many regards.
How Does Corporate Innovation Happen
Corporate innovation is a fluid process that can come to fruition in many ways. As enticing as certain business ideas can be, they may not always be a good fit for your corporate innovation strategy.
In 2015, Forbes published a list of nine rules that businesses should follow to be successful. One of these is that innovation is a process, not a single event. Instead, it should be a series of questions that are designed to help a company identify its ideal solution and transform its industry.
Let’s take a look at an innovation business success story from a well-known company that used innovation challenges to come up with groundbreaking products that we still use today.
For over a century, 3M has been a well-known manufacturer of various products and services. One of its most innovative stories is the story of Richard Drew, an engineer who joined the company in 1921. During his time with MMM, he visited the local auto shops to test different types of sandpaper. He learned that one of the most common problems with the two-tone paint job was the use of homemade glue and newspapers.
After noticing that 3M’s sandpaper was made with a sticky surface, he started creating his product. He then learned that he could make a tape that could stick to its surface and peel off easily. In two years, he had created a tape that was very durable and didn’t damage the paint.
After his boss rejected his idea, Drew invested in and built a machine that was capable of mass production. His hard work and dedication resulted in him being rewarded by his superiors at 3M. His product, which was known as “Scotch Masking Tape,” immediately changed the way painters did their jobs.
NFTs can also help companies gamify their interaction with customers. For example, Burger King. launched an NFT-based sweepstakes around their BK Keep It Real Meals. The promotion is designed and supported by NFT marketplace and brand activation startup Sweet with a focus on experience and easy adoption of the technology. Customers order one of three Keep It Real Meals curated by pop artists Nelly, Anitta and LILHUDDY. They scan the QR code on the meal box with their phone, download the Sweet app, and receive a collectible NFT game piece. Every 12 hours they can scan the box again to receive a new game piece, keeping the participants glued to the game.
Many companies create dedicated innovation teams internally to deal with the challenges of that process. Their job involves reviewing investment opportunities within the startup community as well as conducting proof of concepts (POCs) and pilot programs with the most promising businesses.
This stage can be very telling to both sides. Startups get the necessary resources to grow while corporations get to see if the developed solutions are financially viable and able to meet the market demands.
That said, the process behind corporate innovation may not always look the same, as it relies heavily on the corporate strategy and how far along the development of the project is.
So let’s explore the spectrum of different corporate innovation models.
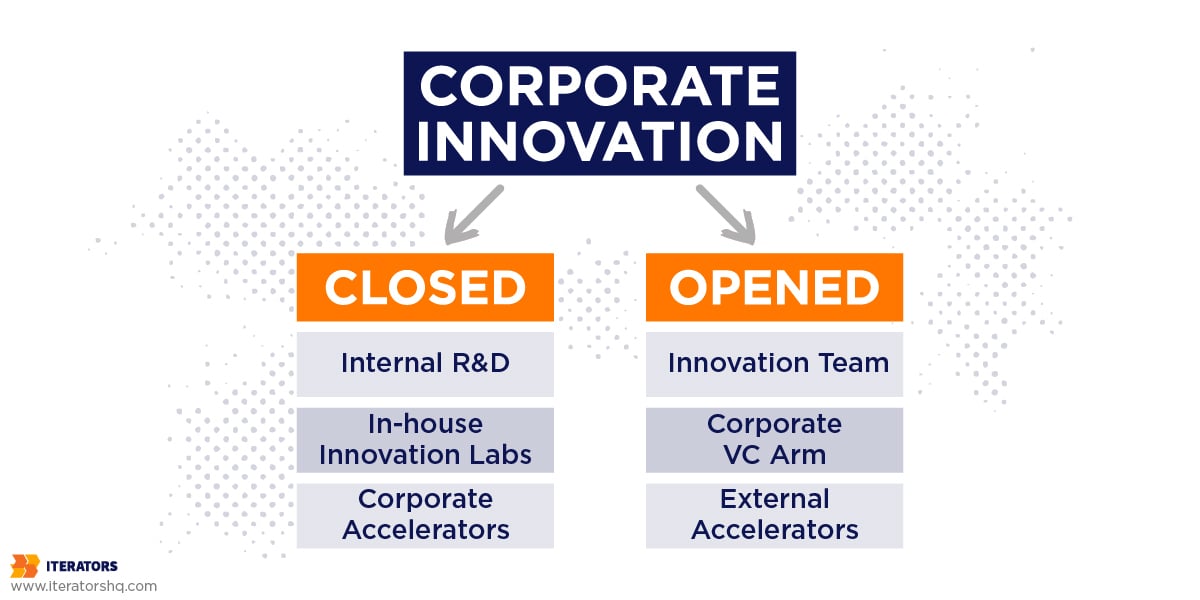
Closed Innovation
Closed innovation is a corporate innovation strategy that involves looking for new solutions internally. For any number of reasons, corporations may prefer to keep their innovation hidden from public scrutiny. After all, potential failure can generate fear among the shareholders, which can be very costly.
Here are some of the models that enterprises turn to when they want to keep their innovation private.
Internal R&D
Internal Research & Development programs have long been a way of funding corporate innovation. This classic method is often preferred by corporate executives as it seems less risky and keeps things close to home. It does require a significant amount of capital to start, though.
The way this works is company selects intrapreneurs internally and their job is to find ideas for improvement by running R&D programs. They’re given resources and often even allowed to launch startups within the company.
Corporate Innovation Labs
Corporate innovation labs are an elaboration on the internal R&D programs. Corporations fund in-house facilities to encourage an innovation culture and create a space for their employees to experiment and try out their ideas.
One such program is Ikea’s Space10 – a research hub and exhibition space built in Copenhagen. The lab collaborates with people from different backgrounds, featuring not only tech experts but also artists and designers. They work on research projects that result in product prototypes, exhibitions, and workshops. Space10 concentrates on sustainability and future innovation related to everything from urban planning to food security.
Corporate Accelerators
Accelerators are a common way of stimulating corporate innovation while boosting a young business at the same time. It’s different from the two previous methods because it involves bringing people from the outside into your corporate structure.
Big companies like Google, Coca-Cola, Budweiser, and AT&T are known for their corporate accelerators, which are funding innovation that revolves around their own business challenges and objectives. It is particularly beneficial for corporations as they can pick the startups that will be a good fit for future cooperation while maintaining a lot of control and leverage over them.

Open Innovation
Open innovation is a corporate innovation strategy that relies on external influence to find creative and fresh solutions for your business.
This strategy is gaining traction, as it is often less costly than R&D programs and corporate accelerators. It is a more risk-oriented strategy, though, as it is often based on “gut feeling” and trust in a particular idea.
Even big enterprises focused on internal innovation can leverage outsourcing and work closely with software development companies. Corporate intrapreneurs appreciate the expertise and value the cooperation of companies like Iterators, which have plenty of experience developing innovative products.
The only potential downside for companies that engage in open innovation is less control over the businesses they choose to fund, as they are outside of their corporate structure.
External Accelerator
Corporate innovation fostered in an external accelerator is preferred by most startups, as it doesn’t limit their options to one company. At the same time, they get to meet and network with VCs, entrepreneurs, and many other industry professionals who are keeping tabs on what’s happening in the accelerator.
One of the most significant advantages of external accelerators is the cost and ease of the investment combined with relatively low risk. Corporations that invest in startups that way don’t need to fund the whole program; instead, they choose their level of engagement in exchange for a say in the direction of their development.
Innovation Outpost
It’s no secret that certain industries are focused in specific areas of the globe – for example, Berlin, Stockholm, and Copenhagen are the startup centers of Europe. At the same time, cities like Frankfurt and London are notorious for their financial focus.
If your company is on the other side of the globe – it might be a good idea to invest in an innovation outpost based in a region that is prominent in your market. Many companies assemble dedicated innovation teams that are investigating the latest developments in their respective industries. Such teams can be sent out to form innovation outposts in many locations to harvest information and network with up-and-coming businesses.
Corporate VC Arm
Instead of building corporate innovation programs from the ground up, many corporations decide to buy or invest in startups through their venture capital funds. Eventually, corporations make a portfolio of young and innovative companies they believe in. Another good reason for using the acquisition strategy is the competition aspect – if Facebook didn’t buy Instagram, they would’ve been in direct competition.
Venture capital resembles stock trading, in the sense that it’s the riskiest strategy, but the reward can be huge as well. Let us remind you of the story of Peter Thiel, who bought 10% of Facebook for $500,000 back in 2004. Needless to say, he turned that money around big time when he sold the shares for the joined sum of over a billion dollars in the following years.

Corporate Innovation: Current Landscape
The approach to corporate innovation can be grouped into three categories.
- Don’t care about innovation.
- Care about looking innovative.
- Actually, care about innovation.
It is worth noting that corporate innovation also carries a lot of PR value. Many companies strive to be innovative. But successful innovation requires a lot of commitment. So eventually, the end goal might get lost somewhere along the way and what’s left is an “innovative” image and massive R&D expenditure.
Lack of commitment to a coherent innovation strategy is one of the worst enemies of corporate innovation, which is visible in BCG’s annual report stating that only 45% of the companies “walk the walk” by prioritizing and investing in innovation.
So which companies stick to their will to innovate?
Which companies are continuously at the forefront of corporate innovation?
Let’s see.

According to BCG’s reports, in the last 14 years, only 8 companies have regularly appeared in the Innovation Top 50 rankings.
Those companies are Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, HP, IBM, Microsoft, Samsung, and Toyota.
What does that mean?
That serial innovation is hard and requires a long-term commitment. And that those who do commit get to reap the rewards.
Those conclusions are also reflected in BCG’s publication – “Almost 60% of (committed innovators) report generating a rising proportion of sales from products and services launched in the past three years, compared with only 30% of the skeptics and 47% of the confused.”
Technologies Behind Corporate Innovation
Ideas are important, but frequently innovation is a result of developments in the field of technology. New technologies open doors for the improvement of products, and processes and even bring about new services.
So what are the technologies that help to shape corporate innovation programs these days?
Let’s take a look at the most prominent ones, along with some examples.
Artificial Intelligence
AI is already notorious for disrupting many industries all across the world. It is worth noting that many of these solutions are in fact machine learning techniques based on artificial neural networks.
An example of such corporate innovation is Schwartz AI – an intelligent accounting solution developed by Iterators.
The system’s goal was to help automate operations such as data validation, description, and posting of the invoices. For example, Schwartz AI uses a system of smart templates to automatically extract data from invoices. Schwartz AI also uses historical data to improve itself – the more invoices go through the system, the better AI becomes.
Results?
Increased efficiency and digitization of invoicing.

Want to know more about how AI can help your business? Read our article: 4 Amazing Ways AI Personal Assistants Can Impact Your Business
Big Data
The impact of big data technologies on innovation across multiple industries can not be overstated. These days, even mid-sized companies can leverage the insights from the processed data, let alone huge corporations. That’s why big data has become a cornerstone for countless innovation models, and it continues to be one of the most important areas of development.
How does big data contribute to facilitating corporate innovation?
Let’s take the manufacturing industry, for example.
Big data technologies enable something called predictive maintenance – a method of using sensor data to estimate the level of equipment degradation over time. Proper analysis of the data allows you to predict when the machine will become less effective and/or break down.
Shell uses predictive maintenance to boost the reliability of its equipment and increase the longevity of its assets. That results in lower operational expenses and reduced environmental risks—the healthier the machinery, the lower the chances of a breakdown.
Want to know more about big data technologies and their business impacts? Make sure you check out our articles: Big Data and Its Business Impacts (+8 Examples) and 7 Big Data Technologies Essential for Optimizing Your Business.
Blockchain
You’d be hard-pressed to find a more exciting and innovative technology than blockchain. Besides being the foundational technology behind cryptocurrencies, blockchain is slowly getting through to other industries, offering innovation in security, digital ownership, and finance.
One of the coolest examples of using blockchain to stimulate corporate innovation can be found in the gaming industry. Games like Decentraland are revolutionizing the experience by creating a fully decentralized world where you can truly own your digital assets and trade them with other players. And it’s not only the “small fish” in the pond that are experimenting with those concepts. Big league gaming companies are also taking notice – just recently, Ubisoft has come out looking for blockchain-based start-ups to support.
NFTs provide significant opportunities for gaming, thanks to the ownership opportunities they introduce. While people spend billions of dollars on digital gaming assets, like buying “skins” or outfits in Fortnite, the consumers do not necessarily own these assets. NFTS allow gamers playing crypto-based games to own assets, port them out of the game and sell the assets elsewhere, such as an open marketplace
Interested in finding out more about blockchain and its applications? Check out our elaborations on the topic: 5 Steps to Unlocking the Value of Blockchain Applications, Blockchain Games: Take Your Game to the Next Level.
Recommender Systems
Another disruptive solution finding its way into many corporate innovation models is recommender systems. A technology built due to the developments in the aforementioned field of big data helps to pinpoint accurate user preferences. That, in turn, allows you to recommend
The most notorious use cases for recommender systems are the entertainment giants like Youtube or Netflix. But this technology isn’t exclusive to those massive media behemoths. It can be universally applied as an innovative solution to boost sales and engagement in a retail environment.
Want to know more about recommender systems? We got you covered – check out An Introduction to Recommender Systems (+9 Easy Examples).
Problems: Reasons Why Most Corporate Innovation Initiatives Fail
The failure rates among startups and corporate innovation initiatives are brutal.
72% of new products and services fail.
So to say that getting a business idea off the ground is difficult is a major understatement. Even with corporate funding, all the necessary resources, and a good business plan, many corporate innovations are still going to fail.
And because it is something inherently human to be interested in fails – here are a few notorious examples:

1. Kodak. The Kodak fiasco was more than just a flop. It was caused by a deliberate ignorance of the company’s management, who wasn’t willing to take a chance on a technology developed by their own engineer. Ironically, that same technology became its demise when digital cameras took over in the 90s and 00s. Even though Kodak tried to change, by then, it was already too late.

2. Google + was a social media platform developed by Google that was supposed to rival Facebook. The platform debuted in 2011, and despite an initial surge of users, Google+ never really took off, as it didn’t really offer anything more than Facebook already had. As a result, in April 2019 Google+ project was shut down for good.
3. Facebook Home. Another example of a Silicon Valley giant overreaching in terms of corporate innovation was the story of Facebook Home. A mobile app that would attempt to turn the vacant space of the home screen into a news feed. The idea came about in 2013 and never really caught on, as users were mostly confused by the functionality of the app. Some of them understandably found it creepy and intrusive. Subsequently, Facebook Home disappeared from the App store less than a year after its release.

4. Windows Phone. This product was Microsoft’s late entry into the smartphone scene. Windows Phone was launched in 2010, long after the market’s initial domination by Apple’s iPhone in 2007 and over two years after the first Android phones. To no surprise, Microsoft wasn’t able to turn the tables, and their product never attracted more than 1% of the smartphone market. The result? Microsoft discontinued the development of the Windows Phone in 2017.
And this is only the tip of the proverbial iceberg.
Ok, so why is this happening?
Why do so many corporate innovation programs, even those developed by successful and resourceful tech giants, fail?
Let’s take a look at some of the main reasons behind corporate initiatives failing.
Innovation For The Sake of Innovating
Many corporations fancy themselves as innovative. But if you look close enough, they don’t have a solid innovation strategy. They’re just spending huge amounts of money to fund R&D programs that are going nowhere, only to maintain an image of an innovative company. They care more about public perception than actual solutions, so you could argue their innovation strategy is just an overly expensive PR stunt.
Only Investing in Core Business
Since corporations are usually built around a unique product, they’re reluctant to invest in anything that’s not in direct relation to it. The problem is, sometimes corporations need to rethink and reassess their products entirely to keep up with the times. There is a difference between being reasonable and shortsighted when it comes to corporate innovation. And sometimes that difference can cost a fortune.
Lack of Executive Support
Working in a corporate structure can be confusing and frustrating because there are bosses on bosses, on bosses. Transferring information up and down the corporate chain of command can lead to misunderstandings and missed opportunities. And let’s face it – getting all the execs on board is just as hard as it is crucial for the success of any corporate innovation initiative. After all, nobody wants their program canceled after some minor setbacks, and if you lack the executive support – it may very well happen.
Insufficient Customer Validation
As the great Mike Tyson once said: “Everybody got a plan until they get punched in the face.” And that very much applies to corporate innovation as well.
You can have the support of executives, enough funding and resources, and even a great idea. But the one thing that verifies whether your product will be a success or not is the customer. Customers are the final test.
And that’s also why many initiatives fail – innovators sometimes believe in their idea so much, they don’t question it enough. And then the reality hits, the product flops, and it’s all because the customer validation phase was overlooked.
Timing
If there is one clear lesson from the history of corporate innovation programs, it is that timing is everything. Timing can make or break a project.
Many successful businesses like Uber or Airbnb were timed perfectly, synchronizing technological possibilities with macroeconomic factors.
On the other hand, many products failed because of poor timing. Take Kodak or Nokia, which waited too long to change, or Google Glass which came way ahead of its time. That’s why the rollout of a corporate innovation initiative should always be timed in a way that satisfies the demands of the market or even creates them.

Solutions: How to Facilitate Succesful Corporate Innovation
Fortunately, not all corporate innovation programs fail. And when they succeed – it’s usually both beautiful and spectacular.
So how do you increase the chances of your solution succeeding?
Here are some of the standard practices that will help you mitigate the risks of failure and hopefully get your innovation out there safely.
- Develop a clear strategy. As cliché as it sounds, this point can not be overstated. Make sure you have a clear vision of approaching innovation within your business structure. This includes building a solid business plan around your idea and estimation of financing and resources needed.
- Get executive support. If corporate innovation is to be successful, you need to have the support of the higher-ups. The execs need to sign off on the strategy and have trust in the team and the process. Otherwise, you might end up as a victim of politics and power play between the management.
- Make sure the investment criteria are transparent. Criteria for engaging in corporate innovation programs should be transparent, so again, make sure you’re on the same page with all the decisive people in your company.
- Build a dedicated team. Depending on the strategy, you might have to either hire a whole group of dedicated employees or reassign them from different departments. Even if you decide you’re only funding start-ups with a VC arm, you’re still going to need a team of people who supervise the investment. So make sure you choose the right people.
- Invest in customer validation. The decision-making process needs to include the phase of customer validation – to put it simply – to make sure the product you’re innovating has some traction among its potential users. You don’t want to lose millions of dollars developing a dud nobody is interested in.
- Don’t be afraid of the risk. It might be counterintuitive for many people working in corporate structures, but those who don’t risk don’t reap the rewards. And this rings very true in the corporate innovation community. Of course, risk should still be calculated and within specific confines. High-performing companies invest in disruptive but risky projects and are not afraid to move on to something first.
- Build an Innovation Culture. Building corporate innovation culture may be the biggest challenge, as it requires an organizational shift and dedication to the cause. It doesn’t happen overnight either, and you have to be patient and prepared to face many obstacles along the way. However, once a company develops a solid innovation infrastructure, and culture behind it – it is bound to succeed.

Conclusion
Corporate innovation is a complex process that is full of hardships and uncertainties. It requires a great business plan, a dedicated team, perfect timing, and most importantly, a vision. Assuming you already have the support of the executives and enough resources to even start it.
That’s why it’s crucial to make sure you’ve crossed all the t’s and dotted all the i’s before initiating the whole process.
Great innovation can happen anywhere, and if there is one place with all the means and reasons to make it happen – it is a big enterprise.
