In today’s fast-paced business world, keeping a finger on the pulse of your company’s performance is crucial. Have you ever found yourself wondering how to gauge your business’s success or identify areas needing improvement? This is where tracking metrics come into play.
Metrics are quantifiable measures used to track and assess the status of specific business processes. By systematically measuring and analyzing data, companies can make informed decisions that drive growth and efficiency.
What are Tracking Metrics
Tracking metrics are the lifeblood of any data-driven organization. They are quantifiable measures that help businesses monitor the performance and effectiveness of various activities and processes. Metrics can range from financial figures, such as revenue and profit margins, to operational indicators, like customer satisfaction and employee productivity. The goal is to translate complex data into understandable insights, enabling businesses to make strategic decisions based on empirical evidence.
Imagine you’re steering a ship. Without navigational tools, you’d be sailing blind, unsure if you’re on the right course. Similarly, without tracking metrics, a business operates in the dark, lacking the necessary insights to guide its strategic direction. By implementing a robust metrics tracking system, companies can navigate their path more effectively, identify trends, and respond proactively to changing conditions.
To provide a solid foundation for understanding the importance of tracking metrics, her are some examples:
- Financial Metrics
- Gross Merchandise Value (GMV): The total value of goods sold through an e-commerce platform.
- Average Order Value (AOV): The average amount spent per order.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Operational Metrics
- Website Traffic: The number of visitors to an e-commerce website.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of website visitors who make a purchase.
- Cart Abandonment Rate: The percentage of customers who add items to their cart but don’t complete the purchase.
- Customer Metrics
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): The total revenue a customer generates over their lifetime.
- Repeat Purchase Rate: The percentage of customers who make multiple purchases.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): A customer satisfaction metric based on recommendations.
- Employee Metrics
- Employee Engagement: Measured through surveys or pulse checks.
- Absenteeism Rate: The percentage of time employees are absent from work.
- Time to Fill: The average time it takes to fill a vacant position.
- Project Management Metrics
- On-Time Delivery Rate: The percentage of projects completed on schedule.
- Budget Variance: The difference between the planned and actual project budget.
- Project Success Rate: The percentage of projects that meet or exceed their objectives.
- Product Development Metrics
- Time to Market: The time it takes to bring a new product to market.
- Product Adoption Rate: The percentage of the target market that adopts a new product.
- Customer Feedback: Collected through surveys or product reviews.
- Product Metrics
- Product Page Views: The number of times a product page is viewed.
- Product Add-to-Cart Rate: The percentage of product page views that result in an add-to-cart action.
- Product Return Rate: The percentage of products returned by customers.
- Marketing Metrics
- Email Open Rate: The percentage of emails that are opened.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of email recipients who click on a link.
- Social Media Engagement: The number of likes, shares, and comments on social media posts.
- Shipping and Logistics Metrics
- Order Fulfillment Time: The average time it takes to ship an order.
- On-Time Delivery Rate: The percentage of orders delivered on time.
- Shipping Costs: The cost of shipping orders.
Importance of Tracking Metrics
But, why are tracking metrics so essential? Let’s break it down:
- Informed Decision-Making: Metrics provide the hard data needed to make informed business decisions. Instead of relying on gut feelings or anecdotal evidence, leaders can base their strategies on concrete numbers, reducing risk and increasing the likelihood of success.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous tracking of metrics allows businesses to monitor performance over time. This ongoing surveillance helps in identifying areas where the company excels and spots potential problems before they escalate.
- Goal Setting and Achievement: Metrics are fundamental in setting realistic business goals. They offer a benchmark against which progress can be measured. Whether it’s improving customer retention rates or increasing production efficiency, metrics help in defining what success looks like and tracking the journey toward achieving it.
- Resource Allocation: By understanding which areas of the business are performing well and which are underperforming, companies can allocate resources more effectively. This ensures that time, money, and effort are invested where they can have the greatest impact.
- Transparency and Accountability: Metrics create a culture of transparency and accountability within an organization. When performance metrics are shared across teams, it promotes a sense of ownership and responsibility, driving everyone to contribute toward the company’s objectives.
- Product Development Metrics: For companies focused on innovation and development, these metrics might include the number of new products developed, time to market, and the success rate of new product launches.
Incorporating a variety of tracking metrics ensures that a business can get a comprehensive view of its performance. Each type of metric provides unique insights, contributing to a holistic understanding of the company’s strengths and areas for improvement.
Ready to take your business to the next level with effective metrics tracking? Stay tuned as we dive deeper into setting goals, identifying the right metrics, and implementing a robust tracking system. Tracking metrics isn’t just about collecting data; it’s about transforming that data into actionable insights that drive success. Let’s embark on this journey to make your business more informed, efficient, and competitive.
Need help implementing Tracking Metrics into your business? The Iterators team can help design, build, and maintain custom software solutions for both startups and enterprise businesses.
Schedule a free consultation with Iterators today. We’d be happy to help you find the right software solution to help your company.
Setting Goals and Objectives
Have you ever set out on a road trip without knowing your destination? It’s unlikely because having a clear goal guides your journey and ensures you arrive at your intended endpoint. Similarly, in business, setting well-defined goals and objectives is crucial for navigating towards success. By establishing specific, measurable, and attainable goals, companies can effectively track their progress and make informed adjustments along the way.
Determining Appropriate Goals
Setting goals isn’t just about picking targets out of thin air. It’s a strategic process that aligns with your overall business strategy and vision. Here’s how you can determine appropriate goals for your business:
- Align with Business Strategy: Your goals should reflect the broader objectives of your business. Whether you’re aiming to increase market share, improve customer satisfaction, or enhance operational efficiency, ensure that your metrics support these overarching goals.
- Understand Your Current Position: Conduct a thorough analysis of your current performance. Identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis). This helps in setting realistic and relevant goals.
- Consult Stakeholders: Engage with stakeholders, including employees, customers, and investors, to gather insights and perspectives. Their input can provide valuable context for setting meaningful goals.
- Use Goal-Setting Frameworks: Frameworks such as SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) or OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) can guide the goal-setting process, ensuring clarity and focus.
Factors to Consider When Setting Objectives
When setting objectives, several factors come into play to ensure they are practical and impactful:
- Relevance: Objectives should be directly related to your business’s core activities and strategic priorities. Irrelevant goals can divert resources and focus away from what truly matters.
- Specificity: Clear and specific objectives provide a roadmap for action. Instead of a vague goal like “improve customer service,” aim for something concrete, such as “reduce customer complaint resolution time by 20% over the next six months.”
- Measurability: If you can’t measure it, you can’t manage it. Ensure your objectives have clear criteria for success. This could be numerical targets, percentages, or completion of specific milestones.
- Achievability: While it’s important to aim high, goals should still be attainable given your resources and constraints. Unrealistic objectives can demoralize your team and lead to burnout.
- Time-bound: Assign a timeframe to your objectives to create a sense of urgency and keep your team focused. Deadlines help in tracking progress and maintaining momentum.
Establishing Specific, Measurable Goals
Establishing specific and measurable goals is a cornerstone of effective metrics tracking. Here’s how to do it:
- Break Down Broad Goals: Start with broad strategic goals and break them down into smaller, actionable objectives. For example, if your goal is to enhance product quality, specific objectives might include reducing defect rates by 15% and increasing customer satisfaction scores by 10%.
- Define Clear Metrics: Identify the metrics that will be used to measure progress. For instance, if your objective is to improve employee productivity, relevant metrics could be output per hour or the number of tasks completed on time.
- Set Benchmarks and Targets: Determine your starting point (benchmark) and set realistic targets. If you’re aiming to increase website traffic, know your current average visits and set a target for improvement.
- Use Historical Data: Leverage historical data to set informed goals. Past performance trends can offer insights into what’s achievable and help in forecasting future performance.
Achieving Business Objectives through Tracking Metrics

Tracking metrics isn’t just about monitoring performance; it’s about using that data to achieve your business objectives. Here’s how metrics can help:
- Monitor Progress: Regularly tracking metrics allows you to monitor progress toward your goals. This continuous feedback loop helps in identifying any deviations from the plan and taking corrective actions promptly.
- Identify Trends: Analyzing metrics over time helps in identifying trends and patterns. This can provide insights into what’s working well and what needs adjustment, enabling data-driven decisions.
- Drive Accountability: Clear metrics and goals create accountability within the organization. When everyone knows what they’re aiming for and how success will be measured, it fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Facilitate Communication: Metrics provide a common language for discussing performance and progress. This facilitates better communication across teams and departments, ensuring everyone is aligned and working towards the same objectives.
- Enhance Motivation: Achieving set targets can be highly motivating for teams. Celebrating milestones and recognizing progress boosts morale and keeps the momentum going.
Case Study: Goal-Setting in Action
Consider a software development company that wants to improve its project delivery times. Using the SMART framework, the company sets the following goal:
- Specific: Reduce project delivery time.
- Measurable: Cut average delivery time from 12 weeks to 10 weeks.
- Achievable: Based on historical data, this is a challenging but realistic target.
- Relevant: Faster delivery times will improve customer satisfaction and competitive positioning.
- Time-bound: Achieve this reduction within the next 12 months.
By setting this specific, measurable goal, the company can track its progress, identify bottlenecks, and implement strategies to enhance efficiency. The result? A more agile, competitive business that meets customer expectations.
Ready to set impactful goals and objectives for your business? Let’s explore ways to identify the most relevant metrics in the next section. Remember, setting clear goals is the first step toward transforming your business through effective metrics tracking.
Identifying Relevant Tracking Metrics

Imagine trying to navigate a complex maze blindfolded. Without any sense of direction, you’d likely stumble around aimlessly, hitting dead ends. This is akin to running a business without tracking the right metrics. To truly harness the power of metrics, it’s essential to identify which ones are relevant to your business objectives. The right metrics act as a compass, guiding you through the intricacies of your operations and helping you stay on course.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are the critical metrics that reflect the performance and success of an organization. They’re quantifiable measures used to gauge how well a company is achieving its key business objectives.
1. Definition and Significance of KPIs
KPIs aren’t just random numbers; they are strategic metrics tied directly to your business goals. They provide a clear picture of performance and are crucial for making informed decisions. For instance, a KPI for a software company might be the monthly recurring revenue (MRR), which directly ties to the company’s financial health and growth potential.
2. Examples of KPIs for Software Companies
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Measures the cost associated with acquiring a new customer. Lowering CAC can significantly improve profitability.
- Churn Rate: Indicates the percentage of customers who stop using your product or service over a given period. A high churn rate signals issues with customer satisfaction or product value.
- Lifetime Value (LTV): Estimates the total revenue a business can expect from a single customer account. Higher LTV suggests strong customer loyalty and recurring revenue.
- Deployment Frequency: For development teams, this KPI tracks how often new code is deployed. Higher frequency can indicate a more agile and responsive development process.
- Average Resolution Time: Measures the time taken to resolve customer issues. Shorter resolution times often lead to higher customer satisfaction.
Aligning Tracking Metrics with Business Processes
Identifying relevant metrics begins with understanding your core business processes and aligning your metrics to measure these effectively.
1. Identifying Core Processes and Relevant Metrics
Each business has unique processes that drive its operations. For a software development company, these might include product development, customer support, and sales. By mapping out these core processes, you can identify which metrics will provide meaningful insights into each area.
- Product Development: Metrics like code commit frequency, bug resolution rate, and feature adoption rate.
- Customer Support: Metrics such as average response time, customer satisfaction score (CSAT), and ticket backlog.
- Sales: Metrics like sales conversion rate, lead response time, and average deal size.
2. Customizing Tracking Metrics to Fit Business Needs
Not all metrics will be relevant to every business. It’s important to customize your metrics to reflect the unique aspects of your operations. For instance, a startup might focus on growth metrics like user acquisition and activation rates, while a more established company might prioritize operational efficiency and profitability metrics.
Leading and Lagging Indicators
Understanding the difference between leading and lagging indicators can significantly enhance your ability to predict and respond to business trends.
- Definitions and Differences
- Leading Indicators: These are predictive metrics that can help forecast future performance. They provide early warnings and opportunities to make proactive adjustments. For example, an increase in website traffic (a leading indicator) might predict future sales growth.
- Lagging Indicators: These metrics reflect past performance. They’re outcomes that have already occurred, such as quarterly revenue or annual customer retention rate. While they’re useful for assessing performance, they don’t offer predictive insights.
- Examples of Leading and Lagging Indicators
- Leading Indicators:
- Website traffic
- Social media engagement
- Customer inquiries or demo requests
- Employee training hours
- Lagging Indicators:
- Revenue growth
- Profit margins
- Customer retention rates
- Project completion rates
- Leading Indicators:
Importance of Both Types of Indicators in Tracking Performance
Both leading and lagging indicators play a crucial role in a comprehensive metrics tracking system. Leading indicators allow businesses to anticipate and influence future outcomes, while lagging indicators provide a clear view of past performance, helping to validate the effectiveness of strategies and initiatives.
Case Study: Using Leading and Lagging Indicators
Consider a startup focused on a new software product. The company identifies several leading indicators, such as the number of free trial sign-ups and social media mentions. These metrics help predict future sales and customer interest. Meanwhile, lagging indicators like monthly recurring revenue (MRR) and churn rate are tracked to assess the actual performance and impact of their marketing efforts.
By balancing both types of indicators, the startup can make proactive adjustments to its marketing strategies based on leading indicators while validating these strategies through lagging indicators.
Next, we’ll explore how to implement a tracking system effectively. By understanding and identifying the right metrics, you’re already on the path to making data-driven decisions that drive success. Let’s continue this journey to optimize your business performance through effective metrics tracking.
Implementing a Tracking Metrics System
Now that you understand the importance of tracking metrics and have identified the relevant ones for your business, the next step is implementing a robust tracking system. This system will enable you to collect, analyze, and act on the data, driving informed decision-making and continuous improvement. Let’s explore the tools, steps, and best practices for setting up an effective metrics tracking system.
Tools and Software for Effective Tracking Metrics
To effectively track and analyze metrics, you need the right tools and software. These tools range from simple spreadsheets to advanced analytics platforms. Here’s a look at some of the most popular options:
- Metabase: A powerful and open-source business intelligence tool that makes it easy to explore and visualize your data. Metabase offers a user-friendly interface, allowing you to create custom dashboards, charts, and reports without requiring extensive technical knowledge. It integrates with various data sources, including databases, CSV files, and cloud data warehouses, making it a flexible option for businesses of all sizes.
- Google Analytics: Ideal for tracking website metrics, such as traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates. It provides detailed and actionable insights into how users interact with your site and helps identify areas for improvement.
- Klipfolio: A business dashboard platform that allows you to visualize and track a wide range of metrics in real-time. It integrates with various data sources and provides customizable dashboards.
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization tool that helps you create interactive and shareable dashboards. Tableau connects to multiple data sources and enables deep data analysis.
- Plecto: A real-time performance dashboard designed for sales and support teams. It tracks KPIs, visualizes data, and motivates teams by displaying real-time results.
- Jira: A project management tool commonly used by software development teams. It tracks project metrics, such as task completion rates, bug resolution times, and sprint progress.
- HubSpot: A comprehensive CRM platform that includes tools for marketing, sales, and service metrics tracking. It provides insights into customer interactions and helps optimize the customer journey.
By selecting the right tools, you can gain valuable insights into your business performance, make data-driven decisions, and drive continuous improvement.
Ensuring Data Accuracy and Reliability
Accurate and reliable data is the cornerstone of effective metrics tracking. Here are steps to ensure the integrity of your data:
- Data Validation: Implement validation rules to ensure data is accurate when entered into your system. This can include checks for data formats, ranges, and consistency.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular data audits to identify and correct errors. This involves reviewing data entries, comparing them with source documents, and verifying their accuracy.
- Automation: Use automation tools to minimize human error in data collection and entry. Automated data collection from integrated systems reduces the risk of inaccuracies.
- Training: Train your team on the importance of data accuracy and the correct procedures for data entry and maintenance. Ensuring everyone understands their role in maintaining data integrity is crucial.
- Centralized Data Sources: Maintain a single source of truth by centralizing your data. Avoid data silos and ensure that all departments are working with the same, consistent data.
Case Study: Implementing a Tracking Metrics System
Let’s consider a startup specializing in e-commerce that decided to implement a comprehensive metrics tracking system to enhance its operations. Here’s how they did it:
- Objectives and Metrics: The startup defined objectives such as increasing customer acquisition, improving customer satisfaction, and optimizing inventory management. Relevant metrics included customer acquisition cost (CAC), net promoter score (NPS), and inventory turnover rate.
- Tool Selection: They chose Google Analytics for website tracking, Metabase for real-time dashboards, and HubSpot for CRM and marketing analytics.
- Data Collection Setup: The team integrated Google Analytics with their website, set up APIs to pull data into Klipfolio, and configured HubSpot to track customer interactions.
- Dashboard Creation: Customized dashboards were created in Klipfolio to visualize key metrics. These dashboards provided real-time updates and were accessible to all team members.
- Assigning Roles: Responsibilities were assigned across departments. The marketing team tracked customer acquisition metrics, the customer support team monitored NPS, and the operations team focused on inventory metrics.
- Training: Comprehensive training sessions were conducted to ensure all team members could effectively use the tools and interpret the data.
- Monitoring and Adjusting: Regular review meetings were scheduled to discuss metric trends and make necessary adjustments. The startup continuously refined its tracking processes to align with changing business needs.
As a result, the startup saw significant improvements in customer acquisition, satisfaction, and inventory management, driven by data-informed decisions.
As you implement a robust tracking system and drive your business towards data-driven success, you’ll see how to analyze and interpret the collected metrics. The right tracking system not only provides insights but also empowers you to make proactive, informed decisions that propel your business forward.
Analyzing and Interpreting Tracking Metrics

Implementing a tracking system is only the beginning. The true power of metrics lies in analyzing and interpreting the data to gain actionable insights. This section will guide you through the process of turning raw data into meaningful information, which can drive informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
Analyzing Collected Tracking Metrics
Effective analysis of collected metrics involves several steps to ensure that the data is not just looked at but truly understood and used to its fullest potential.
- Data Cleaning and Preparation
- Remove Inconsistencies: Clean your data by identifying and correcting errors, removing duplicates, and addressing inconsistencies.
- Standardize Data Formats: Ensure that all data is in a consistent format, making it easier to compare and analyze.
- Segment Data: Break down your data into meaningful segments. For instance, segment customer data by demographics, purchase history, or behavior to uncover specific trends.
- Use Descriptive Statistics
- Summarize Data: Use measures like mean, median, mode, and standard deviation to summarize your data. This helps in understanding the general trends and variations within your data.
- Identify Outliers: Detect and analyze outliers to understand anomalies. Outliers can indicate unique opportunities or highlight potential issues.
- Visualization Techniques
- Graphs and Charts: Utilize bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, and pie charts to visually represent data. Visualization makes it easier to identify patterns and trends.
- Dashboards: Create comprehensive dashboards that provide real-time insights and allow for quick access to key metrics.
- Comparative Analysis
- Benchmarking: Compare your metrics against industry standards or historical data. Benchmarking helps in understanding where your business stands relative to competitors and past performance.
- Trend Analysis: Look at trends over time to identify growth patterns, seasonal variations, and long-term shifts in metrics.
Interpreting Tracking Metrics and Identifying Trends
Interpreting metrics goes beyond numbers; it involves understanding the implications of data and using it to drive strategic decisions.
- Contextual Understanding
- Correlate Metrics: Understand how different metrics relate to each other. For instance, if you notice an increase in website traffic but a decrease in conversion rates, it might suggest that visitors are finding your site but aren’t taking the desired action (e.g., making a purchase).
- Contextual Factors: Consider external factors like market conditions, seasonality, and industry trends that might impact your metrics. For example, a spike in sales during the holiday season might be expected and not necessarily indicative of a long-term trend
- Identify Root Causes
- Drill Down: Dive deeper into your metrics to identify the root causes of changes. If you see a decline in customer satisfaction, analyze customer feedback, support tickets, and product reviews to identify specific issues. For example, you might discover that a recent product update caused usability problems or that shipping delays are leading to customer frustration.
- Hypothesize and Test: Formulate hypotheses about why certain trends are occurring and test them through experiments or additional data collection. If you notice a sudden increase in website traffic from a particular geographic region, hypothesize that it might be due to a successful social media campaign or a partnership with a local influencer. Test your hypothesis by analyzing social media analytics or customer feedback.
- Predictive Analysis
- Forecasting: Use historical data to forecast future demand for your products. Predictive models can help anticipate changes in metrics, allowing for proactive adjustments. This can help you optimize inventory levels, production planning, and marketing efforts.
- Scenario Analysis: Consider different scenarios, such as a competitor launching a new product or a change in government regulations. Analyze how these scenarios might impact your metrics. This also helps in planning and decision-making.
Here are some specific examples:
- E-commerce: If you notice a decline in average order value, analyze factors such as changes in product pricing, shipping costs, or promotions.
- Marketing: If your email marketing campaign is not generating the desired results, analyze open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates to identify areas for improvement.
- Customer Service: If customer satisfaction scores are low, analyze metrics like average response time, first-contact resolution rates, and customer feedback to identify the root causes of dissatisfaction.
Tracking Metrics for Decision-Making and Improving Performance

Data-driven decision-making is about using insights from metrics to make informed and strategic choices that enhance business performance.
- Strategic Planning
- Set Data-Driven Goals: Use your analysis to set realistic and measurable goals. For example, if data shows a trend of increasing customer acquisition cost (CAC), you might set a goal to optimize marketing spend.
- Align Resources: Allocate resources based on data insights. If a particular marketing channel shows high ROI, consider increasing investment in that area.
- Operational Improvements
- Optimize Processes: Identify inefficiencies in your processes through data analysis and implement improvements. For instance, if product development cycles are lengthy, analyze the workflow to find and address bottlenecks.
- Enhance Customer Experience: Use customer metrics to improve service. For example, if NPS scores are low, delve into customer feedback to identify areas for enhancement.
- Performance Tracking
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of your metrics to track progress towards goals. This helps in making timely adjustments and keeping the team aligned.
- Iterative Improvements: Adopt a cycle of continuous improvement by regularly analyzing metrics, implementing changes, and reassessing the impact.
Case Study: Data-Driven Decision Making
Consider a SaaS company that used data analysis to drive decision-making:
- Identifying Trends: The company noticed a decline in user engagement through its metrics dashboard. By analyzing the data, they found that engagement dropped significantly after the initial onboarding phase.
- Root Cause Analysis: They drilled down into user behavior data and discovered that the onboarding process was too complex, causing users to lose interest.
- Strategic Actions: The company simplified the onboarding process based on these insights. They also set up additional support resources and tutorials to help new users.
- Results: Post-implementation, they tracked a significant increase in user engagement and retention, validating their data-driven approach.
Analyzing and interpreting your metrics, you can make informed decisions that drive growth and improve performance. We’ll now talk strategies for continuous improvement and optimization based on your metrics. Let’s leverage the power of data to propel your business to new heights.
Continuous Improvement and Optimization
Embarking on the journey of tracking and analyzing metrics is an ongoing process. It’s not enough to set up a tracking system and analyze data once; the real value lies in continuous improvement and optimization. This section will guide you on how to sustain and enhance your metrics tracking efforts to ensure ongoing business growth and performance enhancement.
Embracing a Culture of Continuous Improvement
A culture of continuous improvement is crucial for any organization aiming to stay competitive and responsive to changing market conditions. This involves fostering an environment where feedback is valued, and iterative processes are standard practice.
Consider a software development team. By adopting agile methodologies, such as regular sprint reviews and retrospectives, the team can continually assess their performance, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes in real-time. This approach ensures that the team remains flexible, learns from each iteration, and progressively enhances their workflows and product quality.
Optimizing Tracking Metrics Processes
Optimization isn’t a one-time task but a continuous effort to refine and enhance the processes used for tracking metrics. This involves regular reviews, adopting new tools, and staying updated with best practices.
Imagine a chart depicting the optimization cycle in a company’s metrics tracking process:
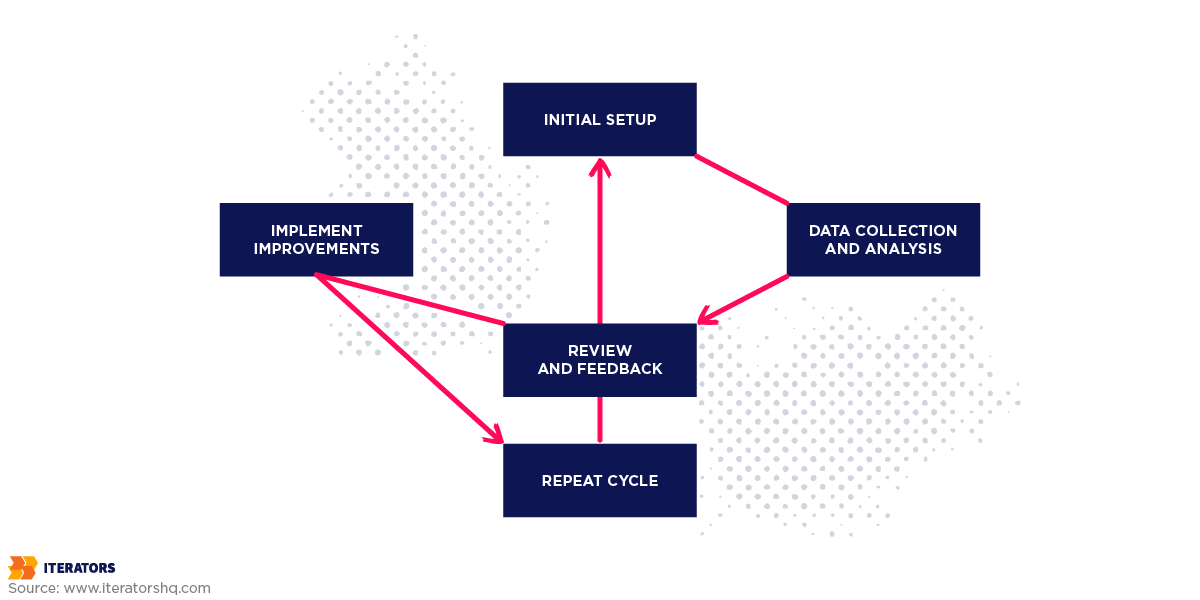
- Initial Setup: The first phase involves setting up the tracking system with chosen metrics and tools.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Data is collected and analyzed regularly to gain insights.
- Review and Feedback: Periodic reviews are conducted to assess the effectiveness of the current tracking system and gather feedback from stakeholders.
- Implement Improvements: Based on feedback and analysis, improvements are implemented to enhance the tracking system.
- Repeat Cycle: The cycle repeats, ensuring that the tracking system evolves with the business needs.
This cyclical approach ensures that the metrics tracking process is always aligned with the company’s goals and market conditions.
Leveraging Feedback and Insights
Utilizing feedback and insights from tracked metrics is crucial for driving continuous improvement. Feedback can come from various sources, including customers, employees, and the metrics themselves. This feedback should be systematically gathered, analyzed, and acted upon.
For example, a company might use customer satisfaction surveys and support tickets to gather feedback. By analyzing this feedback alongside metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), the company can identify pain points in the customer journey. Addressing these issues not only improves customer experience but also enhances overall business performance.
Implementing Strategic Adjustments
Strategic adjustments based on metrics insights involve making informed decisions that lead to tangible improvements. This can include tweaking marketing strategies, refining product features, or optimizing operational processes.
A graphical representation, such as a decision tree, can illustrate how different metrics inform strategic adjustments:
- Root Metrics: At the top, core metrics like revenue, customer acquisition cost (CAC), and churn rate are tracked.
- Branches of Analysis: Each core metric branches into specific areas for deeper analysis. For instance, if churn rate is high, branches might include customer feedback, usage patterns, and support ticket analysis.
- Action Nodes: Based on the analysis, specific actions are identified. If feedback indicates that the onboarding process is complex, an action node might be to simplify and streamline the onboarding process.
- Outcome Leaves: The leaves of the tree represent the expected outcomes of these actions, such as improved customer retention, higher satisfaction scores, and increased revenue.
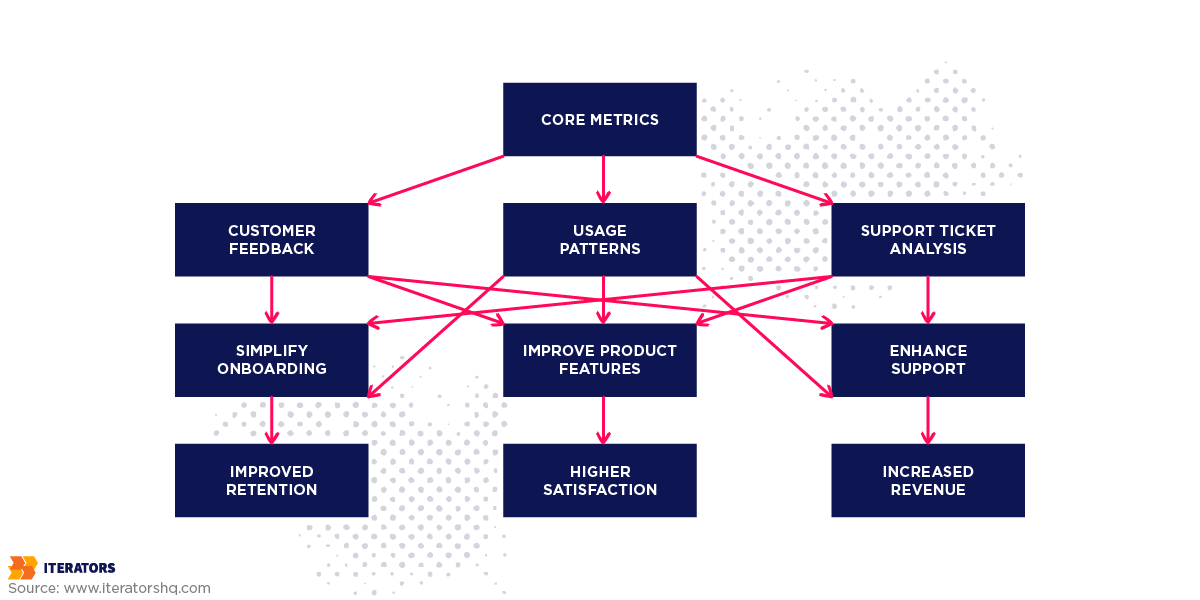
This visual decision tree helps in understanding how metrics drive strategic decisions and lead to continuous improvement.
Case Study: Continuous Improvement in Action
Let’s take the example of a startup focused on mobile app development. Initially, the company set up a basic metrics tracking system to monitor user engagement, app performance, and customer feedback. Over time, they adopted a continuous improvement approach.
In the first quarter, data revealed that user engagement dropped after the initial download. The team conducted a review and gathered feedback, identifying that the onboarding process was cumbersome. They streamlined the onboarding steps, simplifying the user experience.
By the second quarter, engagement metrics improved, but new data showed that users were dropping off after two weeks. Further analysis and feedback indicated that users found the app’s features lacking depth. The team responded by adding more robust features and enhancing existing ones.
By the third quarter, the company saw a significant increase in both engagement and retention rates. Regular reviews and feedback loops allowed the team to continuously optimize the app, resulting in a better user experience and higher satisfaction rates.
Visualizing Continuous Improvement
Visual tools can effectively illustrate the continuous improvement process. Imagine a cycle diagram with stages such as “Collect Data,” “Analyze,” “Review,” “Implement Changes,” and “Measure Impact.” Each stage is interconnected, representing the ongoing nature of the process.
By regularly moving through these stages, businesses can ensure that they aren’t just reacting to issues but proactively seeking ways to enhance performance and meet evolving customer needs.
To embrace a culture of continuous improvement and take your metrics tracking to the next level, you’ll need to continuously optimize your processes, leverage feedback, and make strategic adjustments that help you to drive sustained growth and performance. In the next section, we’ll explore how to incorporate OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) into your tracking system for even greater alignment and effectiveness.
Incorporating OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
Incorporating OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) into your metrics tracking system can elevate your strategic planning and execution, driving alignment and focus within your organization. OKRs bridge the gap between ambitious goals and actionable steps, ensuring that every team member is aligned with the company’s vision and actively contributing to its success.
1. Understanding OKRs
OKRs consist of two key components: Objectives and Key Results. Objectives are the high-level goals you aim to achieve, while Key Results are specific, measurable actions that track your progress towards these objectives. This framework ensures that objectives are clear and achievable, with measurable results providing tangible proof of progress.
Imagine a company-wide objective: “Enhance Customer Satisfaction.” The accompanying Key Results could include specific, measurable targets such as “Increase NPS by 10 points,” “Reduce customer support response time to under 2 hours,” and “Achieve a 95% customer satisfaction rate.” This structure allows for precise tracking and accountability.
2. Aligning OKRs with Business Goals
Aligning OKRs with your broader business goals ensures that every department and team member is working towards the same targets. This alignment is achieved through a cascading process where high-level company objectives are broken down into department-specific and individual OKRs.
3. Creating a Visual Alignment Chart
Consider a chart that visually represents the alignment of OKRs within an organization. At the top, the company’s primary objectives are listed. Beneath these, department-level objectives are linked, followed by individual team member objectives. This visual representation highlights how every team’s efforts contribute to the overall company goals.
Company Objective: Enhance Customer Satisfaction
- Marketing Team Objective: Improve customer communication and engagement.
- Key Result: Increase email open rates by 15%.
- Key Result: Launch a customer feedback campaign.
- Support Team Objective: Reduce customer complaints and response times.
- Key Result: Decrease average response time to under 2 hours.
- Key Result: Achieve a 95% resolution rate on first contact.
- Product Team Objective: Improve product usability based on customer feedback.
- Key Result: Implement top 5 customer-suggested features.
- Key Result: Reduce the average number of user-reported bugs by 30%.
4. Monitoring and Adjusting OKRs
Once OKRs are set, it’s crucial to continuously monitor progress and make adjustments as needed. This is where the synergy between OKRs and metrics tracking becomes evident. Your metrics tracking system should be integrated with your OKR framework, allowing for real-time updates and insights into progress.
5. Visualizing Progress with a Dashboard

Imagine a dashboard that integrates OKRs with your metrics. This dashboard provides a visual representation of progress towards each key result, using color-coded indicators (e.g., green for on-track, yellow for at-risk, and red for off-track). For instance, if the key result of reducing customer support response time is at risk, the dashboard would highlight this in yellow, prompting immediate attention and action.
Case Study: OKRs in Action
Consider a startup focused on a SaaS product. The company sets a primary objective to “Increase Market Share in the SaaS Industry.” Key results include “Achieve a 20% increase in market share by year-end,” “Launch three major product updates,” and “Expand into two new international markets.”
To align with this objective, the sales team sets their objective to “Expand the Customer Base.” Their key results include “Increase new customer acquisitions by 25%,” “Boost sales conversion rate by 10%,” and “Secure partnerships with 10 new resellers.”
The product team, meanwhile, focuses on enhancing the product based on customer feedback. Their objective is to “Improve Product Features and Usability.” Key results involve “Implementing the top 5 requested features,” “Reducing bug reports by 40%,” and “Increasing user satisfaction ratings by 15%.”
Throughout the year, the company tracks these OKRs through their integrated metrics system, allowing for real-time insights and adjustments. By the end of the year, they achieved significant market share growth, largely due to the focused efforts and clear alignment driven by their OKR framework.
Enhancing Strategic Focus
Incorporating OKRs into your metrics tracking system not only enhances alignment and focus but also fosters a culture of accountability and continuous improvement. Each team member understands how their work contributes to the broader company goals, driving engagement and motivation.
With a powerful framework for continuous improvement and aligned to your business goals, you can integrate OKRs into your metrics tracking system, ensuring that every effort is aligned with your strategic objectives.
Case Studies and Examples
Examining real-world applications of tracking metrics and OKRs provides valuable insights into their effectiveness. These case studies highlight how industry leaders like Google, Adobe, LinkedIn, Netflix, and Slack successfully implement these strategies to drive growth, enhance performance, and achieve their business objectives.
Case Study 1: Google’s Use of OKRs
Google is often cited as a pioneer in the use of OKRs (Objectives and Key Results). Their adoption of OKRs has been a significant factor in their rapid growth and innovation. The framework, introduced by venture capitalist John Doerr, helps Google maintain alignment and focus across its expansive and diverse organization.
Objective: “Organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
Key Results:
- Improve search algorithm accuracy by 20%.
- Index 10 million more websites.
- Reduce average search query response time by 50%.
Google’s application of OKRs ensures that even ambitious and broad objectives are broken down into measurable and achievable results. This clear structure allows every team member to understand how their work contributes to the company’s overarching goals. Over time, this practice has enabled Google to maintain its leadership in search technology, continuously improving its algorithms and expanding its index to include more diverse and comprehensive information.
Case Study 2: Adobe’s Transformation with OKRs
Adobe, a leader in digital media and marketing solutions, adopted OKRs to drive its transition from traditional software delivery to a cloud-based subscription model. This shift required significant internal changes, and OKRs played a crucial role in aligning the company’s efforts.
Objective: “Transition to a subscription-based model for all major software products.”
Key Results:
- Migrate 80% of existing customers to the subscription model within two years.
- Increase recurring revenue by 50% within the first year.
- Launch a new cloud-based version of Adobe Photoshop by Q4.
Adobe’s clear objectives and specific key results helped guide the company through this complex transformation. By focusing on measurable outcomes, Adobe successfully shifted its business model, leading to substantial growth in recurring revenue and customer base. This transition was so effective that Adobe is now a leading example of successful digital transformation in the tech industry.
Case Study 3: LinkedIn’s Strategic Use of OKRs
LinkedIn, the world’s largest professional networking site, has leveraged OKRs to manage its rapid growth and expansion. OKRs have enabled LinkedIn to set clear goals and track progress systematically, which is critical for a platform with such a vast and active user base.
Objective: “Increase user engagement and content creation on the platform.”
Key Results:
- Boost daily active users by 25% in six months.
- Increase the number of user-generated posts by 30%.
- Reduce content reporting time from one week to 48 hours.
By focusing on specific, measurable key results, LinkedIn was able to enhance user engagement and encourage more content creation. These efforts resulted in a more dynamic and active platform, attracting new users and retaining existing ones. LinkedIn’s strategic use of OKRs has helped the company stay competitive and continually improve the user experience.
Example: Netflix’s Data-Driven Decision Making
Objective: “Improve user retention and engagement through personalized content.”
Key Results:
- Develop and implement a recommendation algorithm that increases viewing time by 15%.
- Achieve a 20% increase in user retention over the next year.
- Release 50 new original series and films based on user viewing data and preferences.
Netflix’s focus on data and metrics allows it to understand viewer preferences and behaviors deeply. By setting clear OKRs, Netflix can align its content strategy with user demands, ensuring high engagement and retention rates. This data-driven approach has made Netflix a dominant player in the streaming industry, consistently delivering content that resonates with its global audience.
- Netflix’s Data-Driven Culture
- Personalization at Netflix
Example: Slack’s Market Expansion Strategy
Slack, the popular collaboration tool, has used OKRs to manage its market expansion and product development efforts. OKRs help Slack maintain focus and drive growth in a competitive market.
Objective: “Expand market presence and enhance product features.”
Key Results:
- Increase market share in Europe by 20% within a year.
- Introduce five new integrations with major software platforms.
- Achieve a 95% customer satisfaction score for new features.
By setting and tracking these key results, Slack can ensure that its expansion efforts are systematic and aligned with user needs. The focus on customer satisfaction and integration capabilities has helped Slack remain a top choice for businesses seeking efficient collaboration tools.
The Takeaway
In conclusion, tracking metrics and implementing OKRs are indispensable tools for modern businesses seeking sustainable growth and competitive advantage. Through real-world case studies, we’ve witnessed how companies like Google, Adobe, LinkedIn, Netflix, and Slack leverage these strategies to drive success.
Now, it’s your turn to take action. Embrace the lessons learned from these case studies and apply them to your own organization. Start by defining clear objectives, identifying relevant metrics, and implementing robust tracking systems. Then, integrate OKRs into your strategic planning process to align your team and drive measurable results.
By adopting a data-driven approach and continuously refining your strategies, you can unlock new opportunities, optimize performance, and achieve your business goals. Don’t wait any longer – seize the opportunity to transform your organization and pave the way for future success. Iterators can help you get started.
